(Press-News.org) Fatigue, weight gain, chills, hair loss, anxiety, excessive perspiration — these symptoms are a few of the signs that the thyroid gland, which regulates the body's heart rate and plays a crucial role in its metabolism, has gone haywire. Now, new research from Tel Aviv University points to an additional complication caused by thyroid imbalance: congenital deafness.
The study, published in Mammalian Genome, was conducted by Prof. Karen B. Avraham and Dr. Amiel Dror of the Department of Human Molecular Genetics and Biochemistry at TAU's Sackler School of Medicine. Using state-of-the-art imaging, the researchers found that congenital deafness can be caused by an absence of a thyroid hormone during development.
"Since our laboratory mainly focuses on the system of the inner ear, the study of a system such as the thyroid gland was new to us and therefore challenging," said Dr. Dror. "My curiosity as to how these two systems interact together to develop normal hearing led to this multidisciplinary study."
A Colorful Approach
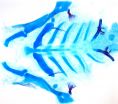
The researchers used mouse populations to study a form of congenital deafness that affects humans. Harnessing electron microscopy at the Sackler Cellular & Molecular Imaging Center, researchers tracked the inner hair cells of the cochlea (the auditory portion of the inner ear) in two groups — control (wild) mice and mutant (congenitally deaf) mice. Inner-ear hair bundles in the affected mice were labelled with bright colors to highlight the disorganization of the ear's hair cells.
Examination of the inner ear showed a spectrum of structural and molecular defects consistent with hypothyroidism or disrupted thyroid hormone action. The researchers' analysis of the images revealed defective formation of the mice's thyroid glands: labelled thyroid follicles did not grow or grew incompletely.
"Our work demonstrated that normal hearing fails to develop when thyroid hormone availability is insufficient as a result of a genetic mutation," said Dr. Dror. "Our model provides a platform to test therapeutic approaches in order to prevent hearing loss before it occurs. There is still long way ahead before we get to the point of practical treatments with our research, but we believe we are moving in the right direction."
A Lifelong Commitment
"My attraction to sound began very early as a child," said Dr. Dror. "I play string instruments and pay great attention to sound quality and perception. As a graduate student in the Avraham laboratory, I was exposed to the fascinating world of genetics and the opportunity to combine two fields of research that I am interested in: genetics and hearing. Now that I have continued this research as a medical student, the direct interaction with patients with hearing impairments encouraged me to explore the clinical significance of my research."
As a physician, Dr. Dror believes it is important to pursue research with clinical consequences for his patients. "The basis of all advanced medicine relies on both basic science and clinical research. I hope that our study will contribute a modest part to global efforts for improved medical care and treatment of hearing impairments," Dr. Dror said.
INFORMATION:
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health and I-CORE Gene Regulation in Complex Human Disease.
American Friends of Tel Aviv University supports Israel's leading, most comprehensive and most sought-after center of higher learning, Tel Aviv University (TAU). Rooted in a pan-disciplinary approach to education, TAU is internationally recognized for the scope and groundbreaking nature of its research and scholarship — attracting world-class faculty and consistently producing cutting-edge work with profound implications for the future. TAU is independently ranked among the world's top universities and #1 in Israel. It joins a handful of elite international universities that rank among the best producers of successful startups.
Lack of thyroid hormone blocks hearing development
Tel Aviv University researchers discover that a genetic form of deafness is due to absence of thyroid hormone
2014-09-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Some concussion education more useful than others, parents say
2014-09-22
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – Many parents whose kids participate in athletics will be asked to sign a waiver about concussion education, but that's not enough to ensure parents are confident about handling the injury, according to a new University of Michigan C.S. Mott Children's Hospital National Poll on Children's Health.
In the poll, about half of the 912 parents of middle and high school children surveyed reported participation in some type of concussion education:
23% have read a brochure or online information
17% have watched a video or attended a presentation
...
King Fire rages on in Eldorado National Forest
2014-09-22
Evacuations of 2,819 people have occurred in the wake of the huge King Fire blazing out of control near the Eldorado National Forest. The King Fire is burning in steep terrain in the South Fork of the American River Canyon, Silver Creek Canyon, and the Rubicon Canyon, north of the community of Pollock Pines. The fire has crossed into Placer County and burned onto the Tahoe National Forest north of the Eldorado National Forest. The anticipated spread is expected to be minimal on Sept. 22 due to thunderstorms that moved through the area overnight, bringing lightning and ...
