NASA sees newborn Tropical Storm Hudhud in Northern Indian Ocean
2014-10-08
(Press-News.org) The Northern Indian Ocean has awakened after a tropical slumber and created Tropical Storm Hudhud on Oct. 8 and NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead.
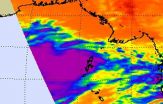
The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Tropical Cyclone Hudhud on Oct. 8 at 6:53 UTC (2:53 a.m. EDT and captured infrared data on the storm revealing bands of strong thunderstorms around the center.
Animated infrared satellite imagery showed that the low-level circulation center was consolidating, and there is an improvement in the banding of thunderstorms wrapping into a defined center. Another image showed tightly-curved banding of thunderstorms and an eye in microwave data.
On Oct. 8 at 1500 UTC (11 a.m. EDT), Hudhud had maximum sustained winds near 45 knots (51.7 mph/83.3 kph). It was centered near 13.2 north and 90.4 east. It was centered about 562 nautical miles (646.7 miles/1,041 kph) south of Chittagong, India. Hudhud was moving to the west-northwest at 9 knots (10.3 mph/16.6 kph).
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center expects Hudhud to reach hurricane strength and make landfall near Visakhapatnam on Oct. 10.
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-08
TORONTO, October 7, 2014 – Health technology company Infonaut, a MaRS client, has released a study showing that hospital patients may be at significant risk of infection due to their own poor hand hygiene. The findings were measured in a Toronto hospital using Infonaut's Hospital Watch Live™ system, innovative technology designed to assist hospitals in monitoring and controlling the spread of infections by analyzing the movement and behaviour of hospital staff, patients and equipment.
The study found that patients on average washed their hands only 30% of the time ...
2014-10-08
Researchers at Children's Hospital Los Angeles (CHLA) have described for the first time a specific perceptual learning deficit in mice with a mutation of the same gene as found in children with Fragile X Syndrome (FXS). Their findings, published on October 8 by PLOS ONE, may offer an effective pre-clinical platform for both investigating how brain circuitry is altered in FXS and testing drugs to improve these symptoms in children.
FXS is the most common inherited form of mental impairment, affecting an estimated 1 in 4,000 males and 1 in 6,000 females. Symptoms include ...
2014-10-08
Four families likely influenced violin shape over four centuries, with many imitating famous designs like Stradivarius, according to a study published October 8, 2014 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Daniel Chitwood from Donald Danforth Plant Science Center in Missouri.
The first violins appeared in 16th century Italy and since then, their designers have continued to incorporate numerous innovations to improve the acoustical properties and playability of violins. However, details of the body outline can vary without significantly compromising sound quality and may ...
2014-10-08
The discovery of new bones from a large land mammal that lived about 48 million years ago has led scientists to identify a new branch of mammals closely related to modern horses, rhinos, and tapirs, according to a study published October 8, 2014 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Lisa Noelle Cooper from Northeast Ohio Medical University and colleagues.
This family of large mammals, Anthracobunidae, is only known from India and Pakistan and was commonly considered to be ancestors of modern elephants and sea cows. Geographically, this was a puzzling idea, because elephants ...
2014-10-08
Healthier foods and beverages have been consistently more expensive than unhealthier ones from 2002-2012, with a gap that's growing, according to a study published October 8, 2014 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by Nicholas Jones from University of Cambridge, UK, and colleagues.
Governments have identified access to affordable healthy diets as a key factor in improving public health, yet methods for tracking prices of more and less healthy foods over time have not been established. The authors of this study analyzed existing government data on national food prices ...
2014-10-08
For the first time, robotic prostheses controlled via implanted neuromuscular interfaces have become a clinical reality. A novel osseointegrated (bone-anchored) implant system gives patients new opportunities in their daily life and professional activities.
In January 2013 a Swedish arm amputee was the first person in the world to receive a prosthesis with a direct connection to bone, nerves and muscles. An article about this achievement and its long-term stability will now be published in the Science Translational Medicine journal.
"Going beyond the lab to allow the ...
2014-10-08
CLEVELAND—Even before he lost his right hand to an industrial accident 4 years ago, Igor Spetic had family open his medicine bottles. Cotton balls give him goose bumps.
Now, blindfolded during an experiment, he feels his arm hairs rise when a researcher brushes the back of his prosthetic hand with a cotton ball.
Spetic, of course, can't feel the ball. But patterns of electric signals are sent by a computer into nerves in his arm and to his brain, which tells him different. "I knew immediately it was cotton," he said.
That's one of several types of sensation ...
2014-10-08
A new study, published today in the journal PLOS One, tracked the price of 94 key food and beverage items from 2002 to 2012. Its findings show that more healthy foods were consistently more expensive than less healthy foods, and have risen more sharply in price over time.
Food prices in the UK have risen faster than the price of other goods in recent years, and this new research shows that the increase has been greater for more healthy foods, making them progressively more expensive over time.
While less healthy foods had a slightly greater price rise relative to ...
2014-10-08
Berkeley — Fad diets come and go, but might there be something to the ones that involve consuming grapefruit and grapefruit juice? New research at the University of California, Berkeley, suggests that a closer look at grapefruit juice is warranted.
A new study, to be published Wednesday, Oct. 8, in the peer-reviewed journal PLOS ONE, found that mice fed a high-fat diet gained 18 percent less weight when they drank clarified, no-pulp grapefruit juice compared with a control group of mice that drank water. Juice-drinking mice also showed improved levels of glucose, ...
2014-10-08
Cut off by freeways and human development, mountain lions in southern California are facing a severe loss of genetic diversity, according to a new study led by the University of California, Davis in partnership with The Nature Conservancy.
The study, published today in the journal PLOS ONE, represents the largest genetic sampling of mountain lions, or pumas, in southern California. It raises concerns about the current status of mountain lions in the Santa Ana and Santa Monica mountains, as well as the longer-term outlook for mountain lions across southern California.
UC ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NASA sees newborn Tropical Storm Hudhud in Northern Indian Ocean


