Click here for more information.
LA JOLLA—Scientists at the Salk Institute and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) in Boston have discovered a new class of molecules—produced in human and mouse fat—that protects against diabetes.
The researchers found that giving this new fat, or lipid, to mice with the equivalent of type 2 diabetes lowered their elevated blood sugar, as detailed October 9 in Cell. The team also found that levels of the new lipids are low in humans with a high risk for diabetes, suggesting that the lipids could potentially be utilized as a therapy for metabolic disorders.
Lipids, like cholesterol, are typically associated with poor health. But in recent years, researchers have discovered that not all lipids are bad for you, such as the much touted omega-3 fatty acids that are found in fish oils. The newly discovered lipids, called fatty acid hydroxy fatty acids, or FAHFAs, were lower in humans with early stages of diabetes and were much higher in mice resistant to diabetes.
"Based on their biology, we can add FAHFAs to the small list of beneficial lipids," says Alan Saghatelian, Salk professor in the Clayton Foundation Laboratories for Peptide Biology and one of the senior authors of the work. "These lipids are amazing because they can also reduce inflammation, suggesting that we might discover therapeutic opportunities for these molecules in inflammatory diseases, such as Crohn's disease and rheumatoid arthritis, as well as diabetes."
FAHFAs had not been noticed previously in cells and tissues because they are present in low concentrations, making them difficult to detect. Using the latest mass spectrometry techniques, Saghatelian and Barbara Kahn, vice chair of the Department of Medicine at BIDMC and the other senior author of the work, uncovered the FAHFAs when they examined the fat of a diabetes-resistant mouse model developed by Kahn.
"We engineered these mice to have more of a sugar transporter, called Glut4, in their fat because we had shown that when levels of this transporter are low, people are prone to developing diabetes," says Kahn. By examining how this sugar transporter might help protect against diabetes, the team noticed more fatty acid synthesis in mice that had improved insulin activity (and thereby were less likely to develop diabetes). The team collaborated to find out what lipids were involved.
"While many of the other lipids were essentially the same between normal mice and these diabetes-resistant mice, we saw these FAHFA lipids elevated by sixteen fold in mice that were resistant to diabetes, standing out really clearly as a big change," says Saghatelian. "After that, we elucidated their structures using a combination of mass spectrometry and chemical synthesis. We basically uncovered a whole new class of molecules using these techniques."
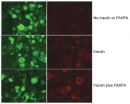
Once they identified FAHFAs as being the lipid that was different between normal mice and these diabetes-resistant mice, they found something else important: when the mice eat FAHFAs, blood sugar levels dropped and insulin levels rose, indicating the potential therapeutic value of FAHFAs.
To determine whether FAHFAs are also relevant in humans, the team measured FAHFA levels in humans who are insulin-resistant (a condition which is often a precursor to diabetes) and found that their FAHFA levels were lower in fat and blood, suggesting that changes in FAHFA levels may contribute to diabetes.
"The higher levels of these lipids seem to be associated with positive outcomes in mice and humans," says Kahn, who is also a professor at Harvard Medical School. "We show that the lipids work through multiple mechanisms. When blood sugar is rising, such as after a meal, the lipids rapidly stimulate secretion of a hormone that signals the pancreas to secrete insulin. In addition, these novel lipids also directly stimulate sugar uptake into cells and reduce inflammatory responses in fat tissue and throughout the body."
These combined effects make the therapeutic potential of the lipids tremendous, say the researchers. Aside from existing in low levels within a wide range of vegetables, fruits and other foods, FAHFAs are also—unlike the other known beneficial lipids—produced and broken down inside the body. Potentially, new drugs could target the pathways that make or break down lipids to control FAHFA levels.
In the new paper, the team also identified the cellular receptor that FAHFAs bind to, called GPR120, to control how much glucose is absorbed into fat cells. The team thinks that increasing the body's levels of FAHFAs may also be a way to activate GPR120 to treat or prevent diabetes.
"This work may suggest that changes in FAHFA levels are a new mechanism in diabetes that was underappreciated before because these lipids weren't known," says Saghatelian. "We hope this work points to novel therapeutics that could boost the body's own way of managing blood sugar."
VIDEO: Salk researchers explain how a new class of lipids may be tied to diabetes.
Click here for more information.
"Because we can detect low FAHFA levels in blood before a person develops diabetes, these lipids could serve as an early marker for diabetes risk," adds Kahn. "We want to test whether restoring the lipids before diabetes develops might potentially reduce the risk or even prevent the disease."
INFORMATION:
Authors of the work include Mark M. Yore, Ismail Syed, Pedro M. Moraes-Vieira, Tejia Zhang, Mark A. Herman, Edwin A. Homan, Rajesh T. Patel, Jennifer Lee, Shili Chen, Odile D. Peroni, Abha S. Dhaneshwar, Ann Hammarstedt, Ulf Smith, Timothy E. McGraw, Alan Saghatelian and Barbara B. Kahn.
Funding for this work was provided by the National Institutes of Health, the JPB Foundation, Searle Scholars Award, Burroughs Wellcome Fund, Sloan Foundation Fellowship and the Harvard Training Program in Nutrition and Metabolism.
About the Salk Institute for Biological Studies:
The Salk Institute for Biological Studies is one of the world's preeminent basic research institutions, where internationally renowned faculty probes fundamental life science questions in a unique, collaborative, and creative environment. Focused both on discovery and on mentoring future generations of researchers, Salk scientists make groundbreaking contributions to our understanding of cancer, aging, Alzheimer's, diabetes and infectious diseases by studying neuroscience, genetics, cell and plant biology, and related disciplines.
Faculty achievements have been recognized with numerous honors, including Nobel Prizes and memberships in the National Academy of Sciences. Founded in 1960 by polio vaccine pioneer Jonas Salk, MD, the Institute is an independent nonprofit organization and architectural landmark.