(Press-News.org) Biologists at Ludwig-Maximilians-Universitaet (LMU) in Munich have assigned a number of 435-million-year-old fossils to a new genus of predatory arthropods. These animals lived in shallow marine habitats and were far less eye-catching than related forms found in Jurassic strata.
Before they sank to the bottom of their shallow marine habitat and were fossilized some 435 million years ago, these arthropods preyed on other denizens of the Silurian seas – although they were not exactly inconspicuous, possessing a bivalved carapace and multiple abdominal limbs. A group of researchers including LMU biologist Carolin Haug recently recognized these fossils as the oldest representatives yet discovered of an enigmatic and now extinct class of arthropods known as Thylacocephala, and assigned them to the new species Thylacares brandonensis. "Where exactly the thylacocephalans belong among the arthropods is still a matter of intense debate," Haug says, but the new specimens shed light on the phylogenetic affinities of this problematic group of animals.
According to the authors of the study just published, certain aspects of the anatomy of T. brandonensis, together with the results of a detailed investigation of more recent specimens attributable to the group, support the hypothesis that the thylocephalans belong among the crustaceans. Moreover, the anatomy of their posteror appendages and an analysis of the organization of their muscles with the aid of fluorescence microscopy strongly suggest that they can be interpreted as a sister group of the so-called Remipedia. Remipedians, which were first described in the 1980s, are blind crustaceans found in flooded limestone caves in coastal settings in the tropics. These cave systems are typically connected to the sea via subsurface channels and are also open to the surface further inland.
"The main reason why it has been so difficult to work out the precise systematic position of thylacocephalans is that their morphology is so bizarre," says Haug. "For a long time, researchers couldn't even agree which end was anterior and which posterior." Most of the specimens so far described come from strata of Jurassic age, and are therefore 200-250 million years younger than the new species. Representatives of the group typically have unusually large compound eyes and are equipped with several paired and anteriorly located raptorial appendages, which are almost as long as the rest of the animal. This combination of characters strongly suggests that they were adapted to a predatory lifestyle. "Actually the eyes were initially not recognized as such, and instead were interpreted as stomach pouches by some researchers," says Haug. By comparison with its spectacular descendants, the new species T. brandonensis can be described as modest and unassuming. "Representatives of this thylacocephalan species have a more 'normal' morphology," says Haug, "their eyes are smaller and the raptorial appendages are shorter."
The authors of the new study therefore conclude that, like more recent representatives of the group, T. brandonensis also earned its living as a predator, but was less highly specialized than the later forms. Consequently, the morphological specializations seen in the latter probably emerged in the course of the further evolution of the class. "It is quite possible that the extreme degree of specialization seen in specimens from the Jurassic proved to be an evolutionary dead end," Haug suggests, "for at the close of the Cretaceous, at a time when many other groups of animals disappeared from the fossil record, Thylacocephala also became extinct." However, we now know that these predators had previously enjoyed a successful career that lasted for more than 350 million years.
INFORMATION:
Paleontology: Oldest representative of a weird arthropod group
2014-08-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Better classification to improve treatments for breast cancer
2014-08-28
Breast cancer can be classified into ten different subtypes, and scientists have developed a tool to identify which is which. The research, published in the journal Genome Biology, could improve treatments and targeting of treatments for the disease.
Cancer arises due to genetic changes which cause normal cells to develop into tumors. As we learn more about breast cancer, we are seeing that it is not one single disease – the mutations in the genes that cause different cancers are not alike, and this is why tumors respond differently to treatment and grow at different ...
New study charts the global invasion of crop pests
2014-08-28
Many of the world's most important crop-producing countries will be fully saturated with pests by the middle of the century if current trends continue, according to a new study led by the University of Exeter.
More than one-in-ten pest types can already be found in around half the countries that grow their host crops. If this spread advances at its current rate, scientists fear that a significant proportion of global crop-producing countries will be overwhelmed by pests within the next 30 years.
Crop pests include fungi, bacteria, viruses, insects, nematodes, viroids ...
The Lancet journals: Three-quarters of depressed cancer patients do not receive treatment for depression but a new approach could transform their care
2014-08-28
Three papers published in The Lancet Psychiatry, The Lancet, and The Lancet Oncology reveal that around three-quarters of cancer patients who have major depression are not currently receiving treatment for depression, and that a new integrated treatment programme is strikingly more effective at reducing depression and improving quality of life than current care.
