(Press-News.org) The hard corals primarily responsible for the construction of coral reefs around the world have attracted the attention of taxonomists for hundreds of years. Despite the important role such corals play in building what are arguably the world's most diverse ecosystems, coral reefs in some parts of the world still hold surprises for modern scientists.
An international team of scientists has recently described a new hard coral species, Pachyseris inattesa, from the Saudi Arabian Red Sea. The study, led by the University of Milano-Biccocain collaboration with the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST), highlights the opportunities for scientific discovery in a region that has historically been difficult to access.
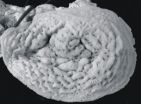
Corals in the genus Pachyseris are reef dwellers often referred to as "elephant skin corals" or "corduroy corals" due to their wrinkled appearance. Tullia I Terraneo, the lead author of the paper, explains that the name for the new species was chosen because of the reaction she and Francesca Benzoni, the co-author who collected the species, had when examining a specimen closely. "We were looking at the SEM [scanning electron microscope] images, and realized that we had something completely unexpected." The word 'inattesa' translates from Italian as 'unforeseen'.
The coral indeed has a superficial resemblance with some common and widespread coral species of the genus Leptoseris and this led others in the past to misidentify it. "After detailed micromorphological and molecular analyses, we can confirm that this is a unique and novel lineage," Terraneo says. The new species was recorded from different reef habitats along the coast of Saudi Arabia, between 10m-35m depth and to date its distribution seems to be limited to the Red Sea region.
The finding is the latest outcome from the "Biodiversity in the Saudi Arabian Red Sea" project organized by Michael Berumen, co-author of the study and PI of the Reef Ecology Lab at KAUST. This project was initiated in 2012 and has brought numerous scientists and taxonomic experts to the Red Sea from around world, with the overall aim to increase our understanding of the biological diversity present in Saudi Arabian coral reefs. Although the Red Sea played a pivotal role in the early history of scientific works on coral reefs, the region has been understudied in more recent times.
The discovery of Pachyseris inattesa highlights that our knowledge regarding the Red Sea is still far from complete, and that our understanding of hard coral diversity globally is likewise not perfect.
"As far as we can tell, this species is endemic to the Red Sea," Terraneo said. "Although our current sampling has only identified it in Saudi Arabia, I suspect that further research in other Red Sea countries would reveal a broader range."
In any case, continued discovery of new species in the Red Sea has been steadily increasing the known endemism of the region. "Findings such as those presented in this paper continue to highlight how special the Red Sea is and provide even more reasons to make sure that conservation efforts in the region preserve these natural treasures, including those that we have yet to discover," said Berumen.
INFORMATION:
Original source
Terraneo TI, Berumen ML, Arrigoni R, Waheed Z, Bouwmeester J, Caragnano A, Stefani F, Benzoni F (2014) Pachyseris inattesa sp. n. (Cnidaria, Anthozoa, Scleractinia): a new reef coral species from the Red Sea and its phylogenetic relationships. ZooKeys 433: 1-30. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.433.803610.3897/zookeys.433.8036
Contact
Dr. Tullia I Terraneo
Reef Ecology Lab
King Abdullah University of Science and Technology
Email: tulliaisotta.terraneo@kaust.edu.sa
Unraveling the mysteries of the Red Sea: A new reef coral species from Saudi Arabia
2014-08-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Artificial cells act like the real thing
2014-08-18
Imitation, they say, is the sincerest form of flattery, but mimicking the intricate networks and dynamic interactions that are inherent to living cells is difficult to achieve outside the cell. Now, as published in Science, Weizmann Institute scientists have created an artificial, network-like cell system that is capable of reproducing the dynamic behavior of protein synthesis. This achievement is not only likely to help gain a deeper understanding of basic biological processes, but it may, in the future, pave the way toward controlling the synthesis of both naturally-occurring ...
Upgrading electronic monitoring, downgrading probation
2014-08-18
Under the Coalition Government which came to power in Britain in May 2010, major changes in the community supervision of offenders are underway in England and Wales. Under the new contract for electronic monitoring (EM) (the third since 1999), the government is planning a huge increase in the use of GPS tracking by 2015. Using GPS tracking could well come to be seen as a more reliable and credible way of 'doing' offender management. The government is planning to create the largest and most advanced electronic monitoring (EM) scheme in the world, using combined GPS tracking ...
