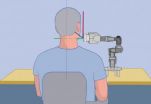
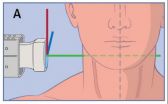
(Press-News.org) While in Germany, Partho P. Sengupta, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai used a computer to perform a robot-assisted trans-Atlantic ultrasound examination on a person in Boston. In another study Kurt Boman, MD, of Umeå University in Sweden in collaboration with Mount Sinai, showed how a cardiologist's video e-consultation, coupled with a remote robot-assisted echocardiogram test, dramatically reduces the waiting time for a diagnosis faced by heart failure patients who live in a rural communities far from the hospital from nearly four months to less than one month.
These two Mount Sinai research studies appear simultaneously in the August issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology- Imaging.
"The two studies give us a glimpse of what to expect in the near future, a patient-friendly imaging technology at your doorstep," says Jagat Narula, MD, PhD, the senior author of both research studies who serves as the Director of the Cardiovascular Imaging Center and Associate Dean of Global Research at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai.
"These studies lift the robotic imaging and telemedicine to the next level," says Sherif F. Nagueh, MD, Medical Director of the Echocardiography Laboratory at the Methodist DeBakey Heart and Vascular Center in Houston, Texas who authored the accompanying editorial about the two studies in JACC-Imaging.
"Our first-in-man experiment shows long-distance, telerobotic ultrasound examinations over standard internet are possible," says Dr. Sengupta, who is Director of Cardiac Ultrasound Research at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and Chair of the New Technology Task Force at the American Society of Echocardiography. "Our successful experiment opens up a new frontier for the use of remote, robotic ultrasound imaging that could potentially be more efficient and cost-effective overall for healthcare access and delivery."
In the first study, Principal Investigator Dr. Sengupta and researchers tested the use of a small, lightweight robotic-arm with built-in ultrasound technology stationed in Boston and connected to a personal computer with a low-bandwidth Internet connection in Munich, Germany. The robotic ultrasound exam of a person's carotid artery in their neck was completed in just four minutes.
"This feasibility and time-efficiency of long-distance, telerobotic ultrasound may help expand the role of imagers to care for patients online virtually lending a true 'helping hand' remotely and providing a patient's care team expert guidance," says Dr. Sengupta of Mount Sinai. Interestingly, in the study experiments both advanced experts and early trainees on robotic ultrasound were able to operate the telerobotic technology.
In the second study, Dr. Boman and colleagues randomized half their study patients to remote consultation and the other half to standard of care referral to the hospital. Remote consultation and the robotic echocardiogram exam were conducted on the same day of a patient's visit to their local Primary Healthcare Center located more than 100 miles away from the hospital. Study results show, the total diagnostic process time was significantly reduced from 114 to 27 days in those patients receiving remote consultation. Also, the patient's wait time until obtaining a specialist consultation was reduced from 86 to 12 days, with 95 percent of remote consult patients claiming remote consult to be a superior strategy.
"As a result of our pilot study, we were able to establish a safe and efficient e-health solution to improve the comprehensive, convenient examination of suspected heart failure patients in a rural community of northern Sweden and improve their physician care team's communication," says Dr. Narula of Mount Sinai. "This pilot study may serve as a future model for use of e-consults and robotic imaging in similar rural communities to improve access to specialists and the latest diagnostic technology globally."
"In clinical medicine, the use of more portable low-cost, safe, non-radiation using ultrasound imaging technology is growing for diagnosis, patient monitoring, and procedural, and surgical planning," says Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, Director of Mount Sinai Heart at Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the new Editor-in-Chief of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC). "The technology may be key to accelerating greater local and global healthcare access more efficiently and cost-effectively for patients, doctors, communities, and hospitals in need."
According to researchers, on-demand, virtual robotic ultrasound could be used in a wide variety of clinical setting collaborations ranging from timely in-hospital or emergency room patient imaging studies, community screenings, or even within dangerous locations such as war zones.
INFORMATION: END
Robotic-assisted imaging: from trans-Atlantic evaluation to help in daily practice
New tele-robotic medicine breakthroughs may lend a virtual 'helping hand' to doctors, hospitals, and communities in need of ultrasound imaging evaluations
2014-08-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The Maldives and the whale shark: The world's biggest fish adds value to paradise
2014-08-12
They are the largest fish in the world but the impact of this majestic and charismatic animal on the economy of the island nation of the Maldives was largely unknown. A new study by scientists of the Maldives Whale Shark Research Programme (MWSRP) reveals that a small group of whale sharks in a single Maldivian Atoll accounts for nearly 3% of the global shark ecotourism and nearly half that of the Maldives'.
"The Republic of Maldives hosts one of few known year round aggregation sites for whale sharks", said James Hancock co-author and a director of MWSRP. "We have seen ...
Is empathy in humans and apes actually different?
