(Press-News.org) Researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have developed a new cocktail that is highly effective at coaxing adult cells to become quality pluripotent stem cells.
Regenerative medicine is a new and expanding area that aims to replace lost or damaged cells, tissues or organs through cellular transplantation. Because stem cells derived from human embryos can trigger ethical concerns, a good solution is reprogramming adult cells back to an embryo-like state using a combination of reprogramming factors.
The resulting cells, called induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), could be used to replace those lost to damage or disease. However, scientists have discovered that the process of reprogramming adult cells can introduce genetic abnormalities that limit the cells' usefulness in research and medicine.
To make iPSCs, scientists expose adult cells to a cocktail of genes that are active in embryonic stem cells. iPSCs can then be coaxed to differentiate into other cell types such as nerve or muscle. However, the standard combination of factors used to reprogram cells leads to a high percentage of serious genomic aberrations in the resulting cells. (The reprogramming factors are Oct4, Sox2, Klf4, and Myc — known collectively as OSKM).
Now researchers at the Hebrew University of Jerusalem have developed a new cocktail of reprogramming factors that produce high-quality iPSCs. Dr. Yosef Buganim, at the Institute for Medical Research Israel-Canada in the Hebrew University's Faculty of Medicine, worked with scientists at the lab of Whitehead Institute founding member Rudolf Jaenisch, a professor of biology at MIT.
The researchers reasoned that changing the reprogramming factors could reprogram the adult cells in a more controlled way and yield high-quality iPSCs. Working with mouse cells, Dr. Buganim and research scientist Styliani Markoulaki used bioinformatic analysis to design a new cocktail of reprogramming factors (Sall4, Nanog, Esrrb, and Lin28, known collectively as SNEL).
Their results showed that the interaction between reprogramming factors plays a crucial role in determining the quantity and quality of resulting iPSCs — and that a different combination of reprogramming factors can in fact produce a much higher quality product.
The new SNEL cocktail created fewer colonies of iPSCs, but approximately 80% of those produced passed the most stringent pluripotency test. This is highly preferable to the traditional OSKM cocktail, which produces a large number of colonies but the majority of which fail the pluripotency test.
Dr. Buganim hypothesizes that SNEL may reprogram cells better than OSKM because it does not rely on the master regulators Oct4 and Sox2, which might activate part of the adult cell genome. According to Buganim, the research demonstrates the effectiveness of bioinformatics tools in producing high quality iPSCs.
This study takes the regenerative medicine field one step closer to the clinic, where it may be able to help patients in need of cellular transplantation therapy. The researchers will now seek to define the optimal combinations for reprogramming human iPSCs, which are harder to reprogram than mouse cells and which could not be reprogrammed using the SNEL cocktail.
INFORMATION:
The research paper, "The Developmental Potential of iPSCs Is Greatly Influenced by Reprogramming Factor Selection," appears in the current issue of the journal Cell Stem Cell. Dr. Buganim was supported by a NIH Kirschstein National Research Service Award, and the research project was supported by a grant from the Israeli Centers of Research Excellence (I-CORE) program. Other researchers received support from the National Institutes of Health, National Science Foundation, Chapman Foundation, Florence Brill Graduate Student Fellowship, and Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
Scientists create therapy-grade stem cells using new cocktail to reprogram adult cells
Cells created at Hebrew University's Faculty of Medicine pass the toughest pluripotency test
2014-09-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NSCLC patients who never smoked or who quit smoking have lower risk of developing secondary cancers
2014-09-16
San Francisco, September 16, 2014— Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) survivors who never smoked or who are former smokers at the time of diagnosis have a lower risk of developing secondary primary lung cancers (SPLC) compared to those who are current smokers, suggesting that increased tobacco exposure is associated with a higher risk of SPLC, according to research presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology's (ASTRO's) 56th Annual Meeting.
The analysis studied the association between patients' smoking histories and their risks of developing SPLC, which ...
Poor body size judgement can lead to increased tolerance of obesity
2014-09-16
Size is relative, especially to people who tend to be on the heavy side. Researchers at the Columbia University Medical Center in the US found that seven in every ten obese adults underestimate how much someone weighs. People of normal weight make this mistake much less often. Mothers of overweight or obese children also tend to misjudge their children's size, as youngsters misjudge their obese mothers' size, says lead author Tracy Paul, now at Weill-Cornell Medical College, in a study¹ in the Journal of General Internal Medicine², published by Springer.
If abnormal weight ...
