Blood levels of Vitamin D may affect liver cancer prognosis
2014-10-06
(Press-News.org) Vitamin D deficiency is linked with advanced stages of liver cancer and may be an indicator of a poor prognosis, according to a study of 200 patients with the disease who were followed for an average of 46 weeks.
Blood levels of vitamin D negatively correlated with stages of the disease, and patients with severe vitamin D deficiency had more than a 2-fold increased risk of dying during the study, according to Dr. Oliver Waidmann, senior author of the Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics study.
INFORMATION:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-06
A new phase 1 safety trial has demonstrated that idarubicin-loaded beads are well tolerated by patients but are toxic to liver cancer cells. Idarubicin is an anthracycline that is currently used to treat leukemias.
Two months into the 21-patient trial, the tumors of 28% of patients had complete responses to the drug, and the tumors of 24% of patients had a partial response. The findings are published in Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
INFORMATION:
...
2014-10-06
Eating lots of white meat (such as poultry) or fish may reduce the risk of developing liver cancer by 31% and 22%, respectively, according to a recent analysis of studies published between 1956 and 2013.
Consuming red meat, processed meat, or total meat was not associated with liver cancer risk. The Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics findings suggest that dietary interventions may be a promising approach for preventing liver cancer.
INFORMATION: ...
2014-10-06
While all prescription opioids can be abused, oxycodone may be more potent in its ability to promote changes in the brain relevant to addiction.
A new study in the European Journal of Neuroscience revealed greater increases of dopamine in the brain following the delivery of oxycodone compared with morphine. The release of dopamine, a chemical messenger between neurons, is consistently tied with reward and motivation.
The study's investigators say that it is essential to understand how drugs differentially alter brain chemistry if we hope to understand addiction and ...
2014-10-06
Efforts to reduce China's carbon dioxide emissions are being offset by the country's rampant economic growth, according to new research from the University of East Anglia (UEA).
Research published today in Nature Climate Change reveals how carbon efficiency has improved in nearly all Chinese provinces. But the country's economic boom has simultaneously led to a growth in CO2-emitting activities such as mining, metal smelting and coal-fired electricity generation – negating any gains.
According to the study, China, the world's largest producer of CO2 emissions, increased ...
2014-10-06
This issue was supported by the Qatar Foundation and World Innovation Summit for Health (WISH), Hamad Medical Corporation, Imperial College London, and The Commonwealth Fund.
How is accountable care taking shape internationally?
Mark McClellan of the Brookings Institution and coauthors seek to offer a global description of an accountable care system and a mechanism to assess related reforms. They suggest five components for a framework applicable internationally: population, outcomes, metrics and learning, payments and incentives, and coordinated delivery. They also ...
2014-10-06
A new and potentially more revealing way of studying how animal evolution is affected by the geography of climate has been designed by researchers at The University of Nottingham and Harvard University.
The research, published in the prestigious journal, The American Naturalist, uses a new approach to investigate how animals across (interspecific) and within (intraspecific) species change in size along temperature gradients, shedding light on a 150-year-old evolutionary puzzle. Bergmann's rule — the tendency for warm-blooded animal body size to increase in colder environments ...
2014-10-06
Life on the Antarctic sea floor is under threat from crabs that could invade the area thanks to favorable conditions as a result of global warming, researchers warn.
In a Journal of Biogeography editorial, experts say invasive species degrade marine ecosystems by preying on or outcompeting local species. Early signs of biological invasion are already apparent.
"Biological invasion is a major worry in the Arctic," said lead author Dr. Richard Aronson, "but we should be just as concerned about the Antarctic." Assessing the extent of the problem requires long-term monitoring ...
2014-10-06
LIVERMORE, California -- Using satellite observations and a large suite of climate models, Lawrence Livermore scientists have found that long-term ocean warming in the upper 700 meters has likely been underestimated.
"This underestimation is a result of poor sampling prior to the last decade and limitations of the analysis methods that conservatively estimated temperature changes in data-sparse regions," said LLNL oceanographer Paul Durack, lead author of a paper appearing in the October 5th issue of the journal Nature Climate Change.
Ocean heat storage is important ...
2014-10-06
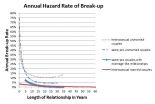
Among couples with marriage-like commitments, same-sex couples have a similar break-up rate as heterosexual couples, according to a recent study. The study also found that same-sex couples with a marriage-like commitment have stable unions regardless of government recognition.
The findings come from a nationally representative survey of 3,009 couples (471 same-sex) who were followed between 2009 and 2013.
"The marriage commitment is associated with a strong benefit in couple stability for both heterosexual couples and same-sex couples," said Dr. Michael J. Rosenfeld, ...
2014-10-06
G-spot, vaginal, or clitoral orgasms are all incorrect terms, experts say. In a recent Clinical Anatomy review, they argue that like 'male orgasm', 'female orgasm' is the correct term.
The authors note that the majority of women worldwide do not have orgasms during intercourse: as a matter of fact, female sexual dysfunctions are popular because they are based on something that does not exist, i.e. the vaginal orgasm.
The key to female orgasm is the female penis—the clitoris, vestibular bulbs and pars intermedia, labia minora, and corpus spongiosum of the female urethra. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Blood levels of Vitamin D may affect liver cancer prognosis