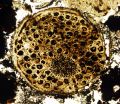
(Press-News.org) A Virginia Tech geobiologist with collaborators from the Chinese Academy of Sciences have found evidence in the fossil record that complex multicellularity appeared in living things about 600 million years ago – nearly 60 million years before skeletal animals appeared during a huge growth spurt of new life on Earth known as the Cambrian Explosion.
The discovery published online Wednesday in the journal Nature contradicts several longstanding interpretations of multicellular fossils from at least 600 million years ago.
"This opens up a new door for us to shine some light on the timing and evolutionary steps that were taken by multicellular organisms that would eventually go on to dominate the Earth in a very visible way," said Shuhai Xiao, a professor of geobiology in the Virginia Tech College of Science. "Fossils similar to these have been interpreted as bacteria, single-cell eukaryotes, algae, and transitional forms related to modern animals such as sponges, sea anemones, or bilaterally symmetrical animals. This paper lets us put aside some of those interpretations."
In an effort to determine how, why, and when multicellularity arose from single-celled ancestors, Xiao and his collaborators looked at phosphorite rocks from the Doushantuo Formation in central Guizhou Province of South China.
They recovered three-dimensionally preserved multicellular fossils that showed signs of cell-to-cell adhesion, differentiation, and programmed cell death — qualities of complex multicellular eukaryotes such as animals and plants.
The discovery sheds light on how and when solo cells began to cooperate with other cells to make a single, cohesive life form.
The complex multicellularity evident in the fossils is inconsistent with the simpler forms such as bacteria and single-celled life typically expected 600 million years ago.
While some hypotheses can now be discarded, several interpretations may still exist, including the multicellular fossils being transitional forms related to animals or multicellular algae.
Xiao said future research will focus on a broader paleontological search to reconstruct the complete life cycle of the fossils.
INFORMATION:
Xiao earned his bachelor's and master's degrees from Beijing University in 1988 and 1991 and his doctoral degree from Harvard University in 1998. He worked for three years at Tulane University before arriving at Virginia Tech in 2003.
He is currently active in an editorial role for seven professional publications and has published more than 130 papers.
More resources are available at Virginia Tech News.
Fossil of multicellular life moves evolutionary needle back 60 million years
Virginia Tech researcher finds evidence of cellular complexity eras earlier than expected
2014-09-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NCI/FDA lung cancer workshop leads to the innovatively designed clinical trials
2014-09-25
DENVER – The recent launch of two clinical trials offer innovative study designs for patients with lung cancer. These clinical trials are the direct result of a National Cancer Institute (NCI) sponsored workshop chaired by Drs. Fred R. Hirsch, Shakun Malik and Claudio Dansky- Ullman, that brought together the NCI Thoracic Malignancies Steering Committee, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), academicians, clinicians as well as industry and government stakeholders to discuss issues and challenges related to clinical trial design and biomarkers for lung cancer targeted-therapies.
The ...
Treatment studied to help patients 'burned to the bone'
2014-09-25
An anti-inflammatory treatment, studied in the labs of regenerative medicine specialists and trauma surgeons, may prevent what's become one of the war-defining injuries for today's troops.
Those burned by high-velocity explosive devices are at-risk for heterotopic ossification (HO), in which bone develops in places it shouldn't be, outside the skeleton, in joints, muscles and tendons. The painful condition can make it difficult to move and function and commonly affects patients who suffer burns, automobile accidents, orthopedic surgery and blast injuries and other combat ...
Live long and phosphor: Blue LED breakthrough for efficient electronics
2014-09-25
ANN ARBOR—In a step that could lead to longer battery life in smartphones and lower power consumption for large-screen televisions, researchers at the University of Michigan have extended the lifetime of blue organic light emitting diodes by a factor of 10.
Blue OLEDs are one of a trio of colors used in OLED displays such as smartphone screens and high-end TVs. The improvement means that the efficiencies of blue OLEDs in these devices could jump from about 5 percent to 20 percent or better in the near future.
OLEDs are the latest and greatest in television technology, ...
Study finds global sea levels rose up to 5 meters per century at the end of the last 5 ice age
2014-09-25
Land-ice decay at the end of the last five ice-ages caused global sea-levels to rise at rates of up to 5.5 metres per century, according to a new study.
An international team of researchers developed a 500,000-year record of sea-level variability, to provide the first account of how quickly sea-level changed during the last five ice-age cycles.
