Ohio University paleontologists discover new species of titanosaurian dinosaur in Tanzania
Study describes rare find of sauropod dinosaur skeleton from Africa
2014-09-08
(Press-News.org) ATHENS, Ohio (Sept. 8, 2014)—Ohio University paleontologists have identified a new species of titanosaurian, a member of the large-bodied sauropods that thrived during the final period of the dinosaur age, in Tanzania. Although many fossils of titanosaurians have been discovered around the globe, especially in South America, few have been recovered from the continent of Africa.
The new species, named Rukwatitan bisepultus, was first spotted by scientists embedded in a cliff wall in the Rukwa Rift Basin of southwestern Tanzania. Using the help of professional excavators and coal miners, the team unearthed vertebrae, ribs, limbs and pelvic bones over the course of two field seasons.
CT scans of the fossils, combined with detailed comparisons with other sauropods, revealed unique features that suggested an animal that was different from previous finds—including those from elsewhere in Africa, according to a study the team published today in the Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology.
"Using both traditional and new computational approaches, we were able to place the new species within the family tree of sauropod dinosaurs and determine both its uniqueness as a species and to delineate others species with which it is most closely related," said lead author Eric Gorscak, a doctoral student in biological sciences at Ohio University.
Rukwatitan bisepultus lived approximately 100 million years ago during the middle of the Cretaceous Period. Titanosaurian sauropods, the group that includes Rukwatitan, were herbivorous dinosaurs known for their iconic large body sizes, long necks and wide stance. Although not among the largest of titanosaurians, Rukwatitan is estimated to have a forelimb reaching 2 meters and may have weighed as much as several elephants.
The dinosaur's bones exhibit similarities with another titanosaurian, Malawisaurus dixeyi, previously recovered in Malawi. But the two southern African dinosaurs are distinctly different from one another, and, most notably, from titanosaurians known from northern Africa, said co-author Patrick O'Connor, a professor of anatomy in the Ohio University Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine.
The fossils of middle Cretaceous crocodile relatives from the Rukwa Rift Basin also exhibit distinctive features when compared to forms from elsewhere on the continent.
"There may have been certain environmental features, such as deserts, large waterways and/or mountain ranges, that would have limited the movement of animals and promoted the evolution of regionally distinct faunas," O'Connor said. "Only additional data on the faunas and paleo environments from around the continent will let us further test such hypotheses."
In addition to providing new data about species evolution in sub-Saharan Africa, the study also contributes to fleshing out the global portrait of titanosaurians, which lived in habitats across the globe through the end of the Cretaceous Period. Their rise in diversity came in the wake of the decline of another group of sauropods, the diplodocoids, which include the dinosaur Apatosaurus, the researchers noted. Scientists have found fossils for more than 30 titanosaurians in South America compared to just four in Africa.
"Much of what we know regarding titanosaurian evolutionary history stems from numerous discoveries in South America—a continent that underwent a steady separation from Africa during the first half of the Cretaceous Period," Gorscak said. "With the discovery of Rukwatitan and study of the material in nearby Malawi, we are beginning to fill a significant gap from a large part of the world."
INFORMATION:
Co-authors on the study are Nancy Stevens, a professor in the Ohio University Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine, and Eric Roberts, a senior lecturer in the James Cook University of Australia.
The study was funded by the National Science Foundation, the National Geographic Society, the Ohio University Heritage College of Osteopathic Medicine and the Ohio University Office of the Vice President for Research and Creative Activity.
Editors: An artist's illustration of the dinosaur in its environment and other images are available.
Contacts: Eric Gorscak, (740) 593-2110, eg377304@ohio.edu; Patrick O'Connor, (740) 593-2110, oconnorp@ohio.edu; Director of Research Communications Andrea Gibson, (740) 597-2166, gibsona@ohio.edu.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
In one of nature's innovations, a single cell smashes and rebuilds its own genome
2014-09-08
Life can be so intricate and novel that even a single cell can pack a few surprises, according to a study led by Princeton University researchers.
The pond-dwelling, single-celled organism Oxytricha trifallax has the remarkable ability to break its own DNA into nearly a quarter-million pieces and rapidly reassemble those pieces when it's time to mate, the researchers report in the journal Cell. The organism internally stores its genome as thousands of scrambled, encrypted gene pieces. Upon mating with another of its kind, the organism rummages through these jumbled genes ...
Gobbling up poison: A method for killing colon cancer
2014-09-08
(PHILADELPHIA) – These days, cancer researchers aim to design targeted and specific therapy – those that kill cancer but spare the surrounding tissue. Immunotoxins, which use cancer-targeted antibodies linked to deadly toxins such as ricin, are one such therapy. However, few have succeeded to date in part because cancer cells share many molecules with normal cells, and because it can be challenging to unlock the deadly chemical only after the antibody has homed to the diseased tissue.
