(Press-News.org) Type 2 diabetes affects an estimated 28 million Americans according to the American Diabetes Association, but medications now available only treat symptoms, not the root cause of the disease. New research from Rutgers shows promising evidence that a modified form of a different drug, niclosamide – now used to eliminate intestinal parasites – may hold the key to battling the disease at its source.
The study, led by Victor Shengkan Jin, an associate professor of pharmacology at Rutgers Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, has been published online by the journal Nature Medicine.
Jin says it is important to find a suitable medication to correct the cause of the disease as quickly as possible because the only way now known to "cure" the disease involves major gastric bypass surgery. "The surgery can only be performed on highly obese people," Jin explains, "and carries significant risks that include death, so it is not a realistic solution for most patients."
And the number of patients continues to rise. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention projects that 40 percent of all Americans now alive will develop type 2 diabetes.
Type 2 is the form of diabetes once known as "adult onset," in which the body produces insulin that ordinarily would keep blood sugar under control, but either it does not produce enough insulin or the body's ability to use that insulin is degraded.
According to Jin, a major cause of insulin resistance is the accumulation of excess fat in the cells of the liver, as well as in muscle tissue. The fat disrupts the process where, ordinarily, insulin would cause body tissues to correctly absorb glucose – blood sugar – and use it as a fuel. With nowhere else to go, much of the excess glucose remains in the bloodstream, where in high concentrations it can damage tissues throughout the body – potentially leading to blindness, kidney damage, cardiovascular diseases and other severe health problems.
"Our goal in this study was to find a safe and practical way of diminishing fat content in the liver. We used mice to perform proof-of-principle experiments in our laboratory," says Jin. "We succeeded in removing fat, and that in turn improved the animals' ability to use insulin correctly and reduce blood sugar."
The modified medication – whose full name is niclosamide ethanolamine salt (NEN) – burned the excess fat in liver cells through a process known as mitochondrial uncoupling. Mitochondria are the microscopic energy source for each cell in the body, and ordinarily – like a well-tuned car engine – they burn fuels including fats and sugars in modest quantities to keep the cells functioning.
"The cell is like a car and the mitochondria are the engine," Jin explains. "What we're doing inside cells is like putting the car's transmission into neutral by uncoupling it from the transmission. Then you step on the gas so the engine runs full throttle but the car doesn't move. If too much of the fuel in the cell is fat, you keep burning it until the fuel gauge reaches empty. Without the interference of fat, you hope that sugar will then enter the cell normally."
Getting rid of the interference of fat in liver and muscle tissue is the key to restoring the cells' ability to respond to insulin properly, which would allow the right amount of sugar to be taken up by cells and ultimately reverse the diabetes entirely. That outcome is far from certain, but Jin says the positive changes he saw in the mice are encouraging.
Jin says it also is significant that the drug he used is a modified form of a medication that the FDA already approved for human use. That was a deliberate choice. "We wanted a safe and practical compound to deplete fat inside cells," says Jin. "We went to the literature and found an approved drug that does in parasitic worms what we wanted to do in liver cells. The modified form of the medication, although itself is not a drug used in humans, has an excellent safety profile in other mammals – so very likely it would have a good safety profile in humans too."
Also, excess fat in the liver is not just a condition of the obese; people of normal weight can develop fatty livers and type 2 diabetes. Jin says this kind of medication, if shown to be effective, could safely treat patients of all weights.
Jin is cofounder of a company called Mito BioPharm, established in 2012, which has the exclusive right to use a patent owned by Rutgers to develop NEN for potential commercial use.
INFORMATION:
Montréal, October 2, 2014 – Scientists at the IRCM discovered a mechanism that promotes the progression of medulloblastoma, the most common brain tumour found in children. The team, led by Frédéric Charron, PhD, found that a protein known as Sonic Hedgehog induces DNA damage, which causes the cancer to develop. This important breakthrough will be published in the October 13 issue of the prestigious scientific journal Developmental Cell. The editors also selected the article to be featured on the journal's cover.
Sonic Hedgehog belongs to a family of proteins that gives ...
