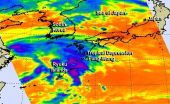
(Press-News.org) Tropical Depression Fung-Wong looked more like a cold front on infrared satellite imagery from NASA than it did a low pressure area with a circulation.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Depression Fung-Wong on Sept. 23 at 12:23 a.m. EDT. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument that flies aboard Aqua gathered infrared temperature data on the storm's clouds. The data was false-colored at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California and showed that the storm resembled a frontal system more than a depression. The center of circulation was southwest of the bulk of thunderstorms and showers, which resembled a curved front. The strongest thunderstorms had cloud-top temperatures near -63F/-53C, and were over Japan's northern Ryuku Islands.
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center issued the final bulletin on Fung-Wong on Sept. 23 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT) when it was centered about 351 miles west of Sasebo, Japan, near 32.4 north latitude and 122.8 east longitude. At the time, the depression had maximum sustained winds near 30 knots (34.5 mph/55.5 kph). It was moving to the northeast at 11 knots (12.6 mph/20.3 kph).
On Sept. 24, the remnants of Fung-Wong, now an extra-tropical storm continued moving to the northeast and into the tropical cyclone history books.
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
NASA sees the end of post-depression Fung-Wong
2014-09-24
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How a single, genetic change causes retinal tumors in young children
2014-09-24
Retinoblastoma is a childhood retinal tumor usually affecting children one to two years of age. Although rare, it is the most common malignant tumor of the eye in children. Left untreated, retinoblastoma can be fatal or result in blindness. It has also played a special role in understanding cancer, because retinoblastomas have been found to develop in response to the mutation of a single gene – the RB1 gene—demonstrating that some cells are only a step away from developing into a life-threatening malignancy.
David E. Cobrinik, MD, PhD, of The Vision Center at Children's ...
New milestone in the search for water on distant planets
2014-09-24
Astronomers have found water vapor in the atmosphere of a planet about four times bigger than Earth, in the constellation Cygnus about 124 light years - or nearly 729 trillion miles - from our home planet. In the quest to learn about planets beyond our solar system, this discovery marks the smallest planet for which scientists have been able to identify some chemical components of its atmosphere.
The researchers' findings were published Sept. 25, 2014 in the journal Nature. The team was led by University of Maryland Astronomy Professor Drake Deming, an expert in the study ...
A single statistic can strengthen public support for traffic safety laws
2014-09-24
Public support for effective road safety laws, already solid, can be strengthened by a single number: a statistic that quantifies the traffic-related injury risks associated with a given law, according to a new study from the Johns Hopkins Center for Injury Research and Policy at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health.
The study, published in the September issue of Accident Analysis & Prevention, surveyed 2,397 adults nationwide about their attitudes toward four types of road-safety laws —mandatory ignition interlock installation for people convicted of driving ...
Alzheimer's patients can still feel the emotion long after the memories have vanished
2014-09-24
A new University of Iowa study further supports an inescapable message: caregivers have a profound influence—good or bad—on the emotional state of individuals with Alzheimer's disease. Patients may not remember a recent visit by a loved one or having been neglected by staff at a nursing home, but those actions can have a lasting impact on how they feel.
The findings of this study are published in the September 2014 issue of the journal Cognitive and Behavioral Neurology, and can be viewed online for free here.
UI researchers showed individuals with Alzheimer's disease ...
Clear skies on exo-Neptune
2014-09-24
Astronomers using data from the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope, the Spitzer Space Telescope, and the Kepler Space Telescope have discovered clear skies and steamy water vapour on a planet outside our Solar System. The planet, known as HAT-P-11b, is about the size of Neptune, making it the smallest exoplanet ever on which water vapour has been detected. The results will appear in the online version of the journal Nature on 24 September 2014.
The discovery is a milestone on the road to eventually finding molecules in the atmospheres of smaller, rocky planets more akin ...
Most metal-poor star hints at universe's first supernovae
2014-09-24
A team of researchers, led by Miho N. Ishigaki, at the Kavli IPMU, The University of Tokyo, pointed out that the elemental abundance of the most iron-poor star can be explained by elements ejected from supernova explosions of the universe's first stars. Their theoretical study revealed that massive stars, which are several tens of times more immense than the Sun, were present among the first stars. The presence of these massive stars has great implications on the theory of star formation in the absence of heavy elements.
Iron-poor stars provide insight about the very ...
A look at Florida's charterboat-based recreational shark fishery
2014-09-24
CORAL GABLES, FLORIDA (September 24, 2014) — The challenge and excitement of catching a large fish makes shark fishing very appealing for recreational anglers. However, many species of sharks have experienced population declines due to commercial overfishing. Although generally overlooked by conservation advocates, catch and release shark fishing can provide a strong economic incentive to protect sharks, benefiting both ecotourism businesses and shark conservation.
Florida is one of the largest recreational shark fishing markets in the world. However, Florida's recreational ...
Realizing the promise of education
2014-09-24
Miami, Fla. (September, 24, 2014)—Two decades after its initiation, the University of Miami (UM) Linda Ray Intervention Program for substance-exposed babies and toddlers demonstrates long-term success.
The program is designed to help children from birth to three years of age who are developmentally delayed, prenatally exposed to drugs and often with the additional risk of maltreatment, ultimately achieve their developmental milestones and be ready to enter kindergarten ready to learn.
The program started in 1993 as an innovative partnership between the UM Linda Ray Intervention ...
Modest acute changes in cardiac biomarkers and electrocardiogram findings following thoracic radiation therapy
2014-09-24
DENVER – There were only modest acute changes in cardiac biomarkers and electrocardiograms and there were no clinically significant cardiac events in patients with high-dose radiation exposure to the heart following thoracic radiation therapy (RT) and short-term follow-up.
Radiation therapy is standard of care for some patients with thoracic malignancies such as lung cancer, esophageal cancer, thymoma, or malignant mesothelioma. Radiation exposure to the heart is avoided when possible but even with advanced radiation therapy techniques there are instances when high radiation ...
Indian scientists significantly more religious than UK scientists
2014-09-24
Indian scientists are significantly more religious than United Kingdom scientists, according to the first cross-national study of religion and spirituality among scientists.
The U.K. and India results from Religion Among Scientists in International Context (RASIC) study were presented at the Policies and Perspectives: Implications From the Religion Among Scientists in International Context Study conference held today in London. The conference was sponsored by the Religion and Public Life Program and the Baker Institute for Public Policy. The U.K. results were also presented ...