Blood test may help determine who is at risk for psychosis
2014-09-22
A study led by University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill researchers represents an important step forward in the accurate diagnosis of people who are experiencing the earliest stages of psychosis.
Psychosis includes hallucinations or delusions that define the development of severe mental disorders such as schizophrenia. Schizophrenia emerges in late adolescence and early adulthood and affects about 1 in every 100 people. In severe cases, the impact on a young person can be a life compromised, and the burden on family members can be almost as severe.
The study published ...
NASA's TRMM satellite tallies Hurricane Odile's heavy rainfall
2014-09-22
During the week of Sept. 15, Hurricane Odile and its weakened remnants produced heavy rainfall that caused dangerous flooding over Mexico's Baja California peninsula and southwestern United States. NASA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite gathers data on rainfall that was used to create a map that showed estimated totals that in one case neared almost three feet!
Some of Odile's may have been welcomed in the U.S. Southwest where some areas have been experiencing extreme to exceptional drought conditions, but some was extreme and led to flooding.
TRMM ...
Dartmouth's new ZEBRA bracelet strengthens computer security
2014-09-22
In a big step for securing critical information systems, such as medical records in clinical settings, Dartmouth College researchers have created a new approach to computer security that authenticates users continuously while they are using a terminal and automatically logs them out when they leave or when someone else steps in to use their terminal.
Dartmouth's Trustworthy Health and Wellness (THaW)/ researchers recently presented their findings at the IEEE Symposium on Security & Privacy.
Common authentication methods based on passwords, tokens or fingerprints perform ...
NASA sees Tropical Storm Fung-Wong move through East China Sea
2014-09-22
Tropical Storm Fung-Wong weakened over the weekend of Sept. 20-21 as it moved over Taiwan and approached Shanghai, China.
NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image of Tropical Storm Fung-Wong when it was approaching Taiwan on Sept. 20 at 1:35 a.m. EDT.
On Sunday, Sept. 21, Tropical Storm Fung-Wong was over Taiwan. It was centered at 26.0 north latitude and 122.0 east longitude, just 60 miles north-northeast of Taipei, Taiwan and moving to the north. Maximum sustained winds were near 50 knots (57 knots/92.6 kph).
By Monday, Sept. 22, Fung-Wong's center was approaching ...
University of Southern California researchers reveal how gene expression affects facial expressions
2014-09-22
A person's face is the first thing that others see, and much remains unknown about how it forms — or malforms — during early development. Recently, Chong Pyo Choe, a senior postdoctoral fellow working in the lab of USC stem cell researcher Gage Crump, has begun to unwind these mysteries.
In a September study published in the journal Development, Choe and Crump describe how a mutation in a gene called TBX1 causes the facial and other deformities associated with DiGeorge syndrome.
During prenatal development, a series of segments form that eventually organize many features ...
New 'star' shaped molecule breakthrough
2014-09-22
Scientists at The University of Manchester have generated a new star-shaped molecule made up of interlocking rings, which is the most complex of its kind ever created.
Known as a 'Star of David' molecule, scientists have been trying to create one for over a quarter of a century and the team's findings are published in the journal Nature Chemistry.
Consisting of two molecular triangles, entwined about each other three times into a hexagram, the structure's interlocked molecules are tiny – each triangle is 114 atoms in length around the perimeter. The molecular triangles ...
Fracking's environmental impacts scrutinized
2014-09-22
Greenhouse gas emissions from the production and use of shale gas would be comparable to conventional natural gas, but the controversial energy source actually faired better than renewables on some environmental impacts, according to new research.
The UK holds enough shale gas to supply its entire gas demand for 470 years, promising to solve the country's energy crisis and end its reliance on fossil-fuel imports from unstable markets. But for many, including climate scientists and environmental groups, shale gas exploitation is viewed as environmentally dangerous and ...
New rules for anticancer vaccines
2014-09-22
Scientists have found a way to find the proverbial needle in the cancer antigen haystack, according to a report published in The Journal of Experimental Medicine.
As cancer cells divide, they accumulate random mistakes (mutations). This process creates new versions of proteins, some of which are recognized as foreign invaders by immune cells called T cells, prompting the cells to attack and eliminate the cancer cells. With our current ability to identify all of the mutations in a patient's cancer and to understand which protein sequences can be recognized by T cells, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
[Press-News.org] Lack of thyroid hormone blocks hearing developmentTel Aviv University researchers discover that a genetic form of deafness is due to absence of thyroid hormone