(Press-News.org) CHICAGO --- A new study from Northwestern Medicine® has found that surgical researchers rarely use female animals or female cells in their published studies -- despite a huge body of evidence showing that sex differences can play a crucial role in medical research.
Editors of the five major surgical journals reviewed in this study have responded to this finding and will now require authors to state the sex of animals and cells used in their studies. If they use only one sex in their studies, they will be asked to justify why.
"Women make up half the population, but in surgical literature, 80 percent of the studies only use males," said Melina R. Kibbe, M.D., senior author of the study and a vascular surgeon at Northwestern Medicine®.
"We need to do better and provide basic research on both sexes to ultimately improve treatments for male and female patients."
To be published Aug. 28 in the journal Surgery, the study follows a "60 Minutes" segment in February about the problem of overlooking sex differences in biomedical research, featuring Northwestern Medicine® scientists Teresa Woodruff and Kibbe.
Following the "60 Minutes" piece, the National Institutes of Health announced that they are developing a policy that will require all of its funded researchers to study both sexes for all pre-clinical research (the animal and cell studies performed before human studies).
Basic science research has shown repeatedly that male and female animals metabolize drugs differently. Accordingly, the research shows that men and women may experience differences in the ways they manifest diseases, experience illnesses and benefit from treatments.
"Requiring the sex of animals and cells is a very small thing to ask of authors," Kibbe said. "It should be a requirement of all medical journals."
Kibbe is a member of the Women's Health Research Institute and is the Edward G. Elcock Professor of Surgical Research at Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine.
For the paper, 2,347 studies from Annals of Surgery, American Journal of Surgery, JAMA Surgery, Journal of Surgical Research, and Surgery from 2011 to 2012 were reviewed. Just over 600 of those articles included animal or cell research.
More highlights from the study:
22 percent of publications using animals did not state the sex studied.
In studies that stated the sex of the animal, 80 percent used male animals, 17 percent used females and three percent used both.
Most of the studies using cell research did not specify the sex (76 percent).
In cell research that did specify the sex, 71 percent used only male cells, 21 percent only female cells and seven percent used cells from both sexes.
Only one percent of studies reported sex-based results.In female-prevalent diseases, 44 percent did not report the sex; when reported, only 14 percent studied females.
A few years ago Kibbe was encouraged to include female rats in her vascular research by fellow Northwestern scientist Teresa Woodruff. Like many researchers, Kibbe only used males because they were "easier" to study -- they lacked the hormonal changes of female rats.
Kibbe soon discovered a critical difference between female and male rats, which may be important to human health.
"I started out with ignorance," Kibbe said. "After Teresa enlightened me, I saw in my own research huge differences between the sexes. I immediately became aware of the significance of this problem."
Kibbe hopes a law will be passed, much like the Revitalization Act of 1993, which increased the enrollment of women in clinical trials, to focus on sex disparity in basic and translational research.
"The majority of research is based on the study of male animals and cells and this practice does harm to both sexes," Kibbe said. "By studying therapies and drugs in males and females, we will develop better drugs that will be more efficacious and lead to less adverse effects in both sexes."
INFORMATION:
Females ignored in basic medical research
Five surgical journals will now require studies to report sex of animals and cells
2014-08-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UTHealth researchers find up to 3,000 times the bacterial growth on hollow-head toothbrushes
2014-08-28
HOUSTON – (Aug. 28, 2014) — Solid-head power toothbrushes retain less bacteria compared to hollow-head toothbrushes, according to researchers at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth) School of Dentistry.
The results of the study are published in the August issue of the Journal of Dental Hygiene. Lead author and professor at the UTHealth School of Dentistry, Donna Warren Morris, R.D.H., M.Ed., notes that microbial counts were lower in the solid-head toothbrush group than in the two hollow-head toothbrush groups in 9 out of 10 comparisons.
"Toothbrushes ...
Together, humans and computers can figure out the plant world
2014-08-28
As technology advances, science has become increasingly about data—how to gather it, organize it, and analyze it. The creation of key databases to analyze and share data lies at the heart of bioinformatics, or the collection, classification, storage, and analysis of biochemical and biological information using computers and software. The tools and methods used in bioinformatics have been instrumental in the development of fields such as molecular genetics and genomics. But, in the plant sciences, bioinformatics and biometrics are employed in all fields—not just genomics—to ...
