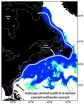
(Press-News.org) AMHERST, Mass. – Using a first-of-its-kind, high-resolution numerical model to describe ocean circulation during the last ice age about 21,000 year ago, oceanographer Alan Condron of the University of Massachusetts Amherst has shown that icebergs and meltwater from the North American ice sheet would have regularly reached South Carolina and even southern Florida. The models are supported by the discovery of iceberg scour marks on the sea floor along the entire continental shelf.
Such a view of past meltwater and iceberg movement implies that the mechanisms of abrupt climate change are more complex than previously thought, Condron says. "Our study is the first to show that when the large ice sheet over North America known as the Laurentide ice sheet began to melt, icebergs calved into the sea around Hudson Bay and would have periodically drifted along the east coast of the United States as far south as Miami and the Bahamas in the Caribbean, a distance of more than 3,100 miles, about 5,000 kilometers."
His work, conducted with Jenna Hill of Coastal Carolina University, is described in the current advance online issue of Nature Geosciences. "Determining how far south of the subpolar gyre icebergs and meltwater penetrated is vital for understanding the sensitivity of North Atlantic Deep Water formation and climate to past changes in high-latitude freshwater runoff," the authors say.
Hill analyzed high-resolution images of the sea floor from Cape Hatteras to Florida and identified about 400 scour marks on the seabed that were formed by enormous icebergs plowing through mud on the sea floor. These characteristic grooves and pits were formed as icebergs moved into shallower water and their keels bumped and scraped along the ocean floor.
"The depth of the scours tells us that icebergs drifting to southern Florida were at least 1,000 feet, or 300 meters thick," says Condron. "This is enormous. Such icebergs are only found off the coast of Greenland today."
To investigate how icebergs might have drifted as far south as Florida, Condron simulated the release of a series of glacial meltwater floods in his high-resolution ocean circulation model at four different levels for two locations, Hudson Bay and the Gulf of St. Lawrence.
Condron reports, "In order for icebergs to drift to Florida, our glacial ocean circulation model tells us that enormous volumes of meltwater, similar to a catastrophic glacial lake outburst flood, must have been discharging into the ocean from the Laurentide ice sheet, from either Hudson Bay or the Gulf of St. Lawrence."
Further, during these large meltwater flood events, the surface ocean current off the coast of Florida would have undergone a complete, 180-degree flip in direction, so that the warm, northward flowing Gulf Stream would have been replaced by a cold, southward flowing current, he adds.
As a result, waters off the coast of Florida would have been only a few degrees above freezing. Such events would have led to the sudden appearance of massive icebergs along the east coast of the United States all the way to Florida Keys, Condron points out. These events would have been abrupt and short-lived, probably less than a year, he notes.
"This new research shows that much of the meltwater from the Greenland ice sheet may be redistributed by narrow coastal currents and circulate through subtropical regions prior to reaching the subpolar ocean. It's a more complicated picture than we believed before," Condron says. He and Hill say that future research on mechanisms of abrupt climate change should take into account coastal boundary currents in redistributing ice sheet runoff and subpolar fresh water.
INFORMATION:
VIDEO:
Researchers have developed a technique to jump-start the body's systems for creating blood vessels, opening the door for potential new treatments for diseases whose impacts include amputation and blindness....
Click here for more information.
INDIANAPOLIS -- Researchers have developed a technique to jump-start the body's systems for creating blood vessels, opening the door for potential new treatments for diseases whose impacts include amputation and blindness.
The ...
DURHAM, N.C. -- Duke University researchers have made fluorescent molecules emit photons of light 1,000 times faster than normal -- setting a speed record and making an important step toward realizing superfast light emitting diodes (LEDs) and quantum cryptography.
This year's Nobel Prize in physics was awarded for the discovery of how to make blue LEDs, allowing everything from more efficient light bulbs to video screens. While the discovery has had an enormous impact on lighting and displays, the slow speed with which LEDs can be turned on and off has limited their ...
From joint replacements to cardiac implants and dialysis machines, medical devices enhance or save lives on a daily basis. However, any device implanted in the body or in contact with flowing blood faces two critical challenges that can threaten the life of the patient the device is meant to help: blood clotting and bacterial infection.
A team of Harvard scientists and engineers may have a solution. They developed a new surface coating for medical devices using materials already approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). The coating repelled blood from more ...
In spite of its dangerous reputation, cholesterol is in fact an essential component of human cells. Manufactured by the cells themselves, it serves to stiffen the cell's membrane, helping to shape the cell and protect it. By mapping the structure of a key enzyme involved in cholesterol production, Rockefeller University researchers and a colleague in Italy have gained new insight into this complex molecular process.
"This is the first report to pinpoint the location of every atom — in this case nearly 3,000 of them — in one of the membrane-embedded enzymes ...
CAMBRIDGE, Mass--A surprising phenomenon has been found in metal nanoparticles: They appear, from the outside, to be liquid droplets, wobbling and readily changing shape, while their interiors retain a perfectly stable crystal configuration.
The research team behind the finding, led by MIT professor Ju Li, says the work could have important implications for the design of components in nanotechnology, such as metal contacts for molecular electronic circuits.
The results, published in the journal Nature Materials, come from a combination of laboratory analysis and computer ...
Two research teams working in the same laboratories at UNSW Australia have found distinct solutions to a critical challenge that has held back the realisation of super powerful quantum computers.
The teams created two types of quantum bits, or "qubits" – the building blocks for quantum computers – that each process quantum data with an accuracy above 99%. The two findings have been published simultaneously today in the journal Nature Nanotechnology.
"For quantum computing to become a reality we need to operate the bits with very low error rates," says Scientia ...
Concerns over human-insecticide exposure has stimulated the development of alternative bed bug control materials, and many essential oil-based pesticides and detergent insecticides have been developed in recent years. But how well do they work? To find out, researchers from Rutgers University evaluated the efficacy of nine essential oil-based products and two detergents that are labeled and marketed for bed bug control. The results are published in an article in the Journal of Economic Entomology.
The non-synthetic bed bug pesticides — which contain ingredients ...
A noninvasive method of delivering a promising therapy for persistent Clostridium difficile (C. difficile) infection appears to be as effective as treatment via colonoscopy or through a nasogastric tube. In their JAMA report, receiving early online release to coincide with a presentation at the Infectious Diseases Society of America's ID Week conference, investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) report that oral administration of the therapy called fecal microbiota transplant (FMT) in acid-resistant capsules was as successful as more invasive methods in eliminating ...
A preliminary study has shown the potential of treating recurrent Clostridium difficile infection (a bacterium that is one of the most common causes of infection of the colon) with oral administration of frozen encapsulated fecal material from unrelated donors, which resulted in an overall rate of resolution of diarrhea of 90 percent, according to a study published in JAMA. The study is being released early online to coincide with its presentation at IDWeek 2014.
Recurrent Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) is a major cause of illness and death, with a recent increase ...
DETROIT – Patients who have plastic surgery to reshape their bodies after bariatric procedures are able to maintain "significantly greater" weight loss than those who do not have surgery, according to a new study by Henry Ford Hospital researchers.
"As plastic and reconstructive surgeons, we are encouraged by the idea that improved body image can translate into better long-term maintenance of a healthier weight, and possibly a better quality of life for our patients," says Donna Tepper, M.D., a Henry Ford plastic surgeon and senior author of the study.
Study results ...