The Lancet Respiratory Medicine: Household air pollution puts more than 1 in 3 people worldwide at risk of ill health and early death
2014-09-03
(Press-News.org) Household air pollution, caused by the use of plant-based or coal fuel for cooking, heating, and lighting, is putting nearly three billion people worldwide at risk of ill health and early death, according to a new Commission, published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine journal.
A third of the world's population use plant-based solid fuels such as wood or charcoal, or coal, to cook, heat, and light their homes, primarily in Asia and Africa. These smoky, dirty fuels are often used in an open fire or simple stove, resulting in high levels of household air pollution in poorly ventilated homes.
Studies in India have found that in some areas, household air pollution is so high that it actually increases outdoor (ambient) air pollution – leading to pollution levels more than three times higher than a typical London street, and well above WHO-recommended safety levels.
The Commission, which was led by Professor Stephen Gordon, from the Liverpool School of Tropical Medicine, UK, and Professor William Martin, from The Ohio State University, USA, examines evidence for the effects of household air pollution on health. They conclude that an estimated 600-800 million families worldwide are at increased risk of illnesses such as respiratory tract infections, pneumonia, COPD, asthma, and lung cancer.
Estimates suggest that household air pollution killed 3•5 to 4 million people in 2010 [1]. Although overall rates of exposure to household air pollution have been declining slowly in recent years, population growth means that the number of people exposed has remained stagnant, at around 2•8 billion people worldwide.
Despite this huge toll of premature death and ill health, coordinated international and country-led efforts to tackle household air pollution have thus far been insufficient, say the authors, and public awareness of the risks of cooking with solid fuels in poorly ventilated homes remains low in the areas most badly affected.
The women and children living in poverty who are most affected by household air pollution are also likely to have poor access to healthcare – especially the complex and expensive treatments required for much of the respiratory illness and cancer caused by household air pollution.
"Although a number of clean cooking technologies – such as advanced cook stoves, LPG or solar power systems – exist, providing affected homes with cleaner ways to cook, heat, and light their homes with biomass fuel will not be the long term solution", says Professor Gordon. "In communities where solid fuel cooking methods are currently the norm, cleaner fuel and cooking methods need to be at least as affordable, efficient, and long-lasting as the traditional style methods they replace. They also need to be fit for the different cultures and regions in which they're used – if families only partially adopt cleaner cooking methods, using them alongside more polluting technologies, we are potentially looking at an expensive failure, and no reduction in the millions of people currently at risk from household air pollution."*
The Commission provides a comprehensive review of the evidence for the effect on ill health and premature death of household air pollution, examines interventions currently available, and promising future developments. It concludes by outlining research priorities which will need to be tackled if this problem is to be effectively reduced.
According to Professor Martin, "All of the evidence we examined in this Commission points to a serious need for improved commitment to tackling the problem of household air pollution. Scientists and health professionals in countries where household air pollution is still widespread need to work with governments and international health agencies to increase awareness of the huge toll that it is exacting on the population. There are many gaps in our knowledge of how to effectively measure and prevent household air pollution, but this problem cannot be solved until the global community recognises the scale of this problem and commits to coordinated and concerted action."*
INFORMATION:
NOTES TO EDITORS:
* Quotes direct from authors, and cannot be found in text of Commission
[1] Estimates taken from http://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(12)61766-8/fulltext
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers reveal carbon emissions of PlayStation 3 game distribution
2014-09-03
It's not always true that digital distribution of media will have lower carbon emissions than distribution by physical means, at least when file sizes are large.
That's the conclusion of a study published in Yale's Journal of Industrial Ecology that looked at the carbon footprint of games for consoles such as PlayStation®3. Researchers found that Blu-ray Discs delivered via retail stores caused lower greenhouse gas emissions than game files downloaded over broadband Internet. For their analysis, the investigators estimated total carbon equivalent emissions for an 8.8-gigabyte ...
'Prepped' by tumor cells, lymphatic cells encourage breast cancer cells to spread
2014-09-03
Breast cancer cells can lay the groundwork for their own spread throughout the body by coaxing cells within lymphatic vessels to send out tumor-welcoming signals, according to a new report by Johns Hopkins scientists.
Writing in the Sept. 2 issue of Nature Communications, the researchers describe animal and cell-culture experiments that show increased levels of so-called signaling molecules released by breast cancer cells. These molecules cause lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) in the lungs and lymph nodes to produce proteins called CCL5 and VEGF. CCL5 attracts tumor ...