New analytical technology reveals 'nanomechanical' surface traits
2014-08-28
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – A new research platform uses a laser to measure the "nanomechanical" properties of tiny structures undergoing stress and heating, an approach likely to yield insights to improve designs for microelectronics and batteries.
This new technique, called nanomechanical Raman spectroscopy, reveals information about how heating and the surface stress of microscale structures affect their mechanical properties. Researchers have discussed the merits of surface-stress influence on mechanical properties for decades. However, the nanomechanical Raman spectroscopy ...
Sensory-tested drug-delivery vehicle could limit spread of HIV, AIDS
2014-08-28
A unique method for delivering compounds that could positively impact the global battle against HIV and AIDS may be possible, thanks to researchers in Penn State's College of Agricultural Sciences.
A semi-soft vaginal suppository made from the seaweed-derived food ingredient carrageenan and loaded with the antiviral drug Tenofovir provides a woman-initiated, drug-delivery vehicle that can protect against the spread of sexually transmitted infections during unprotected heterosexual intercourse, the researchers said.
With more than 34 million people worldwide living with ...
The Lancet: Respiratory infection controls being used for ebola patients are unnecessary and may contribute to public panic
2014-08-28
Respiratory infection control measures – which have been adopted by most health agencies to deal with the Ebola epidemic in west Africa – are unnecessary, and may heighten panic and fear among the public, according to the authors of a new letter, published in The Lancet, and written by Professor Jose M. Martin-Moreno from the University of Valencia in Spain, and colleagues.
Ebola virus is primarily transmitted through contact with infected patients' blood, vomit, faeces and other secretions, both direct and indirect, from contaminated needles and other materials. This ...
Indoor mold poses health risk to asthma sufferers
2014-08-28
Damp and mould in homes could pose a significant health risk to people with asthma according to a new study published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.
By critically reviewing the findings from 17 studies in eight different countries, the research has found that the presence of several types of mould can lead to breathing problems in asthma sufferers, as well as increasing the likelihood of developing the condition.
The research has been conducted by a team at the University of Exeter Medical School and is the first time all of the information relating ...
Synthesis produces new antibiotic
2014-08-28
HOUSTON – (Aug. 28, 2014) – A fortuitous collaboration at Rice University has led to the total synthesis of a recently discovered natural antibiotic.
The laboratory recreation of a fungus-derived antibiotic, viridicatumtoxin B, may someday help bolster the fight against bacteria that evolve resistance to treatments in hospitals and clinics around the world.
As part of the process, Rice organic chemist K.C. Nicolaou and structural biologist Yousif Shamoo and their colleagues created and tested a number of variants of viridicatumtoxin B that could lead to the simplified ...
Inter-dependent networks stress test
2014-08-28
Energy production systems are good examples of complex systems. Their infrastructure equipment requires ancillary sub-systems structured like a network—including water for cooling, transport to supply fuel, and ICT systems for control and management. Every step in the network chain is interconnected with a wider network and they are all mutually dependent. A team of UK-based scientists has studied various aspects of inter-network dependencies, not previously explored. The findings have been published in EPJ B by Gaihua Fu from Newcastle University, UK, and colleagues. These ...
Quantum physics enables revolutionary imaging method
2014-08-28
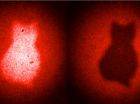
This news release is available in German. Researchers from the Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information (IQOQI), the Vienna Center for Quantum Science and Technology (VCQ), and the University of Vienna have developed a fundamentally new quantum imaging technique with strikingly counterintuitive features. For the first time, an image has been obtained without ever detecting the light that was used to illuminate the imaged object, while the light revealing the image never touches the imaged object.
In general, to obtain an image of an object one has to illuminate ...
This is your brain's blood vessels on drugs
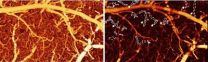
2014-08-28
WASHINGTON, Aug. 28, 2014—A new method for measuring and imaging how quickly blood flows in the brain could help doctors and researchers better understand how drug abuse affects the brain, which may aid in improving brain-cancer surgery and tissue engineering, and lead to better treatment options for recovering drug addicts. The new method, developed by a team of researchers from Stony Brook University in New York, USA and the U.S. National Institutes of Health, was published today in The Optical Society's (OSA) open-access journal Biomedical Optics Express.
The researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
[Press-News.org] Females ignored in basic medical researchFive surgical journals will now require studies to report sex of animals and cells