Prostate cancer patients who receive hypofractionated RT report consistent QoL
2014-09-16
San Francisco, September 15, 2014—Prostate cancer patients who received hypofractionated (HPFX) radiation therapy (RT) reported that their quality of life, as well as bladder and bowel function were at similar levels before and after RT, according to research presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology's (ASTRO's) 56th Annual Meeting. Additionally, results indicate that parallel quality of life outcomes occurred between groups of patients who receive different regimens of HPFX RT.
The phase I/II trial enrolled 343 patients with low-to-intermediate risk ...
Prostate cancer patients surveyed 5 years after vessel-sparing RT report preserved sexual function
2014-09-16
San Francisco, September 15, 2014—A comparison of five-year sexual function outcomes, as reported by patients treated with external beam radiotherapy (EBRT) versus combination EBRT plus brachytherapy, indicates that the utilization of vessel-sparing radiation therapy makes cure possible without compromising long-term sexual function, according to research presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology's (ASTRO's) 56th Annual Meeting.
The study examined the patient-reported outcomes of 91 men with prostate cancer who received MRI-guided, vessel-sparing ...
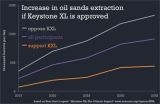
Keystone XL would likely raise oil sands production and greenhouse gas emissions
2014-09-16
Approval of the Keystone XL pipeline (KXL) would likely increase oil sands extraction, according to 26 oil sands professionals and researchers surveyed by the non-profit organization Near Zero. The results are detailed in the report, "Keystone XL: The Climate Impact," and includes both supporters and opponents of the pipeline.
This additional extraction of oil sands could lead to significantly higher greenhouse gas emissions, with the exact amount depending largely on how markets respond.
"This report examines three main scenarios discussed by participants in our ...
Single fraction RT as effective as multiple fraction RT for bone metastases
2014-09-16
San Francisco, September 15, 2014—A prospective study that compared patient-reported outcomes of a broad set of cancer patients with bone metastases demonstrates that single fraction radiation therapy (SFRT) is equally as effective as multiple fraction radiation therapy (MFRT) when pain, function and quality of life are considered, according to research presented today at the American Society for Radiation Oncology's (ASTRO's) 56th Annual Meeting. The multi-center study indicates that improvements in patients' pain, function and degree of distress were similar between the ...
Microbiome research shows each tree species has a unique bacterial identity
2014-09-16
EUGENE, Ore. -- Each tree species has its own bacterial identity. That's the conclusion of University of Oregon researchers and colleagues from other institutions who studied the genetic fingerprints of bacteria on 57 species of trees growing on a Panamanian island.
"This study demonstrates for the first time that host plants from different plant families and with different ecological strategies possess very different microbial communities on their leaves," said lead author Steven W. Kembel, a former postdoctoral researcher in the UO's Institute of Ecology and Evolution ...
Molecular mechanisms of the suppression of axon regeneration by KLF transcription factors
2014-09-16
Molecular mechanisms of the Krüppel-like family of transcription factors (KLFs) have been studied more in proliferating cells than in post-mitotic cells such as neurons. Prof. Jeffrey L. Goldberg who comes from University of California San Diego, USA and his team recently found that KLFs regulate intrinsic axon growth ability in central nervous system (CNS) neurons including retinal ganglion cells, and hippocampal and cortical neurons. With at least 15 of 17 KLF family members expressed in neurons and at least 5 structurally unique subfamilies, it is important to ...
Give progesterone a chance
2014-09-16
There is currently no standard pharmacological treatment for spinal cord injury. Here, Dr. Florencia Labombarda, who comes from Buenos Aires University, Argentina suggests that progesterone, a steroid hormone, may be a promising therapeutical candidate as it is already for traumatic brain injury, where it has reached phase II clinical trials. We rely on previous works showing anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective and promyelinating roles for progesterone after spinal cord injury and in our recent paper, in which we demonstrate that progesterone diminishes lesion, preserves ...
The role of DJ-1 in the oxidative stress cell death cascade after stroke
2014-09-16
Oxidative stress is closely associated with secondary cell death in many disorders of the central nervous system including stroke, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's disease. Among many aberrant oxidative stress-associated proteins, DJ-1 has been associated with the oxidative stress cell death cascade primarily in Parkinson's disease. Although principally expressed in the cytoplasm and nucleus, DJ-1 can be secreted into the serum under pathological condition. Recently, a close pathological association between DJ-1 and oxidative stress in stroke has been implicated. To this ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
[Press-News.org] Scientists create therapy-grade stem cells using new cocktail to reprogram adult cellsCells created at Hebrew University's Faculty of Medicine pass the toughest pluripotency test