Exposure of pregnant women to certain phenols may disrupt the growth of boys
2014-09-03
A research consortium bringing together teams from Inserm, the Nancy and Poitiers University Hospitals, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC, Atlanta, USA), and coordinated by the Inserm and University of Grenoble Environmental Epidemiology team (Unit 823), has just published an epidemiological study indicating that exposure to certain phenols during pregnancy, especially parabens and triclosan, may disrupt growth of boys during foetal growth and the first years of life. Bisphenol A was not associated with any definite modification in growth. These results ...
Survey: Number of Texans without health insurance drops under Affordable Care Act
2014-09-03
HOUSTON – (Sept. 3, 2014) – The percentage of Texans without health insurance dropped after the first enrollment period of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), according to a report released today by the Episcopal Health Foundation and Rice University's Baker Institute for Public Policy.
The report found that since the opening of the ACA's Health Insurance Marketplace, the percentage of uninsured adult Texans dropped by a little more than 2 percent. The report estimates 378,000 more Texans had health insurance in June 2014 than in September 2013.
The small gain in Texans ...
Tree frogs speed up their life cycle when becoming lunch
2014-09-03
Think again if you've always believed that events in the life cycle of animals happen consistently, almost rigidly, as part of the natural rhythm of nature. Studies by Sinlan Poo and David Bickford of the National University of Singapore, Singapore, show that Mother Nature is much more flexible than you might think. In a paper in Springer's journal Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, the researchers describe how Hansen's tree frog (Chiromantis hansenae) speeds up its life cycle to hatch earlier once its eggs are preyed upon.
Hansen's tree frog is found in Thailand and ...
UTHealth researchers gain insights into severe form of dwarfism
2014-09-03
HOUSTON – (Sept. 3, 2014) – A better understanding of the pathology of a severe form of dwarfism as well as a possible window of treatment have been discovered by researchers at The University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston (UTHealth).
The preclinical research was published in a recent issue of the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research.
Pseudoachondroplasia (PSACH) is a disorder that affects the cells in the growth plate, resulting in dwarfism, limb deformities, joint pain and early onset osteoarthritis. Children with PSACH show no signs of it at birth. Slowing ...
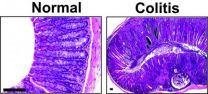
UCLA-led study identifies genetic factors involved in pediatric ulcerative colitis
2014-09-03
UCLA researchers were part of a team that has discovered the interplay of several genetic factors that may be involved in the development of early-onset ulcerative colitis, a severe type of inflammatory bowel disease.
The early research findings in mice suggest possible new targets for prevention and treatment strategies to address the inflammation generated by early-onset ulcerative colitis. The rare disease affects infants and young children and can lead to early development of colon cancer and an increased risk of liver damage.
Scientists from the David Geffen School ...
Are rising health care costs inevitable?
2014-09-03
New Rochelle, NY, September 3, 2014–If continuing increases in health care costs are inevitable, as some economists predict, is it possible for health care delivery reform to succeed in reducing the overall burden of health care expenditures on the U.S. economy? According to the results of a new study, the focus should shift from cost control to improving utilization rates and quality outcomes, as described in detail in an article in Population Health Management, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Population ...
Lowering coal-fired power plant emissions may have saved 1,700 lives in 1 year
2014-09-03
After scoring a Supreme Court victory this spring, the Environmental Protection Agency can move forward with its strategy to cut air pollution from coal-fired power plants in several states — and new research suggests the impact could be lifesaving. Scientists assessed the effects of one state's prescient restrictions on plant emissions in a report in the ACS journal Environmental Science & Technology. They estimated that the state's legislation prevented about 1,700 premature deaths in 2012.
Jacqueline MacDonald Gibson and Ya-Ru Li explain that the U.S. has been working ...
'Drink responsibly' messages in alcohol ads promote products, not public health
2014-09-03
Alcohol industry magazine ads reminding consumers to "drink responsibly" or "enjoy in moderation" fail to convey basic public health information, according to a new study from the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
A report on the research, published in the September issue of Drug and Alcohol Dependence, analyzed all alcohol ads that appeared in U.S. magazines from 2008 to 2010 to determine whether messages about responsibility define responsible drinking or provide clear warnings about the risks associated with alcohol consumption.
According to the study, ...