(Press-News.org) South Africa is entering what is described by the Volunteer Wildfire Services of South Africa as "Cape Fire Season." The Eastern Cape provincial government warned residents in certain parts of the province on Monday (8/25) of strong winds and veld fires. A high veld fire danger rating is expected in the north-western interior and along the coast in the Great Kei and Mnquma area. Strong winds often occurred along coastal regions, and during thunderstorms. The thunderstorms bring lightning strikes and subsequent fire and the wind serves to spread the fire from one place to another. The risk of veld fires was linked to prolonged periods of little or no rain, coupled with warm, dry winds. Residents are also warned not to throw bottles in the veld as they can magnify the sun's rays and start fires.
In South Africa, this fire index map shows the daily fire danger for various areas: http://www.weathersa.co.za/home/fire-index. Today's fire danger map (8/27) shows most of the area at Very Dangerous to Extremely Dangerous levels.
Zimbabwe is by and large a savannah grassland country, with a few stretches of level, unforested grassy plains (steppes) here and there, plus some thick wooded sub-tropical forests in some regions. This type of typography makes veld fires spread more quickly as there is ample fuel for the fire across the grasslands. Veld fires which are dangerous to begin with, are also destroying farmland and making yearly food production difficult in this area as it takes time before the land can be tilled again.
Mozambique is also being plagued with veld fires in this satellite image from Aqua.
This natural-color satellite image was collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Aqua satellite on August 26, 2014. Actively burning areas, detected by MODIS's thermal bands, are outlined in red.
INFORMATION:
NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team. Caption: NASA/Goddard, Lynn Jenner with information from the Volunteer Wildfire Services in South Africa, and Weather South Africa.
Veld Fires in South Africa
2014-08-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Karina's remnants drawn into Hurricane Marie's spin
2014-08-27
Karina finally became a remnant low pressure area after roaming around in the Eastern Pacific for two weeks. Satellite data on August 27 showed that the now shapeless former hurricane was being drawn into nearby Hurricane Marie's circulation.
The last bulletin on Karina was issued by the National Hurricane Center on August 27 at 0300 UTC (11 p.m. EDT on Tuesday, August 26).
At that time, Karina's maximum sustained winds were near 30 mph (45 kph). It was centered near latitude 15.9 north and longitude 126.5 west. That's 1,185 miles (1,905 km) west-southwest of the southern ...
Group identity emphasized more by those who just make the cut
2014-08-27
People and institutions who are marginal members of a high-status or well-esteemed group tend to emphasize their group membership more than those who are squarely entrenched members of the group, according to new research published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
Research has long shown that people prefer to be in groups that are thought to have higher status or cultural value as a way of boosting self-image and projecting an impressive image to others. Despite the fact that separations between groups are often arbitrary, ...
Baicalin suppresses iron accumulation after substantia nigra injury
2014-08-27
A growing number of studies have shown that excessive iron is closely associated with the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease. Previous studies from Chunyan Guo and co-workers from Capital Medical University in China have shown that baicalin prevented iron accumulation after substantia nigra injury, reduced divalent metal transporter 1 expression, and increased ferroportin 1 expression in the substantia nigra of rotenone-induced Parkinson's disease rats. However, the relationship between iron concentration and transferrin expression is still unclear. Based on the previous ...
Factors predicting functional recovery of the upper limb after peripheral nerve injuries
2014-08-27
Currently, the main factors thought to be associated with outcomes after the repair of peripheral nerve injuries are the age of the patient, mechanism of injury, nerve injured, injury location, defect length, repair time, repair method, operation technique, and repair materials. However, despite numerous studies of outcomes after the repair of peripheral nerve injuries, there is no agreement regarding the independent predictors of a good prognosis, and the dose-effect relationship of the predictors has not been quantified. A study by Dr. Bo He and co-workers from the First ...
Gifts that generate gratitude keep customers loyal
2014-08-27
Despite major retailers investing tens of millions of dollars a year into loyalty programs, they are a dying breed, with customers struggling to see the benefits of signing up, according to QUT research.
But benefits that stimulate gratitude in customers have the power to strengthen the seller-customer relationship and ensure loyalty, researchers Dr Syed Hasan, Professor Ian Lings, Associate Professor Larry Neale and Dr Gary Mortimer, from QUT's School of Advertising, Marketing and Public Relations, found.
Lead researcher Dr Hasan, a Postdoctoral Research Fellow, said ...
Piglet weaning age no bar to litter frequency
2014-08-27
University of Adelaide research has shown that piglets can be weaned later with no negative effects on sow birthing frequency.
The outcome of the study at the University's Roseworthy campus, published in the journal Animal Reproduction Science, is an important finding for pig producers. It allows improvements in piglet health and welfare without loss of production.
"Sows don't usually start their oestrous cycles again during lactation, only coming on heat after their piglets have been weaned," says Ms Alice Weaver, PhD candidate with the School of Animal and Veterinary ...
Measurement at Big Bang conditions confirms lithium problem
2014-08-27
The field of astrophysics has a stubborn problem and it's called lithium. The quantities of lithium predicted to have resulted from the Big Bang are not actually present in stars. But the calculations are correct – a fact which has now been confirmed for the first time in experiments conducted at the underground laboratory in the Gran Sasso mountain in Italy. As part of an international team, researchers from the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) studied how much lithium forms under Big Bang conditions. The results were published in "Physical Review Letters".
Lithium, ...
Gamblers are greedy bird-brains, University of Warwick research finds
2014-08-27
Gamblers are greedy bird-brains, University of Warwick research finds
Gamblers show the same tendencies as pigeons when they make risky decisions, new research has shown.
Researchers, led by Dr Elliot Ludvig of the University of Warwick's Department of Psychology, conducted tests that found that both human gamblers and pigeons were 35% more likely to gamble for high-value than low-value rewards.
Published in Biology Letters, the researchers argue that the test results show the important role that memories of previous biggest wins and losses play when we make risky ...
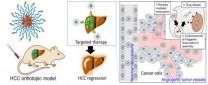
The thunder god vine, assisted by nanotechnology, could shake up future cancer treatment
2014-08-27
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the second leading cause of cancer-associated death worldwide. These regrettably poor prognoses are due to the difficulty in treating this cancer using conventional chemotherapeutic drugs such as doxorubicin, epirubicin, cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil, etoposide or combinations therein. This may be attributed to that the conventional medicines are not able to reach in a sufficient concentration in the liver tumor cells at levels that are not harmful to the rest of the body. Considering the large percentage of patients that are deemed ineligible ...
DTU researchers film protein quake for the first time
2014-08-27
One of nature's mysteries is how plants survive impact by the huge amounts of energy contained in the sun's rays, while using this energy for photosynthesis. The hypothesis is that the light-absorbing proteins in the plant's blades quickly dissipate the energy throughout the entire protein molecule through so-called protein quakes. Researchers at DTU Physics have now managed to successfully 'film' this process.
Both plants, algae and bacteria contain light-absorbing proteins which play a role in photosynthesis and thus how the organisms produce energy. However, it has ...