Now researchers at Thomas Jefferson University have discovered the unique biological ...
Soft robot squirms over fire, ice, and withstands crushing force
2014-09-08
ITHACA, N.Y. – Engineers have created a shape-changing "soft" robot that can tread over a variety of adverse environmental conditions including snow, puddles of water, flames, and the crushing force of being run over by an automobile.
Videos: https://cornell.box.com/softrobot
The engineers from Cornell and Harvard Universities will detail the robot in an upcoming edition of the journal Soft Robotics. An early online version of the study can be found at: http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/soro.2014.0008
The pneumatically powered, fully untethered robot was ...
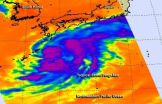
NASA sees large Tropical Storm Fengshen skirting eastern Japan's coastline
2014-09-08
Tropical Storm Fengshen is a large storm and infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite shows that it's about as long as the big island of Japan.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Storm Fengshen on September 7 and the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder instrument known as AIRS gathered temperature data about the storm's cloud tops and surrounding sea surface temperatures. The infrared data showed strong thunderstorms surrounded the center of circulation and also appeared in large bands south and northeast of the storm's center. Another large and fragmented band on ...
Yale study shows how conversion of forests to cropland affected climate
2014-09-08
The conversion of forests into cropland worldwide has triggered an atmospheric change that, while seldom considered in climate models, has had a net cooling effect on global temperatures, according to a new Yale study.
Writing in the journal Nature Climate Change, Professor Nadine Unger of the Yale School of Forestry & Environmental Studies (F&ES) reports that large-scale forest losses during the last 150 years have reduced global emissions of biogenic volatile organic compounds (BVOCs), which control the atmospheric distribution of many short-lived climate pollutants, ...
Brain damage caused by severe sleep apnea is reversible
2014-09-08
DARIEN, IL – A neuroimaging study is the first to show that white matter damage caused by severe obstructive sleep apnea can be reversed by continuous positive airway pressure therapy. The results underscore the importance of the "Stop the Snore" campaign of the National Healthy Sleep Awareness Project, a collaboration between the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, American Academy of Sleep Medicine, Sleep Research Society and other partners.
Results show that participants with severe, untreated sleep apnea had a significant reduction in white matter fiber integrity ...
A bird-pollinated flower with a rather ingenious twist
2014-09-08
VIDEO:
When a bird forages on nectar, the flower twists as the spur complies with the shape of the
bird's bill. In consequence, pollen is placed in an unusual location on...
Click here for more information.
When researchers studying several bird-pollinated species of Impatiens flowers in the mountains of western Cameroon noticed one with an odd, upwardly curving nectar spur, they couldn't imagine how any sunbird could ever sip from it. After recording visitors to the flower continuously ...
Coral trout pick their collaborators carefully
2014-09-08
VIDEO:
Coral trout are choosey about moray collaborators.
Click here for more information.
Coral trout not only work with moray eels to improve their chances of a meal, but they can also be choosy when it comes to picking the best moray partner. The findings reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on September 8 show that such sophisticated collaborative abilities are not limited to apes and humans.
The fish's behavior is remarkable in other ways too, the researchers ...
Fish as good as chimpanzees at choosing the best partner for a task
2014-09-08
Coral trout are fast when chasing prey above the reefs of their habitat, but can't pursue their quarry if it buries itself into a hard-to-reach reef crevice.
When this happens, the trout will team up with a snake-like moray eel to flush out the unfortunate fish in a remarkable piece of interspecies collaboration: either the eel takes the prey in the reef, or scares it back into the open so the trout can pounce.
Coral trout - along with close relative the roving coral grouper - will use gestures and signals to flag the location of prey to an eel, including head shakes ...
Hog workers carry drug-resistant bacteria even after they leave the farm
2014-09-08
A new study suggests that nearly half of workers who care for animals in large industrial hog farming operations may be carrying home livestock-associated bacteria in their noses, and that this potentially harmful bacteria remains with them up to four days after exposure.
Researchers had believed that livestock-associated bacteria would clear from the noses of hog workers quickly – within 24 hours. But this small study of hog workers in North Carolina, reported online Sept. 8 in the journal Occupational and Environmental Medicine, suggests it can stick around longer. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
[Press-News.org] Ohio University paleontologists discover new species of titanosaurian dinosaur in TanzaniaStudy describes rare find of sauropod dinosaur skeleton from Africa