(Press-News.org) Scientists from the Biogerontology Research Foundation (BGRF), a UK-based charity founded to support ageing research and address the challenges of a rapidly ageing population, propose a new concept for signalome-wide analysis of changes in intracellular pathways, called OncoFinder, which allows for accurate and robust cross-platform analysis of gene expression data. This new technique will allow scientists to derive useful information from and compare the hundreds of thousands of data sets obtained using legacy equipment as well as data sets obtained from biological samples preserved in paraffin blocks and partially-degraded samples.
The original research, published in the journal Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences, shows that the OncoFinder method significantly reduces errors introduced by transcriptome-wide experimental techniques. Scientists compared gene expression data for the same biological samples obtained by both next generation sequencing (NGS) and microarray methods, finding that these different techniques have almost no correlation between the gene expression values for all datasets analysed. In contrast, when the OncoFinder algorithm is applied to the data, a clear correlation between next generation sequencing and microarray gene expression datasets was seen.
"For several years the potential for the use of gene expression data in research and clinical applications has been underappreciated due to the inconsistency of the data coming from the various types of equipment. There is just too much variation and complexity when comparing the massive number of individual genes. But when this complexity is reduced and the gene expression is mapped onto signalling pathways, we can evaluate the pathway activation drift and analyse the changes and transitions much more effectively. The OncoFinder algorithm enables scientists to characterise the functional states of transcriptomes more accurately than before and we hope that this will become a method of choice in genetics, physiology, biomedicine and molecular diagnostics," said Alex Zhavoronkov, PhD, director of the BGRF and co-author of the study.
INFORMATION:The original research paper is available to view and download at http://journal.frontiersin.org/Journal/10.3389/fmolb.2014.00008/abstract.
BGRF announces OncoFinder algorithm for reducing errors in transcriptome analysis
2014-08-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
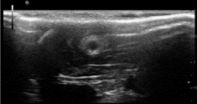
Ultrasound imaging of chitosan nerve conduits that bridge sciatic nerve defects in rats
2014-08-18
New simple and effective methods are needed to better evaluate the outcomes of repair using nerve conduits in vivo. Ultrasound is a common noninvasive clinical detection modality that has been used in many fields. However, ultrasound has only rarely been used to observe implanted nerve conduits in vivo. Hongkui Wang and co-workers from Affiliated Hospital of Nantong University report the first use of ultrasound to noninvasively observe the changes in chitosan nerve conduits implanted in rats over time. The ultrasound imaging clearly showed whether there are unsatisfactory ...
An inside-out vein graft filled with PRP for repair of a short sciatic nerve defect
2014-08-18
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) containing various growth factors can promote nerve regeneration. An inside-out vein graft can substitute nerve autograft to repair short nerve defects. It is hypothesized that an inside-out vein graft filled with platelet-rich plasma shows better effects in the repair of short sciatic nerve defects. In a study reported on the Neural Regeneration Research (Vol. 9, No. 14, 2014), an inside-out vein autograft filled with platelet-rich plasma was used to bridge a 10 mm-long sciatic nerve defect in rats. At 6 and 8 weeks, the sciatic nerve function ...
Club cells are 'bad guys' during flu infection
2014-08-18
A specialized subset of lung cells can shake flu infection, yet they remain stamped with an inflammatory gene signature that wreaks havoc in the lung, according to a study published in The Journal of Experimental Medicine.
Seasonal flu is caused by influenza virus, which can infect a variety of cell types in the lung. Infected cells are typically destroyed by the virus itself or by immune cells that attack infected cells. The resulting inflammation can linger on long after the virus has been eliminated leading to persistent symptoms and, in some cases, severe tissue damage.
Club ...
Myc inhibition is an effective therapeutic strategy against most aggressive brain tumors
2014-08-18
Barcelona, 18 August 2014. Research led by the Vall d'Hebron Institute of Oncology (VHIO) evidence the most conclusive preclinical results to-date validating Myc inhibition as a therapeutic strategy in glioma – a highly agressive tumor type that notoriously outsmarts current anti-cancer therapies. The study led by Laura Soucek, Principal Investigator of VHIO´s Mouse Models of Cancer Therapies Group, published today in Nature Communications, not only represents an important step forward in ultimately providing brain glioma patients with new therapeutic avenues, but also ...
Sun's activity influences natural climate change
2014-08-18
For the first time, a research team has been able to reconstruct the solar activity at the end of the last ice age, around 20,000-10,000 years ago, by analysing trace elements in ice cores in Greenland and cave formations from China. During the last glacial maximum, Sweden was covered in a thick ice sheet that stretched all the way down to northern Germany and sea levels were more than 100 metres lower than they are today, because the water was frozen in the extensive ice caps. The new study shows that the sun's variation influences the climate in a similar way regardless ...
Antibiotics in early life may alter immunity long-term
2014-08-18
New University of British Columbia research found that receiving antibiotic treatments early in life can increase susceptibility to specific diseases later on.
Most bacteria living in the gut play a positive role in promoting a healthy immune system, but antibiotic treatments often do not discriminate between good and bad bacteria. The study published today in Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology helps scientists understand how different antibiotics affect good bacteria.
"This is the first step to understanding which bacteria are absolutely necessary to develop ...
Promising ferroelectric materials suffer from unexpected electric polarizations
2014-08-18
UPTON, NY—Electronic devices with unprecedented efficiency and data storage may someday run on ferroelectrics—remarkable materials that use built-in electric polarizations to read and write digital information, outperforming the magnets inside most popular data-driven technology. But ferroelectrics must first overcome a few key stumbling blocks, including a curious habit of "forgetting" stored data.
Now, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory have discovered nanoscale asymmetries and charge preferences hidden within ferroelectrics ...
International scientific team criticizes adoption of 'novel ecosystems' by policymakers
2014-08-18
Embracing "novel" ecosystems is dangerous, according to a new study by an international team.
Novel ecosystems arise when human activities transform biological communities through species invasions and environmental change. They are seemingly ubiquitous, and thus many policymakers and ecologists argue for them to be accepted as the "new normal"—an idea the researchers say is a bad one.
In the study, published in the September edition of the academic journal Trends in Ecology and Evolution, the international team argues that adopting novel ecosystems is based on faulty, ...
Visual 'gist' helps us figure out where a crowd is looking
2014-08-18
Have you ever seen a crowd of people looking off into the distance, perhaps toward a passing biker or up to the top of a building? There's a good chance you looked there, too, instantly, even without paying attention to the individuals in the group. How can we tell where a crowd is looking with so little effort?
Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley and the University of Denver have discovered that we rely on a specialized visual process known as "ensemble coding" to perceive where a crowd is looking. Their new study shows that we are able to tell where ...
Prioritizing suicide research can help lead to fewer suicide attempts and deaths
2014-08-18
Ann Arbor, MI, August 18, 2014 – In a new supplement to the September issue of the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, experts address the state of the science on suicide prevention and provide useful recommendations for research to inform effective suicide prevention. Suicide has been a challenging and perplexing public health issue to study as it has many dimensions and underlying factors. Although much is known about the patterns and potential risk factors of suicide, the national suicide rate does not appear to have dropped over the last 50 years.
This groundbreaking ...