(Press-News.org) The way neurons are interconnected in the brain is very complicated. This holds especially true for the cells of the hippocampus. It is one of the oldest brain regions and its form resembles a see horse (hippocampus in Latin). The hippocampus enables us to navigate space securely and to form personal memories. So far, the anatomic knowledge of the networks inside the hippocampus and its connection to the rest of the brain has left scientists guessing which information arrived where and when.
Signals spread through the brain
Accordingly, Dr Martin Pyka and his colleagues from the Mercator Research Group have developed a method which facilitates the reconstruction of the brain's anatomic data as a 3D model on the computer. This approach is quite unique, because it enables automatic calculation of the neural interconnection on the basis of their position inside the space and their projection directions. Biologically feasible network structures can thus be generated more easily than it used to be the case with the method available to date.
Deploying 3D models, the researchers use this technique to monitor the way neural signals spread throughout the network time-wise. They have, for example, found evidence that the hippocampus' form and size could explain why neurons in those networks fire in certain frequencies.
Information become memories
In future, this method may help us understand how animals, for example, combine various information to form memories within the hippocampus, in order to memorise food sources or dangers and to remember them in certain situations.
INFORMATION:
About the Mercator Research Group "Structure of Memory"
In a joined project with the Mercator Foundation, Ruhr-Universität Bochum has set up the Mercator Research Group "Structure of Memory". Experimental and theoretical neuroscientists as well as philosophers make up the team, which has been studying episodic and semantic memory processes and the way they relate to other cognitive functions since 2010.
A glimpse into the 3-D brain: How memories form
Novel technology: Computer simulation of the hippocampus
2014-10-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
No need for water, enzymes are doing it for themselves
2014-10-06
New research by scientists at the University of Bristol has challenged one of the key axioms in biology - that enzymes need water to function. The breakthrough could eventually lead to the development of new industrial catalysts for processing biodiesel.
Enzymes are large biological molecules that catalyse thousands of different chemical reactions that are essential for all life, from converting food into energy, to controlling how our cells replicate DNA.
Throughout this diverse range of biological environments in which enzymes perform their various roles, the only ...
Research paves way for new generation of fungicides
2014-10-06
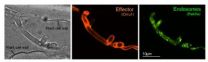
Plants that come under attack from pathogens have an automatic immune response. Fungi get around this plant immunity by injecting proteins into the host plant cells. These 'effector proteins' enable the fungi to escape the plant's immune system and allow the fungal cells to enter the plant unrecognised.
Exeter scientists have now shown that signalling organelles, known as 'early endosomes' act as long distance messengers in the fungi. They travel rapidly along long tube-like cells between the plant-invading fungal cell tip and the fungal cell nucleus. This rapid communication ...
Online games and remote experiments could reduce scientific fraud, cherry-picking
2014-10-06
PITTSBURGH—One way to combat the rising level of errors and fraud in life sciences research is through massive online laboratories, which use videogames to engage large numbers of non-professional investigators and prevent scientists from manually testing their own hypotheses, researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and Stanford University say.
Though unconventional, CMU's Adrien Treuille and Stanford's Rhiju Das argue that this online, game-like approach actually is more scientifically rigorous than the standard practice of scientists proposing an explanation for ...
Treatments for HIV-visceral leishmaniasis co-infected patients
2014-10-06
This news release is available in Spanish. [Gondar, Ethiopia and Geneva, Switzerland – October 6, 2014] - The international research & development (R&D) consortium, AfriCoLeish, formed by six research organizations from East Africa and Europe, has launched a Phase III clinical study to address the extreme difficulty in treating visceral leishmaniasis (VL) in patients who also are HIV-positive. The study will assess the efficacy and the safety of two treatments: a combination treatment of AmBisome® and miltefosine, and AmBisome® alone. This is the first randomized clinical ...
A vicious cycle in osteoarthritis: Sleep disturbance-pain-depression-disability
2014-10-06
New research confirms that sleep disturbances are linked to pain and depression, but not disability, among patients with osteoarthritis (OA). Study results published in Arthritis Care & Research, a journal of the American College of Rheumatology (ACR), found that poor sleep increases depression and disability, but does not worsen pain over time.
Arthritis is one of the top three health concerns that cause disability in the U.S., with OA being the most common form of arthritis. Medical evidence reports that nearly 30 million Americans are affected by OA, which has increased ...
A new way to extract bone-making cells from fat tissue
2014-10-06
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — Within our fat lives a variety of cells with the potential to become bone, cartilage, or more fat if properly prompted. This makes adipose tissue, in theory, a readily available reservoir for regenerative therapies such as bone healing if doctors can get enough of those cells and compel them to produce bone.
In a new study in the journal Stem Cell Research & Therapy, scientists at Brown University demonstrate a new method for extracting a wide variety of potential bone-producing cells from human fat. They developed a fluorescent tag ...
Innovative stroke patient management system cuts hospital bed usage by more than 25 percent
2014-10-06
An innovative patient management system at the acute stroke unit of Kelowna (BC) General Hospital has reduced the number of stroke patient bed days by more than 25 per cent, according to a study of the system presented at the annual Canadian Stroke Congress in Vancouver.
In total, it is estimated the new system is saving the 380-bed hospital more than 1,000 bed days per year. This represents annual savings of up to $800,000, all achieved without the need for any new investment in devices, treatments or personnel.
"It's a win-win situation," says Dr. John B. Falconer, ...
Code stroke on the ward
2014-10-06
At the first sign of a stroke, time is of the essence. For every minute of delay in treatment, people typically lose almost two million brain cells. Yet a new study presented at the Canadian Stroke Congress reveals that those delays – in getting the right tests and the right drugs – can be longer when people experience a stroke in a hospital.
Investigators from the University of Toronto Faculty of Medicine, the Institute for Clinical Evaluative Sciences (ICES) and the University Health Network looked at data from acute care facilities in Ontario over nine years. They ...
Teen hormones and cellphones
2014-10-06
Researchers at the University of Texas Medical Branch at Galveston say that sexting may be the new "normal" part of adolescent sexual development and is not strictly limited to at-risk teens. The findings, published in the journal Pediatrics, are from the first study on the relationship between teenage sexting, or sending sexually explicit images to another electronically, and future sexual activity.
The study results indicate that sexting may precede sexual intercourse in some cases and further cements the idea that sexting behavior is a credible sign of teenage sexual ...
Trying to share our 'epic' moments may leave us feeling left out
2014-10-06
We might love to reminisce and tell others about our extraordinary experiences — that time we climbed Mt. Kilimanjaro, got to taste a rare wine, or ran into a celebrity on the street — but new research suggests that sharing these extraordinary experiences may come at a social cost. The findings are published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science.
"Extraordinary experiences are pleasurable in the moment but can leave us socially worse off in the long run," says psychological scientist and study author Gus Cooney of Harvard University. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] A glimpse into the 3-D brain: How memories formNovel technology: Computer simulation of the hippocampus