(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
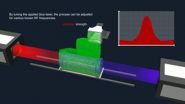
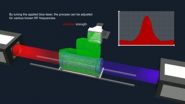
This is an animation of NIST's new method for measuring electric field strength based on the quantum properties of atoms. The technique works for abroad range of frequencies, 1-500 gigahertz,...
Click here for more information.
Researchers at the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and the University of Michigan have demonstrated a technique based on the quantum properties of atoms that directly links measurements of electric field strength to the International System of Units (SI).*
The new method could improve the sensitivity, precision and ease of tests and calibrations of antennas, sensors, and biomedical and nano-electronic systems and facilitate the design of novel devices.
Conventional electric field probes have limited frequency range and sensitivity, often disturb the field being measured, and require laboratory calibrations that are inherently imprecise (because the reference field depends on the geometry of the source). Furthermore, linking these measurements to SI units, the highest level of calibration, is a complex process.
NIST's new electric-field probe spans enormous ranges. It can measure the strength of fields from 1 to 500 gigahertz, including the radio, microwave, millimeter-wave and sub-terahertz bands. It can measure fields up to 100 times weaker than conventional methods can (as weak as 0.8millivolts per meter, the SI unit of measure). Researchers used the new method to measure field strengths for a wide range of frequencies, and the results agreed with both numerical simulations and calculations.
Importantly, the new method can calibrate itself, as well as other instruments, because it is based on predictable quantum properties: vibrations in atoms as they switch between energy levels. This self-calibration feature improves measurement precision and may make traceable calibrations possible in the millimeter and sub-terahertz bands of the spectrum for the first time.
"The exciting aspect of this approach is that an atom is rich in the number of transitions that can be excited," NIST project leader Chris Holloway says. "This results in a broadband measurement probe covering a frequency range of 1 to 500 gigahertz and possibly up to 1 terahertz."
The NIST instrument currently is tabletop sized, but researchers are working on miniaturizing it using photonic structures.
The basic method has already been demonstrated for imaging applications.** Briefly, researchers use a red and a blue laser to prepare atoms contained in a cylinder to high-energy ("Rydberg") states, which have novel properties such as extreme sensitivity and reactivity to electromagnetic fields. An antenna or other source generates an electric field, which, depending on its frequency, affects the spectrum of light absorbed by the atoms. By measuring this effect, researchers can calculate the field strength. Various atoms can be used—NIST uses rubidium or cesium—to measure field strength in different parts of the frequency spectrum.
Among possible applications, the NIST probe may be suitable for measuring and optimizing compatibility in densely packaged electronics that include radar and wireless communications and control links, and for integration into endoscopic probes with medical applications such as investigating implants in the body. The technique might also be included in a future "NIST on a chip" offering multiple measurement methods and standards in a portable form.
Importantly, the technique also enables, for the first time, calibrated measurements of frequencies above 100 GHZ, in the millimeter wave and sub-terahertz bands.*** This capability will be crucial for the development of advanced communications systems and climate change research, among other applications.
INFORMATION:
Five co-authors of the new paper are with the University of Michigan, which provided the blue laser and aided in the experiments. The project is funded in part by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency.
* C.L. Holloway, J.A. Gordon, S. Jefferts, A. Schwarzkopf, D. A. Anderson, S.A. Miller, N. Thaicharoen and G. Raithelet. Broadband Rydbergatom-based electric-field probe: From self-calibrated measurements to sub-wavelength imaging. IEEE Trans. on Antennas and Propagation. 99. Accepted for publication. DOI: 10.1109/TAP.2014.2360208.
** See 2014 NIST Tech Beat article, "NIST Technique Could Make Sub-wavelength Images at Radio Frequencies," at http://www.nist.gov/pml/electromagnetics/subwave-061714.cfm.
*** J.A. Gordon, C.L. Holloway, A. Schwarzkopf, D. A. Anderson, S. Miller, N. Thaicharoen and G. Raithel. Millimeter wave detection via Autler-Townes splitting in rubidium Rydberg atoms. Applied Physics Letters, 2014. Vol. 105, Issue 2.DOI:10.1063/1.4890094.
