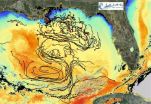
(Press-News.org) MIAMI – A new study of the ocean circulation patterns at the site of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill reveals the significant role small-scale ocean currents play in the spread of pollutants. The findings provide new information to help predict the movements of oil and other pollutants in the ocean.
Nearly two years to the day after the Deepwater Horizon incident, scientists from the Consortium for Advanced Research on Transport of Hydrocarbon in the Environment (CARTHE), based at the University of Miami (UM) Rosenstiel School of Marine and Atmospheric Science, conducted a drifter experiment in the northern Gulf of Mexico spill site to study small-scale ocean currents ranging from 100 meters to 100 kilometers.
"Our results conclusively show that ocean flows at small scales, below 10 kilometers, contain significant energy fluctuations to control the initial spread of pollutant clouds," said UM Rosenstiel School Professor and CARTHE Director Tamay Özgökmen. "Now that we have quantified this missing piece of the puzzle, we can improve our real-time predictive capabilities in the event of a future oil spill."
During the 12-day at-sea experiment called GLAD (Grand Lagrangian Deployment), the research team deployed 300 GPS-equipped custom drifters off the UM Rosenstiel School research vessel F.G. Walton Smith in a region where wind-driven continental shelf currents mix with buoyancy-driven Mississippi River outflow currents and deep eddy-driven currents in the Gulf of Mexico. The drifters flowed along the Gulf of Mexico currents for several months post deployment to capture a multi-dimensional picture of the upper-ocean movements in the presence of wind and waves at DeSoto Canyon, the site of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. This was the first experiment to deploy so many drifters at once. Data about their whereabouts was retrieved every five minutes.
The study, aimed at quantifying the small-scale circulation that cannot be captured by satellite-based altimeter measurements or general circulation models, has immediate practical applications to help better predict the path of catastrophic pollutant events, such as from future oil spills or nuclear disaster events. The results provide new information about the significant dispersion patterns currently un-accounted for in ocean circulation models, according to the authors.
"This experiment is helping to answers questions that arise in all major oil spills, such as 'where will the oil go?' and 'how fast will it get there?' which are important when allocating limited response resources and to determine the overall socio-economic impact of the spill," said Özgökmen.
INFORMATION:
The GLAD research experiment study was made possible by a grant from the Gulf of Mexico Research Initiative (GoMRI). The GoMRI is a 10-year, $500 million independent research program established by an agreement between BP and the Gulf of Mexico Alliance to study the effects of the Deepwater Horizon incident and the potential associated impact of this and similar incidents on the environment and public health. For more information, visit http://gulfresearchinitiative.org/.
The CARTHE program includes 26 principal investigators from 14 research institutions in eight states. Together these scientists are engaged in novel research through the development of a suite of integrated models and state-of-the-art computations that bridge the scale gap between existing models and natural processes. For more information about CARTHE, please visit http://www.carthe.org or on Facebook at http://www.Facebook.com/carthe.gomri.
The study, titled "Submesoscale dispersion in the vicinity of the Deepwater Horizon spill," was published in the Aug. 18 issue of the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS). The study co-authors include: lead author Andrew Poje from the City University of New York; Özgökmen, Brian Haus, Edward Ryan, Angelique Haza, Ad Reniers, Maria Josefina Olascoaga, Guillaume Novelli, Francisco Beron-Vera, Shuyi Chen and Arthur Mariano from the Univeristy of Miami Rosenstiel School; Bruce Lipphardt, Albert Kirwan and Helga Huntley from the University of Delaware; Gregg Jacobs, Emanuel Coelho and Patrick Hogan from the Stennis Space Center's Naval Research Laboratory; and Annalisa Griffa from the Istituto di Scienze Marine in Italy.
About the University of Miami's Rosenstiel School
The University of Miami is one of the largest private research institutions in the southeastern United States. The University's mission is to provide quality education, attract and retain outstanding students, support the faculty and their research, and build an endowment for University initiatives. Founded in the 1940's, the Rosenstiel School of Marine & Atmospheric Science has grown into one of the world's premier marine and atmospheric research institutions. Offering dynamic interdisciplinary academics, the Rosenstiel School is dedicated to helping communities to better understand the planet, participating in the establishment of environmental policies, and aiding in the improvement of society and quality of life. For more information, visit: http://www.rsmas.miami.edu.
Study at Deepwater Horizon spill site finds key to tracking pollutants
Science consortium offers new information to predict how oil and other pollutants move in the ocean
2014-08-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Graphene rubber bands could stretch limits of current healthcare, new research finds
2014-08-19
Although body motion sensors already exist in different forms, they have not been widely used due to their complexity and cost of production. Now researchers from the University of Surrey and Trinity College Dublin have for the first time treated common elastic bands with graphene, to create a flexible sensor that is sensitive enough for medical use and can be made cheaply.