An analysis of data from more than 21 000 patients attending cancer clinics in Scotland, UK, published in The Lancet Psychiatry, found that major depression is substantially more common in cancer patients than ...
Better health care as important as controlling risk factors for heart health
2014-08-28
Hamilton, ON (August 27, 2014) – Keeping a healthy heart may have as much to do with the quality of health care you have available as it does you avoiding risk factors such as smoking, bad diet and little exercise.
A large international study led by researchers at the Population Health Research Institute at McMaster University and Hamilton Health Sciences has found a that low-income countries which have people with the lowest risk factors for cardiovascular problems have the highest rates of cardiovascular events and death, while the high-income countries of people with ...
Researchers investigating new treatment for multiple sclerosis
2014-08-27
MINNEAPOLIS – A new treatment under investigation for multiple sclerosis (MS) is safe and tolerable in phase I clinical trials, according to a study published August 27, 2014, in Neurology® Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation, a new online-only, freely accessible, specialty medical journal. The publication is part of the Neurology® family of journals, published by the American Academy of Neurology.
The phase I studies were the first to test the drug candidate in humans. Studies with animals showed that the drug, which is called anti-LINGO-1, or BIIB033, may be able to ...
Bundled approach to reduce surgical site infections in colorectal surgery
2014-08-27
Bottom Line: A multidisciplinary program (called a "bundle") that spanned the phases of perioperative care helped reduce surgical site infections (SSIs) in patients undergoing colorectal surgery (CRS) at an academic medical center.
Author: Jeffrey E. Keenan, M.D., of the Duke University Medical Center, Durham, N.C., and colleagues.
Background: SSIs are associated with increased complications, length of hospital stay, readmission rates and health care costs. Efforts that have used systematic approaches, called bundles, that aim to incorporate best practices across the ...
Photodynamic therapy vs. cryotherapy for actinic keratoses
2014-08-27
Bottom Line: Photodynamic therapy (PDT, which uses topical agents and light to kill tissue) appears to better clear actinic keratoses (AKs, a common skin lesion caused by sun damage) at three months after treatment than cryotherapy (which uses liquid nitrogen to freeze lesions).
Author: Gayatri Patel, M.D., M.P.H., of the University of California Davis Medical Center, in Sacramento, and colleagues.
Background: AKs are rough, scaly lesions on the skin typically found on individuals with fair complexions who have had lots of sun exposure. The lesions have the potential ...
APOE, diagnostic accuracy of CSF biomarkers for Alzheimer disease
2014-08-27
Bottom Line: Cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) levels of β-amyloid 42(Aβ42) are associated with the diagnosis of Alzheimer disease (AD) and (Aβ) accumulation in the brain independent of apolipoprotein E (APOE) gene makeup.
Authors: Ronald Lautner, M.D., of Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Sweden, and colleagues.
Background: With the emergence of biomarker dementia diagnostics, interest in CSF biomarkers associated with AD, including Aβ42 and tau proteins, is increasing. The APOE gene is the most prominent susceptibility gene for late-onset AD. For the ...
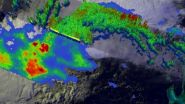
NASA's TRMM Satellite sees powerful towering storms in Cristobal
2014-08-27
VIDEO:
NASA's TRMM Satellite Sees Powerful Towering Storms in Cristobal On Aug. 26, NASA's TRMM Satellite saw a band of thunderstorms with heights of over 15km (about 9.3 miles) and was...
Click here for more information.
NASA's TRMM satellite identified areas of heavy rainfall occurring in Hurricane Cristobal as it continued strengthening on approach to Bermuda.
NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite flew above Hurricane Cristobal on August 26 at 11:35 ...
Experiments explain why some liquids are 'fragile' and others are 'strong'
2014-08-27
Only recently has it become possible to accurately "see" the structure of a liquid. Using X-rays and a high-tech apparatus that holds liquids without a container, Kenneth Kelton, PhD, the Arthur Holly Compton Professor in Arts & Sciences at Washington University in St. Louis, was able to compare the behavior of glass-forming liquids as they approach the glass transition.
The results, published in the August 6 issue of Nature Communications, are the strongest demonstration yet that bulk properties of glass-forming liquids, such as viscosity, are linked to microscopic ...