The results, published in the latest issue of Nature Communications, also found that more than 100 smaller events of sea-level rise took place in between the five major events.
Dr Katharine Grant, from the Australian National ...
Calming down immune cells could hold key to melanoma treatment
2014-09-25
Immune cells may be responsible for drug resistance in melanoma patients, according to research published in Cancer Discovery.
Cancer Research UK scientists at The University of Manchester found that chemical signals produced by a type of immune cell, called macrophages, also act as a survival signal for melanoma cells.
When the researchers blocked the macrophages' ability to make this signal - called TNF alpha - melanoma tumours were much smaller and easier to treat.
When melanoma patients are given chemotherapy or radiotherapy it causes inflammation, increasing ...
Interactive website helps lower-income smokers to stop smoking
2014-09-25
People with lower incomes attempting to quit smoking are 36% more likely to succeed if they use a new interactive website called 'StopAdvisor' than if they use a static information website, finds a randomised controlled trial led by UCL researchers. The trial was funded by the National Prevention Research Initiative, a consortium of 16 UK health research funders.
A total of 4,613 smokers took part in the study, of whom 2,142 were classified into a 'lower income' group who had never worked, were long term unemployed or from routine or manual occupations (lower socioeconomic ...
Skirt size increase linked to 33 percent greater postmenopausal breast cancer risk
2014-09-25
Overall weight gain during adulthood is known to be a risk factor for breast cancer, but a thickening waist seems to be particularly harmful, indicating the importance of staving off a midriff bulge, the research shows.
The researchers base their findings on almost 93,000 women taking part in the UK Collaborative Trial of Ovarian Cancer Screening (UKCTOCS) in England.
The women were all aged over 50, had gone through the menopause, and had no known breast cancer when they entered the study between 2005 and 2010.
At enrolment they provided detailed information on height ...
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology: Working long hours linked to increased risk of type 2 diabetes
2014-09-25
People working for more than 55 hours per week doing manual work or other low socioeconomic status jobs have a 30% greater risk of developing type 2 diabetes, according to the largest study in this field so far, published in The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.
Mika Kivimäki, Professor of Epidemiology at University College London, UK, and colleagues conducted a systematic review and meta-analysis of published studies and unpublished individual-level data examining the effects of long working hours on type 2 diabetes up to 30 April 2014.
Analysis of data from 4 published ...
Identification of genetic risk factors for stroke
2014-09-25
Stroke is one of the leading causes of death worldwide. While many lines of evidence suggest that stroke risk is heritable, only a small number of genes associated with stroke have been identified. A new study in the Journal of Clinical Investigation identifies two genes that underlie cerebral small-vessel disease (CSVD), a risk factor for stroke. Ordan Lehmann and colleagues at the University of Alberta analyzed genome-wide association data from individuals that received brain MRI scans as part of the Cohorts for Heart and Aging Research in Genomic Epidemiology (CHARGE) ...
Wound healing response promotes breast cancer metastasis in postpartum mice
2014-09-25
Within the first 5 years after the birth of a child, women are at an increased risk of developing metastatic breast cancer. Women diagnosed with postpartum breast cancer have a decreased disease free survival time compared to women that have never given birth. The aggressive tendency of postpartum breast cancer suggests that the post-birth breast environment promotes tumor metastasis. A new study in the Journal of Clinical Investigation, suggests that dying tumor cells in postpartum breast tissue promote metastatic disease. Rachel Cook and colleagues at Vanderbilt University ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mount Sinai, Uniformed Services University join forces to predict and prevent diseases before they start
Science of fitting in: Do best friends or popular peers shape teen behavior?
USF study: Gag grouper are overfished in the Gulf; this new tool could help
New study from Jeonbuk National University finds current climate pledges may miss Paris targets
Theoretical principles of band structure manipulation in strongly correlated insulators with spin and charge perturbations
A CNIC study shows that the heart can be protected during chemotherapy without reducing antitumor efficacy
Mayo Clinic study finds single dose of non-prescribed Adderall raises blood pressure and heart rate in healthy young adults
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
Painless skin patch offers new way to monitor immune health
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
[Press-News.org] Fossil of multicellular life moves evolutionary needle back 60 million yearsVirginia Tech researcher finds evidence of cellular complexity eras earlier than expected