Once treated, the rubber bands remain highly pliable. By fusing this material with graphene - which imparts an electromechanical response on movement – the team discovered that the material can be ...
Scaling up health innovation: Fertility awareness-based family planning goes national
2014-08-19
WASHINGTON, DC -- There is no guarantee that a successful pilot program introducing a health innovation can be expanded successfully to the national, regional, state or even metropolitan level because scaling up is typically complex and difficult.
A new study from Georgetown University's Institute for Reproductive Health reports on the results of the successful large-scale implementation, in a low resource environment, of the Standard Days Method®, a highly effective fertility awareness-based family planning method developed by Institute researchers. Lessons learned ...
Intimacy a strong motivator for PrEP HIV prevention
2014-08-19
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Men in steady same-sex relationships where both partners are HIV negative will often forgo condoms out of a desire to preserve intimacy, even if they also have sex outside the relationship. But the risk of HIV still lurks. In a new study of gay and bisexual men who reported at least one instance of condomless anal sex in the last 30 days, researchers found that the same desire for intimacy is also a strong predictor of whether men would be willing to take antiretroviral medications to prevent HIV, an emerging practice known as pre-exposure ...
Sequencing at sea
2014-08-19
SAN DIEGO, Calif. (August 19, 2014) — Daylight was breaking over the central Pacific and coffee brewing aboard the MY Hanse Explorer. Between sips, about a dozen scientists strategized for the day ahead. Some would don wetsuits and slip below the surface to collect water samples around the southern Line Islands' numerous coral reefs. Others would tinker with the whirring gizmos and delicate machinery strewn throughout the 158-foot research vessel. All shared a single goal: Be the first research group to bring a DNA sequencer out into the field to do remote sequencing in ...
Physically fit kids have beefier brain white matter than their less-fit peers
2014-08-19
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A new study of 9- and 10-year-olds finds that those who are more aerobically fit have more fibrous and compact white-matter tracts in the brain than their peers who are less fit. "White matter" describes the bundles of axons that carry nerve signals from one brain region to another. More compact white matter is associated with faster and more efficient nerve activity.
The team reports its findings in the open-access journal Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.
"Previous studies suggest that children with higher levels of aerobic fitness show greater ...
Fish study links brain size to parental duties
2014-08-19
Male stickleback fish that protect their young have bigger brains than counterparts that don't care for offspring, finds a new University of British Columbia study.
Stickleback fish are well known in the animal kingdom for the fact that the male of the species, rather than the female, cares for offspring. Male sticklebacks typically have bigger brains than females and researchers wanted to find out if the difference in size might relate to their role as caregivers.
In the study, published recently in Ecology and Evolution, researchers compared regular male sticklebacks ...
Natural (born) killer cells battle pediatric leukemia
2014-08-19
Researchers at Children's Hospital Los Angeles have shown that a select team of immune-system cells from patients with leukemia can be multiplied in the lab, creating an army of natural killer cells that can be used to destroy the cancer cells. Results of their in vitro study, published August 19 in the journal Leukemia, could one day provide a less toxic and more effective way to battle this cancer in children.
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) is the most common cancer of childhood. This disease hinders the development of healthy blood cells while cancer cells proliferate. ...
Anesthesia professionals not sufficiently aware of risks of postoperative cognitive side effects
2014-08-19
New York, NY, August 19, 2014 – Postsurgical cognitive side effects can have major implications for the level of care, length of hospital stay, and the patient's perceived quality of care, especially in elderly and fragile patients. A nationwide survey of Swedish anesthesiologists and nurse anesthetists has found there is low awareness of the risks of cognitive side effects following surgery. Furthermore, only around half of the respondents used depth-of-anesthesia monitors. Results are published in Annals of Medicine and Surgery.
Patients generally expect to make a rapid ...
What's in your gut? Certain bacteria may influence susceptibility to infection
2014-08-19
The specific composition of bacterial species in a person's gut may protect against or increase susceptibility to Campylobacter, the most common cause of human bacterial intestinal inflammation, according research published this week in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology. The study also found that Campylobacter infection can yield lasting changes to one's gut bacteria composition.
"It has been known for a long time that the microbiota, or microorganisms in the gut, can protect a person from colonization by organisms that cause ...
Daughters provide as much elderly parent care as they can, sons do as little as possible
2014-08-19
SAN FRANCISCO — Parents are better off having daughters if they want to be cared for in their old age suggests a new study, which finds that women appear to provide as much elderly parent care as they can, while men contribute as little as possible.
"Whereas the amount of elderly parent care daughters provide is associated with constraints they face, such as employment or childcare, sons' caregiving is associated only with the presence or absence of other helpers, such as sisters or a parent's spouse," said study author Angelina Grigoryeva, a doctoral candidate in sociology ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
[Press-News.org] Study at Deepwater Horizon spill site finds key to tracking pollutantsScience consortium offers new information to predict how oil and other pollutants move in the ocean