IAS calls for universal condom acceptance in wake of Pope Benedict's comments
2010-11-24
(Press-News.org) 23 November 2010 (Geneva, Switzerland) – The International AIDS Society (IAS) cautiously notes the comments from Pope Benedict that condom use could, in specific circumstances, be acceptable, but calls on the Pope and the Catholic Church to come out clearly and strongly in support of all evidence-based methods of HIV prevention, including condom use.
By implying that there can only be some exceptional circumstances that could allow for condom usage, such as that of male prostitutes, the Pope is ignoring scientific evidence that shows that both male and female condoms, used correctly and consistently, can reduce the risk of sexual transmission of HIV by 80 to 90 percent.
Although the Pope's concession is a step in the right direction, the IAS remains sceptical especially after the Pope's comments in 2009 when he stated that condoms aggravated the AIDS problem. At that time the IAS reacted saying that his comments were "irresponsible and dangerous'' and that there was "not a shred" of evidence suggesting condom use raises the risk of HIV transmission.
The IAS President Elly Katabira expressed his mixed reaction to the Pope's comments, 'While I appreciate this is a significant shift in policy by the Pope, there is still a long way to go in convincing the Catholic church that condom usage is key to the elimination of the HIV virus which currently claims two million lives every year'.
The IAS calls on all other civil society organisations and religious communities to join the IAS in pushing for a more substantial change in the Catholic Church's policy to HIV prevention arguing that a piece-meal approach to HIV prevention will have only a marginal impact in the fight against HIV/AIDS.
In July 2011 the IAS will be holding its bi annual conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention in Rome, Italy, and will use this platform to further advocate for universal access to all HIV prevention methods.
INFORMATION:
About the IAS
The International AIDS Society (IAS) is the world's leading independent association of HIV professionals, with over 19,000 members from more than 190 countries working at all levels of the global response to AIDS. Our members include researchers from all disciplines, clinicians, public health and community practitioners on the frontlines of the epidemic, as well as policy and programme planners. The IAS is the custodian of the biennial International AIDS Conference and lead organizer of the IAS Conference on HIV Pathogenesis, Treatment and Prevention, which will be held in Rome, Italy in July 2011.
www.iasociety.org | www.ias2011.org
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2010-11-24
November 23, 2010 – Geneva, Switzerland – The International AIDS Society (IAS) calls on the Burmese Government to reverse a ruling made on November 18 to shut down a charitable HIV/AIDS clinic in Rangoon. The government demand came just one day after Aung San Suu Kyi, the recently released Nobel Peace Prize laureate visited the centre to show her support.
The clinic known as the HIV/AIDS Patients Care Center has been given up to November 25 to close. The Burmese Government has repealed the clinic's permit as well as refusing to renew residence permits to the 80 patients ...
2010-11-24
TORONTO, ON – Many people say they wouldn't cheat on a test, lie on a job application or refuse to help a person in need.
But what if the test answers fell into your lap and cheating didn't require any work on your part? If you didn't have to face the person who needed your help and refuse them? Would that change your behaviour?
New research out of the University of Toronto Scarborough shows it might. In two studies that tested participants' willingness to behave immorally, the UTSC team discovered people will behave badly – if it doesn't involve too much work on their ...
2010-11-24
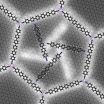
In the nanoworld many things are different. Scientists only recently started unveiling and harnessing the underlying laws and principles. A team associated with Professor Johannes Barth from the Physics Department of the TU Muenchen have now succeeded in capturing rod-shaped molecules in a two-dimensional network in such a way that they autonomously form small rotors that turn in their honeycomb-like cages.
Nature itself provides the role model for such self-organizing systems. This is how proteins bring reactants so close together that reactions can take place – reactions ...
2010-11-24
CHICAGO (November 23, 2010) - Even though most people are aware that good oral health is essential for the overall health of both mother and child, misunderstandings about the safety of dental care during pregnancy may cause pregnant women to avoid seeing their dentist. The fact is that dentists can create a treatment plan that is safe, effective, and essential for combating the adverse effects of oral disease during pregnancy.
During the course of pregnancy, a woman's oral health can undergo significant changes. According to an article published in the November/December ...
2010-11-24
Even when equipped with compressed-air bottles and diving regulators, humans reach their limits very quickly under water. In contrast, unmanned submarine vehicles that are connected by cable to the control center permit long and deep dives. Today remote-controlled diving robots are used for research, inspection and maintenance work. The possible applications of this technology are limited, however, by the length of the cable and the instinct of the navigator. No wonder that researchers are working on autonomous underwater robots which orient themselves under water and carry ...
2010-11-24
While Africa is certainly no stranger to violence, the response to the Kenyan presidential elections of 2007 came as a surprise. Political unrest evolved into outright and unmitigated violence, marring the relatively peaceful history of Kenya's educated and mainly urban population. During allegations of voter manipulation and election fraud, two of Kenya's largest tribes, the Kalenjin and the Kikuyu, found themselves divided by anger, fueled by another tribe's promises of power and control.
Wesley Shrum, LSU professor of sociology, had experience dealing with human tragedy ...
2010-11-24
AMES, Iowa - Most living plant and animal species have a certain, relatively small, amount of variation in their genetic make-up.
Differences in height, skin and eye color of humans, for example, are very noticeable, but are actually the consequences of very small variations in genetic makeup.
Researchers at Iowa State University, China Agricultural University and the Beijing Genomics Institute in China recently re-sequenced and compared six elite inbred corn (maize) lines, including the parents of the most productive commercial hybrids in China.
When comparing the different ...
2010-11-24
Tel Aviv -- Ferrography, a practice used by the American and Israeli air forces to monitor the condition of machinery, extracts tiny iron particles from lubricants such as oil and grease to analyze wear in machines. Determining whether a system requires preventative maintenance can be the key to preventing catastrophic failure.
Now Tel Aviv University scientists are exploring a modification of this technique for human analysis -- called "bio-ferrography" -- to diagnose diseases in their early stages, determine the efficacy of drugs, and ascertain the condition of orthopedic ...
2010-11-24
Lions, bears, monkeys, crocodiles, parrots and iguanas may seem inoffensive at first glance when they're behind bars in zoos. But some exotic species can escape and become invasive species. This has been confirmed by a scientific team that has checked 1,568 animal houses in 63 Spanish zoos. Birds are the animals most likely to escape.
"As zoos house a large number of exotic (non-indigenous) species, they could become an entry channel for these species if they escape, with the potential environmental risk that this implies", María C. Fàbregas, lead author of the study ...
2010-11-24
(Boston) – Researchers from the Boston University School of Medicine (BUSM) have demonstrated that commensal species of the genus Neisseriae are low inducers of human airway epithelial cell responses as compared to the pathogenic species. Specifically, the study indicates that a Neisserial outer membrane component appears to play a differential role in the host inflammatory responses via interaction with a receptor on the surface of human airway epithelial cells.
Paola Massari, an assistant professor in the section of infectious diseases at BUSM, is lead author of this ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] IAS calls for universal condom acceptance in wake of Pope Benedict's comments