2014-08-12
Whether or not humans are the only empathic beings is still under debate. In a new study, researchers directly compared the 'yawn contagion' effect between humans and bonobos (our closest evolutionary cousins). By doing so they were able to directly compare the empathic abilities of ourselves with another species, and found that a close relationship between individuals is more important to their empathic response than the fact that individuals might be from the same species.
The ability to experience others' emotions is hard to quantify in any species, and, as a result, ...
Sniffing out billions in US currency smuggled across the border to Mexico
2014-08-12
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 12, 2014 — Criminals are smuggling an estimated $30 billion in U.S. currency into Mexico each year from the United States, but help could be on the way for border guards, researchers will report here today. The answer to the problem: a portable device that identifies specific vapors given off by U.S. paper money.
They will present the new research at the 248th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS), the world's largest scientific society. The meeting features nearly 12,000 reports on new advances in science and other ...
Could hemp nanosheets topple graphene for making the ideal supercapacitor?
2014-08-12
SAN FRANCISCO, Aug. 12, 2014 — As hemp makes a comeback in the U.S. after a decades-long ban on its cultivation, scientists are reporting that fibers from the plant can pack as much energy and power as graphene, long-touted as the model material for supercapacitors. They're presenting their
research, which a Canadian start-up company is working on scaling up, at the 248th National Meeting & Exposition of the American Chemical Society (ACS), the world's largest scientific society.
The meeting features nearly 12,000 presentations on a wide range of science topics and ...
Stinky gases emanating from landfills could transform into clean energy
2014-08-12
SAN FRANCISCO — A new technique that transforms stinky, air-polluting landfill gas could produce the sweet smell of success as it leads to development of a fuel cell generating clean electricity for homes, offices and hospitals, researchers say. The advance would convert methane gas into hydrogen, an efficient, clean form of energy.
The researcher's report is part of the 248th National Meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS), the world's largest scientific society.
The meeting, attended by thousands of scientists, features nearly 12,000 reports on new advances ...
Climate change, predators, and the trickle down effects on ecosystems
2014-08-12
Predators play important roles in maintaining diverse and stable ecosystems. Climate change can push species to move in order to stay in their climatic comfort zones, potentially altering where species live and how they interact, which could fundamentally transform current ecosystems.
A symposium focusing on climate's effects on predators—causing cascading effects on whole ecosystems -- will take place on Tuesday, August 12th during the Ecological Society of America's 99th Annual Meeting, held this year in Sacramento, California.
There will be "winners" and "losers" ...
Blacks, women face greater burden from CVD risk factors
2014-08-11
The impact of major cardiovascular risk factors combined is greater in women than men and in blacks than whites. While the gender gap may be narrowing, differences by race may be increasing, according to new research in the American Heart Association journal Circulation.
"We've been targeting traditional risk factors in public health campaigns for many years," said Susan Cheng, M.D., M.P.H., study lead author and Assistant Professor of Medicine at Brigham and Women's Hospital in Boston, Mass. "We wanted to take a look at how well we've been doing over time at keeping ...
Bone drugs may not protect osteoporotic women from breast cancer
2014-08-11
Osteoporosis drugs known as bisphosphonates may not protect women from breast cancer as had been thought, according to a new study led by researchers at UC San Francisco (UCSF).
The drugs' protective effect was widely assumed after several observational studies showed that women who took them were less likely to get breast cancer.
But when researchers assessed the effect of two of the most widely used osteoporosis drugs – sold under the brand names, Fosamax and Reclast – in two large randomized clinical trials, neither drug protected women with osteoporosis from getting ...
Novel study maps infant brain growth in first 3 months of life using MRI technology
2014-08-11
A recent study conducted by researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine and the University of Hawaii demonstrates a new approach to measuring early brain development of infants, resulting in more accurate whole brain growth charts and providing the first estimates for growth trajectories of subcortical areas during the first three months after birth. Assessing the size, asymmetry and rate of growth of different brain regions could be key in detecting and treating the earliest signs of neurodevelopmental disorders, such as autism or perinatal ...
Gloves after hand washing associated with fewer infections in preterm babies
2014-08-11
Extremely premature babies in a neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) had fewer infections when medical staff wore gloves after washing their hands compared with hand washing alone.
The author is David A. Kaufman, M.D., of the University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, and colleagues.
Late-onset infections (more than 72 hours after birth) and necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC, tissue death in the intestines) can cause death and neurodevelopmental impairment in extremely premature babies. Even after hand washing, medical staff can still have microorganisms ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
[Press-News.org] Robotic-assisted imaging: from trans-Atlantic evaluation to help in daily practiceNew tele-robotic medicine breakthroughs may lend a virtual 'helping hand' to doctors, hospitals, and communities in need of ultrasound imaging evaluations