Poor health literacy poses risks for pacemaker and defibrillator patients
2014-08-18
(NEW YORK, NY, August 18, 2014) – Patients who rely on pacemakers and defibrillators to maintain a normal heart rhythm run the risk of serious health complications if they don't fully understand how the devices work and what to do when they experience an irregular heartbeat. But a study from Columbia University School of Nursing published this month in the Journal of Cardiovascular Nursing found that 40 percent of patients with these devices had little to no ability to understand information about their cardiac health.
"As a nurse practitioner, I use every patient encounter ...
IU study examines how genes, gender and environment influence substance abuse
2014-08-18
Social integration, including strong family ties, can protect one's well-being and even reduce the impact high-risk genes have on health. Scientists call this phenomenon a gene-environment interaction. An Indiana University study focusing on substance abuse, however, found that a three-way interplay of gender, genetics and social integration produced the different outcomes for men and women.
The study looked at men and women with a genetic sensitivity to stressful situations. Strong family and community ties were protective for such men, reducing their risk of abusing ...
Provider and parental assumptions on teen sex yield 'missed opportunities' for HPV vaccine
2014-08-18
(Boston)—Probing deeper into the complex decisions that parents and providers face regarding the human papilloma virus (HPV) vaccine, researchers found that though both parties appreciated importance of the HPV vaccine, their personal assumptions surrounding timing of administration relative to onset of sexual activity resulted in decreased vaccination rates.
Researchers at Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) conducted hundreds of interviews to offer new insights into this frequent—and often controversial—clinic room conversation. Their findings and recommendations ...
Study finds women seek anti-aging clinicians to treat menopausal symptoms
2014-08-18
Feeling that conventional doctors did not take their suffering seriously, women instead sought out hormonal treatments for menopausal symptoms from anti-aging clinicians, according to a Case Western Reserve University study that investigated the appeal of anti-aging medicine.
Some women also feared the harmful side effects from conventional hormone replacement therapy (HRT) that had shown increased risks for cancer, heart disease and high blood pressure. Yet, they thought that the bioidentical, "natural" hormones their anti-aging doctors prescribed were safe, despite ...
Men viewed more favorably than women when seeking work-life balance
2014-08-18
SAN FRANCISCO — While some suggest that flexible work arrangements have the potential to reduce workplace inequality, a new study finds these arrangements may exacerbate discrimination based on parental status and gender.
Study author Christin Munsch, an assistant professor of sociology at Furman University, analyzed the reactions both men and women received when making flexible work requests — meaning that they either asked to work from home or to work non-traditional hours.
Among those who made flexible work requests, men who asked to work from home two days a week ...
Study identifies 'bonus effect' for certain multiracial daters
2014-08-18
SAN FRANCISCO — While previous research has documented the existence of a racial hierarchy within the dating world with white women and men on top, a new study finds that in certain circumstances multiracial daters are actually seen as more desirable than individuals from all other racial groups, including whites.
"The most interesting and surprising finding from our study is that some white-minority multiracial daters are, in fact, preferred over white and non-white daters," said Celeste Vaughan Curington, a doctoral student in sociology at the University of Massachusetts-Amherst ...
'Super-parent' cultural pressures can spur mental health conditions in new moms and dads
2014-08-18
SAN FRANCISCO — Mental health experts in the past three decades have emphasized the dangers of post-partum depression for mothers, but a University of Kansas researcher says expanding awareness of several other perinatal mental health conditions is important for all new parents, including fathers.
This awareness has become even more critical as "super mom" and "super dad" pressures continue to grow, said Carrie Wendel-Hummell, a KU doctoral candidate in sociology, who will present her study on perinatal mental health disorders at the 109th Annual Meeting of the American ...
Surprising number of older adults weathered the 'Great Recession' without financial strain
2014-08-18
SAN FRANCISCO — The "Great Recession" may have put a dent in many older adults' pocketbooks, but a new study, which will be presented at the 109th Annual Meeting of the American Sociological Association, finds that more than 40 percent reported a decrease in "financial strain" between 2006 and 2010.
Researcher Lindsay R. Wilkinson, an assistant professor of sociology in Baylor University's College of Arts & Sciences, drew on 5,205 respondents from the Health and Retirement Study (HRS) to examine the effect of financial strain on the mental health and use of mood-altering ...