UPTON, NY - Increasing the oil content of plant biomass could help fulfill the nation's increasing demand for renewable energy feedstocks. But many of the details of how plant leaves make and break down oils have remained a mystery. Now a series of detailed genetic studies conducted at the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and published in The Plant Cell reveals previously unknown biochemical details about those metabolic pathways-including new ways to increase the accumulation of oil in leaves, an abundant source of biomass for fuel production.
Using ...
ST. LOUIS -- A vaccine that protects against an old strain of avian flu primes the immune system to mount a rapid response when a vaccine designed to protect against a related but different and new strain of avian flu is given a year later, according to Saint Louis University research findings reported in JAMA.
In addition, when combined with an adjuvant, which is a chemical that stimulates the immune system to produce more antibodies, a lower dose of the new avian flu vaccine worked better in triggering an immune response than a stronger dose without adjuvant. That means ...
A one-day prevalence survey of 183 hospitals found that approximately 50 percent of hospitalized patients included in the survey were receiving antimicrobial drugs, and that about half of these patients were receiving 2 or more antimicrobial drugs, according to a study in the October 8 JAMA, a theme issue on infectious disease. Most antimicrobial use was for infection treatment.
Despite the evidence supporting early, appropriate antimicrobial therapy, a substantial proportion of antimicrobial use in U.S. acute care hospitals may be inappropriate, based on factors such ...
Two randomized trials in the October 8 issue of JAMA examine new vaccination strategies for the prevention and control of avian influenza, often referred to as "bird flu." This is a theme issue on infectious disease.
In one study, Mark J. Mulligan, M.D., of the Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, and colleagues compared the safety and antibody responses (immunogenicity) of different doses of influenza A/Shanghai/2/13 (H7N9) vaccine mixed with or without the MF59 adjuvant (a component that improves immunogenicity and enhances efficacy of inactivated influenza ...
Despite no lapses in the disinfection process recommended by the manufacturer being identified, specialized gastrointestinal endoscopes called duodenoscopes had bacterial contamination associated with an outbreak of a highly resistant strain of E coli at a hospital in Illinois, according to a study in the October 8 JAMA, a theme issue on infectious disease.
The duodenoscope is different than that used for routine upper gastrointestinal endoscopy or colonoscopy. The procedure associated with these specialized scopes is endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP), ...
Study participants who reported tobacco use or had higher levels of biomarkers of tobacco exposure had a higher prevalence of the sexually transmitted infection, oral human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV-16), according to a study in the October 8 JAMA, a theme issue on infectious disease.
Oral HPV-16 is believed to be responsible for the increase in incidence of oropharyngeal squamous cell cancers in the United States. An association between self-reported number of cigarettes currently smoked per day and oral HPV prevalence has been observed, according to background information ...
Johns Hopkins scientists have shown a strong association between tobacco use or exposure and infection with oral human papillomavirus type 16 (HPV16), the sexually transmitted virus responsible for mouth and throat cancers worldwide. The numbers of such cancers have increased 225 percent in the United States over the past two decades.
HPV16 is found in 80 percent of cancers located in the back of the throat and is transmitted through oral sex. "The practice of oral sex is common, but this cancer is rare. So there must be cofactors in the process that explain why some ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. — A decade ago, America's health care community took on heart attacks with gusto, harnessing the power of research and data to make sure that every patient got the best possible care.
It worked: Death rates for heart attack have dropped. The same has happened with heart failure and pneumonia. Now, say a pair of University of Michigan Medical School experts, it's time to do the same for sepsis.
Sepsis may not have the same name recognition as heart attacks -- but it now affects more hospital patients, and leads to more hospital costs, than any ...
An experimental vaccine to protect people against H7N9 avian influenza prompted immune responses in 59 percent of volunteers who received two injections at the lowest dosage tested, but only if the vaccine was mixed with adjuvant—a substance that boosts the body's response to vaccination. Without adjuvant, immune responses produced by the investigational vaccine were minimal regardless of vaccine dosage, according to findings from a clinical trial sponsored by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID), part of the National Institutes of Health.
The ...
A large, NIH-sponsored clinical trial of an experimental H7N9 avian influenza vaccine found an immune response that was believed to be protective in 59 percent of study participants who received two injections of the inactivated vaccine at the lowest dosage tested when mixed with an adjuvant – a component that boosts the body's immune response and enhances the effectiveness of inactivated influenza vaccines.
Participants who received a vaccine without the adjuvant had a minimal immune response.
The results are published in the Journal of the American Medical ...