(Press-News.org) An international team of researchers is challenging a commonly held view that explains how so many species of birds came to inhabit the Neotropics, an area rich in rain forest that extends from Mexico to the southernmost tip of South America. The new research, published today in the journal Nature, suggests that tropical bird speciation is not directly linked to geological and climate changes, as traditionally thought, but is driven by movements of birds across physical barriers such as mountains and rivers that occur long after those landscapes' geological origins.
"The Neotropic zone has more species of birds than any other region on Earth," said Brian Smith, lead author of the publication and an assistant curator at the American Museum of Natural History who started this work as a postdoctoral researcher at Louisiana State University. "The unanswered question has been—how did this extraordinary bird diversity originate?"
In the Neotropics, bird speciation—the process by which new species are formed—is usually linked to changes in Earth's landscape over time. When rivers change course, mountains rise, and continents drift, a once-continuous population can be divided into two or more smaller populations that eventually become different species. But an alternative model attributes Neotropical bird speciation to the movement of the animals across these geographical barriers, not necessarily linked to a change in landscape.
To examine these two models, the scientists compared genetic patterns among a diverse array of bird lineages that occur in the Neotropics. Each of the 27 lineages analyzed contained populations situated on the opposite side of large dispersal barriers, and with genetic data the scientists were able to estimate the time that the populations became isolated from one another. They found that most speciation occurred in the Pleistocene, which began about 2.6 million years ago, long after the origin of the Andes Mountains and the Amazonian river system, aligning with the alternative speciation model. Under this model, bird lineages with a longer occupation of the landscape have a higher likelihood of moving across geographical barriers and diversifying.
"It may be only in birds that the genetic sampling is sufficiently dense to examine how interactions between the landscape and natural populations of birds influence the speciation process," said Louisiana State University professor Robb Brumfield, lead investigator on the project. "The thousands of samples used in the study represent the culmination of over 30 years of field expeditions led by generations of LSU students and scientists, plus similar work done by ornithologists at other research collections. Biological research collections such as these are priceless."
INFORMATION:
Other institutions involved in this research include City College of New York; Museu Paraense Emílio Goeldi (Brazil); Universidad de los Andes (Colombia); Universidad Central de Venezuela; Colección Ornitológica Phelps; University of California, Los Angeles; and the University of Georgia, in Athens.
Research identifies drivers of rich bird biodiversity in Neotropics
Findings contradict leading model, link speciation to bird movement across land barriers
2014-09-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
UT Arlington research uses nanotechnology to help cool electrons with no external sources
2014-09-10
A team of researchers has discovered a way to cool electrons to −228 °C without external means and at room temperature, an advancement that could enable electronic devices to function with very little energy.
The process involves passing electrons through a quantum well to cool them and keep them from heating.
The team details its research in "Energy-filtered cold electron transport at room temperature," which is published in Nature Communications on Wednesday, Sept. 10.
"We are the first to effectively cool electrons at room temperature. Researchers have done ...
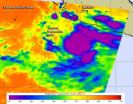
NASA catches birth of Tropical Storm Odile
2014-09-10
The Eastern Pacific Ocean continues to turn out tropical cyclones and NASA's Aqua satellite caught the birth of the fifteenth tropical depression on September 10 and shortly afterward, it strengthened into a tropical storm and was renamed Odile.
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured infrared data on Tropical Depression 15-E on September 10 at 8:53 UTC (4:53 a.m. EDT) when it developed. The National Hurricane Center named the depression at 5 a.m. EDT, when the center was located near latitude 14.4 north and ...
A new way to look at diabetes and heart risk
2014-09-10
People with diabetes who appear otherwise healthy may have a six-fold higher risk of developing heart failure regardless of their cholesterol levels, new Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health research suggests.
In nearly 50 percent of people with diabetes in their study, researchers employing an ultra-sensitive test were able to identify minute levels of a protein released into the blood when heart cells die. The finding suggests that people with diabetes may be suffering undetectable – but potentially dangerous – heart muscle damage possibly caused by their ...
