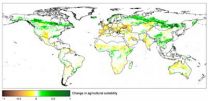
(Press-News.org) According to a simulation of the impact of climate change on agricultural production over the course of the 21st century, carried out by researchers led by Professor Wolfram Mauser at LMU's Department of Geography, some two-thirds of all land potentially suitable for agricultural use is already under cultivation. The study indicates that climate change will expand the supply of cropland in the high latitudes of the Northern hemisphere (Canada, Russia, China) over the next 100 years. However, in the absence of adaptation measures such as increased irrigation, the simulation projects a significant loss of suitable agricultural land in Mediterranean regions and in parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. The results of the study appear in the online journal PLOS ONE.
Ecological factors such as climate, soil quality, water supply and topography determine the suitability of land for agriculture. In the new study the LMU team focused on the probable impact of climate change on the supply of land suitable for the cultivation of the 16 major food and energy crops worldwide, including staples such as maize, rice, soybeans and wheat. "Based on the environmental requirements for growth of these plants, in terms of climate, soil and terrain, one can determine whether or not a given location on Earth provides conditions required by specific crops," says Dr. Florian Zabel, one of the authors of the new study.
The results show that, if one includes areas, such as the Nile Valley, which are already dependent on irrigation today, some 80 million square kilometers (km2) of the Earth's land surface is potentially suitable for agricultural use. This figure is equivalent to about half the total land surface of the Earth. However, approximately one-third of this land is currently designated as protected or consists of densely forested areas. If one assumes that these areas retain their status, this reduces the size of the pool of land suitable for agricultural use to some 54 million km2 – and of this, 91% is already under cultivation.
Limits to the expansion of cropland
"In the context of current projections, which predict that the demand for food will double by the year 2050 as the result of population increase, our results are quite alarming. In addition, one must consider the prospect of increased pressure on land resources for the cultivation of forage crops and animal feed owing to rising demand for meat, and the expansion of land use for the production of bioenergy," says Zabel.
One obvious way to expand the pool of land available for agricultural production would be to convert existing forest areas into cropland. "This approach has been increasingly adopted over the past several decades in countries such as Brazil and Indonesia. The problem is such forest areas provide crucial ecosystem services which, among other things, help to regulate climate. Loss of these sources of natural regulation could make whole regions infertile," says Prof. Wolfram Mauser. For this reason, alternatives to this form of expansion of farming land will have to be developed and at the same time the necessary global increase in agricultural production needs to be achieved. "And this will require a detailed understanding of the agricultural potential at every point on the land surface." In helping to provide such knowledge, the LMU team hopes to create a basis for the optimal allocation of land resources while protecting and preserving crucial ecosystems. This would enable agricultural efficiency to be sustainably increased, while minimizing the accompanying social and environmental costs.
As input for their simulation study, the LMU scientists used data obtained with the global climate model ECHAM5. This model makes it possible to predict the climatic effects of various scenarios and rates of increase of CO2 emissions. The researchers chose the projections of one particular scenario (A1B), which leads to an increase of land suitable for agriculture by 5 million km2 by the year 2100. "Much of the additional area is, however, at best only moderately suited to agricultural use, so the proportion of highly fertile land used for crop production will decrease," says Zabel. Moreover, in the tropical regions of Brazil, Asia and Central Africa, climate change will significantly reduce the chance of obtaining multiple harvests per year.
INFORMATION:
The LMU team carried out the simulation as part of a nationwide research project devoted to the "Global Assessment of Land Use Dynamics, Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Ecosystems Services", which focuses on aspects of sustainable land management, and is financially supported by the Federal Ministry for Education and Research.
Publication:
Florian Zabel, Birgitta Putzenlechner, Wolfram Mauser:
Global agricultural land resources – a high-resolution suitability evaluation and its perspectives until 2100 under climate change conditions.
In: PLOS ONE
Link: http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107522
DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107522
Date of Publication: 17.09.2014
Contact:
Dr. Florian Zabel
Department of Geography, LMU Munich
Phone: +49 (0) 89 2180-6689
Email: f.zabel@lmu.de
Global agriculture: More land, fewer harvests
2014-09-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Withdrawal from the evolutionary race
2014-09-18
This news release is available in German. In ecology, disease tolerance is defined as a host strategy not to fight a pathogen tooth and nail, but rather tolerate it to live (and survive) better in the long term. One key feature of tolerance is that the disease only progresses very slowly – if at all – even if the host carries a high pathogen load.
Roland Regoes, a senior scientist at ETH Zurich's Institute of Theoretical Biology, has now transferred this approach to HIV. He set about investigating whether there are infected people who are more tolerant of the HI virus ...