Despite the legalization of same-sex marriage in 19 states and the District of Columbia and an executive order to prohibit federal contractors from discrimination against lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender employees, LGBT individuals face tremendous hurdles in access to health care and basic human rights. A special report published by The Hastings Center, LGBT Bioethics: Visibility, Disparities, and Dialogue, is a call to action for the bioethics field to help right the wrongs in the ways that law, medicine, and society have treated LGBT people.
The editors are Tia ...
FALLS CHURCH, Va. (October 3, 2014) — A new National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) study, published online in the Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene, found that recommended safe handling practices for workers who administer antineoplastic drugs in healthcare settings are not always followed.
Results are derived from the 2011 Health and Safety Practices Survey of Healthcare Workers, the largest federally-sponsored survey of healthcare workers in the U.S., which addresses safety and health practices relative to use of hazardous chemicals. ...
Men who consume more alcohol have a greater risk of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection, according to a recent study by Moffitt Cancer Center researchers.
HPV is a common sexually transmitted virus, with more than six million new infections in the United States each year. HPV causes genital warts in both men and women and is a contributing factor to a number of different cancers in women, including cervical, vaginal and anal cancers. More recent studies have shown that HPV can also cause penile, anal and oropharyngeal cancer in men. However, there is limited data regarding ...
A snaking, extended filament of solar material currently lies on the front of the sun-- some 1 million miles across from end to end. Filaments are clouds of solar material suspended above the sun by powerful magnetic forces. Though notoriously unstable, filaments can last for days or even weeks.
NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, or SDO, which watches the sun 24 hours a day, has observed this gigantic filament for several days as it rotated around with the sun. If straightened out, the filament would reach almost across the whole sun, about 1 million miles or 100 times ...
In response to the rise of drug-resistant pathogens, doctors are routinely cautioned against overprescribing antimicrobials. But when a patient has a confirmed bacterial infection, the advice is to treat aggressively to quash the infection before the bacteria can develop resistance.
A new study questions the accepted wisdom that aggressive treatment with high drug dosages and long durations is always the best way to stem the emergence and spread of resistant pathogens. The review of nearly 70 studies of antimicrobial resistance, which was authored by researchers at Princeton ...
Two NASA satellites captured data on Typhoon Phanfone as it continues to strengthen as it moves through the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.
The Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite flew over Typhoon Phanfone on Oct. 2, 2014 at 0939 UTC (5:39 a.m. EDT). The rainfall pattern observed using TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) and Precipitation Radar (PR) data showed that Phanfone was much better organized than a day earlier. This precipitation analysis revealed that intensifying typhoon Phanfone had formed a large eye. The heaviest rainfall was shown falling at a ...
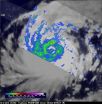
NASA's Terra satellite spotted the birth of Tropical Storm Vongfong in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean on Oct. 3. Vongfong is the nineteenth tropical storm of the Northwestern Pacific typhoon season.
The MODIS or Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer instrument that flies aboard NASA's Terra satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Storm Vongfong on Oct. 3 at 00:30 UTC (Oct. 2 at 8:30 p.m. EDT). At the time of the image, the center of Tropical Storm Vongfong was located just to the northeast of Pohnpei, one of four states in the Federated States of Micronesia. ...
Tropical Storm Simon is following the path of several other tropical storms that formed in the Eastern Pacific Ocean by crawling northward along the western coastline of Mexico. NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured an infrared image of Simon on Oct. 3 that showed the eastern side of the storm over Mexico.
An infrared image taken from NOAA's GOES-West satellite on Oct .3 at 7:45 a.m. EDT showed strong thunderstorms circling Tropical Storm Simon's center and a fragmented band of thunderstorms in Simon's eastern quadrant bringing rainfall to western Mexico. Simon's center ...
Scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy's Argonne National Laboratory have created a new model to more accurately describe the greenhouse gases likely to be released from Arctic peatlands as they warm. Their findings, based on modeling how oxygen filters through soil, suggest that previous models probably underestimated methane emissions and overrepresented carbon dioxide emissions from these regions.
Peatlands, common in the Arctic, are wetlands filled with dead and decaying organic matter. They are the result of millions of years of plants dying and breaking down ...