Study: Sports broadcasting gender roles echoed on Twitter
2014-09-10
Twitter provides an avenue for female sports broadcasters to break down gender barriers, yet it currently serves to express their subordinate sports media roles.
This is the key finding of a new study by Clemson University researchers and published in the most recent issue of Journal of Sports Media.
"Social media has been embraced by the sports world at an extraordinary pace and has become a viable avenue for sports broadcasters to redefine their roles as celebrities," said Melinda Weathers, lead author on the study and assistant professor of communication studies ...
Cyberbullying increases as students age
2014-09-10
RIVERSIDE, Calif. — As students' age they are verbally and physically bullied less but cyberbullied more, non-native English speakers are not bullied more often than native English speakers and bullying increases as students' transition from elementary to middle school.
Those are among the findings of a wide-ranging paper, "Examination of the Change in Latent Statuses in Bullying Behaviors Across Time," recently published in the journal School Psychology Quarterly.
Authors of the paper are: Cixin Wang, an assistant professor at the University of California, Riverside's ...
Even small stressors may be harmful to men's health, new OSU research shows
2014-09-10
CORVALLIS, Ore. – Older men who lead high-stress lives, either from chronic everyday hassles or because of a series of significant life events, are likely to die earlier than the average for their peers, new research from Oregon State University shows.
"We're looking at long-term patterns of stress – if your stress level is chronically high, it could impact your mortality, or if you have a series of stressful life events, that could affect your mortality," said Carolyn Aldwin, director of the Center for Healthy Aging Research in the College of Public Health and Human ...
Unnecessary antibiotic use responsible for $163 million in potentially avoidable hospital costs
2014-09-10
Arlington, Va. (September 10, 2014) – The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and Premier, Inc. have released new research on the widespread use of unnecessary and duplicative antibiotics in U.S. hospitals, which could have led to an estimated $163 million in excess costs. The inappropriate use of antibiotics can increase risk to patient safety, reduce the efficacy of these drugs and drive up avoidable healthcare costs. The study is published in the October issue of Infection Control and Hospital Epidemiology, the journal of the Society for Healthcare Epidemiology ...
Blocking one receptor could halt rheumatoid arthritis
2014-09-10
Researchers at the University of Illinois at Chicago College of Medicine have shown for the first time how the activation of a receptor provokes the inflammation and bone degradation of rheumatoid arthritis -- and that activation of this one receptor, found on cells in the fluid of arthritic joints, is all that is required.
Their findings, published online in the Journal of Immunology, point to a new therapeutic target to interrupt the vicious cycle of inflammation and bone erosion in rheumatoid arthritis.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a progressive autoimmune inflammatory ...
NTU partners international universities to build a network of citizen oceanographers
2014-09-10
Nanyang Technological University (NTU) is working with other international universities to build a global network of 'citizen scientists' on a free-to-access database for oceanographic data.
While much attention is placed on mammals and fish in the sea, it is the tiny, marine microbes that supports the nutrient cycle and forms the foundation of the food web. Known as the marine microbiome, they are the most abundant organisms in the ocean but also the least understood.
To gain a better understanding of such marine life and its environment, NTU scientists at the Singapore ...
Residual hydraulic fracturing water not a risk to groundwater
2014-09-10
Hydraulic fracturing -- fracking or hydrofracturing -- raises many concerns about potential environmental impacts, especially water contamination. Currently, data show that the majority of water injected into wells stays underground, triggering fears that it might find its way into groundwater. New research by a team of scientists should help allay those fears.
In a paper published in the current issue of the Journal of Unconventional Oil and Gas Resources, Terry Engelder, professor of geosciences, Penn State; Lawrence Cathles, professor of earth and atmospheric sciences, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Research identifies drivers of rich bird biodiversity in NeotropicsFindings contradict leading model, link speciation to bird movement across land barriers