Decision-support program helps keep seniors out of the emergency room
2014-09-18
New Rochelle, NY, September 18, 2014–An Emergency Room Decision-Support (ERDS) program can significantly reduce ER visits and hospital admissions among older adults on Medicare. This could have important economic implications, helping to reduce the nearly 33% of avoidable ER visits that contribute to about $18 billion in unnecessary healthcare costs each year. Details of a successful ERDS program that had a positive return on investment are published in an article in Population Health Management, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article ...
Language evolution: Quicker on the uptake
2014-09-18
The ability to acquire and creatively manipulate spoken language is unique to humans. "The genetic changes that occurred over the past 6 million years of human evolution to make this possible are largely unknown, but Foxp2 is the best candidate gene we now have," says Wolfgang Enard, Professor of Anthropology and Human Biology at LMU. In his efforts to understand the molecular biological basis of language Enard has now taken an important step forward. The results of his latest study, undertaken in collaboration with scientists at several universities, including the Massachusetts ...
First eyewitness accounts of mystery volcanic eruption
2014-09-18
This eruption occurred just before the 1815 Tambora volcanic eruption which is famous for its impact on climate worldwide, with 1816 given memorable names such as 'Eighteen-Hundred-and-Froze-to-Death', the 'Year of the Beggar' and the 'Year Without a Summer' because of unseasonal frosts, crop failure and famine across Europe and North America. The extraordinary conditions are considered to have inspired literary works such as Byron's 'Darkness' and Mary Shelley's Frankenstein.
However, the global deterioration of the 1810s into the coldest decade in the last 500 years ...
Lunar explorers will walk at higher speeds than thought
2014-09-18
Anyone who has seen the movies of Neil Armstrong's first bounding steps on the moon couldn't fail to be intrigued by his unusual walking style. But, contrary to popular belief, the astronaut's peculiar walk was not the result of low gravity. Wyle Science, Engineering and Technology scientist John De Witt explains that the early space suits were not designed for walking, so the astronauts adapted their movements to the restrictions of the suit. Michael Gernhardt, the head of NASA's Extravehicular Activity Physiology, Systems and Performance Project, wants to learn more about ...
Wild berry extract may strengthen effectiveness of pancreatic cancer drug
2014-09-18
A wild berry native to North America may strengthen the effectiveness of a chemotherapy drug commonly used to treat pancreatic cancer, reveals research published online in the Journal of Clinical Pathology.
The study by researchers at King's College Hospital and the University of Southampton suggests that adding nutraceuticals to chemotherapy cycles may improve the effectiveness of conventional drugs, particularly in hard to treat cancers, such as pancreatic cancer.
The team tested the effectiveness of extract of chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) in killing off cancer ...
Violence rates can be halved in just 30 years, say leading experts
2014-09-18
New evidence will be presented at the first Global Violence Reduction Conference in Cambridge this week which shows that homicide rates have been declining since the mid-1990s in many parts of the world - in some cases dramatically.
Nations as diverse as Estonia, Hong Kong, South Africa, Poland, and Russia have seen average recorded homicide rates drop by 40% or more in the course of just 15 years. Out of 88 countries where trend data could be found, 67 showed a decline and only 20 showed an increase between 1995 and 2010, a new analysis of data from the United Nations ...
The Lancet Haematology: PET-CT predicts lymphoma survival better than conventional imaging
2014-09-18
Positron emission tomography/computed tomography (PET-CT) is more accurate than conventional CT scanning in measuring response to treatment and predicting survival in patients with follicular lymphoma, and should be used routinely in clinical practice, according to new research published in The Lancet Haematology.
"Our findings have important implications for patients with follicular lymphoma, a common and usually slow-growing lymphoma. Compared to conventional CT scanning, PET-CT is more accurate in mapping-out the lymphoma, and better identifies the majority of patients ...
Peacock's train is not such a drag
2014-09-18
The magnificent plumage of the peacock may not be quite the sacrifice to love that it appears to be, University of Leeds researchers have discovered.
Dr Graham Askew, from the University's School of Biomedical Sciences, filmed five Indian peacocks taking off using two high-speed video cameras to try to work out what price male birds pay for carrying the spectacular iridescent feathers they use in displays to attract females.
"These feathers weigh about 300g and can exceed 1.5m, so it's expected that the male birds would be making a significant sacrifice in their flight ...
'Office life' of bacteria may be their weak spot
2014-09-18
Scientists at the University of Leeds think we may be able to drown deadly bacteria in their own paperwork.
A research team in the University's Astbury Centre for Structural Molecular Biology has identified for the first time how the "paper shredder" that keeps the bacteria E. coli on top of its day job works.
Now the group are looking for ways to jam the mechanism and leave E. coli and similar bacteria in filing hell.
Dr Kenneth McDowall, Associate Professor in Molecular Microbiology, who led the research, said: "If we block the 'shredder' using genetics in the ...