(Press-News.org) The fifth named Atlantic storm didn't maintain hurricane status long. Fay became a hurricane late on Oct. 12 and by early on Oct. 13, had weakened back to a tropical storm.
A visible image from NOAA's GOES-East satellite on Oct. 13 at 1145 UTC (7:45 a.m. EDT) showed Tropical Storm Fay northeast of Bermuda and Tropical Storm Gonzalo over the Lesser Antilles. Fay appeared circular, but didn't have the signature shape of a tropical storm like Gonzalo, with bands of thunderstorms spiraling into the center. The image was created by the NASA/NOAA GOES Project at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland.
The National Hurricane Center noted that microwave imagery showed Fay has begun extra-tropical transition. NHC discussion said: The cloud pattern has become quite asymmetric and the remaining central deep convection, situated well to the northeast of the center of circulation, is decreasing.
At 5 a.m. EDT on Oct. 13, Tropical Storm Fay's maximum sustained winds were near 65 mph (100 kph) and gradually weakening. It was centered near latitude 34.3 north and longitude 55.3 west. Fay was about 565 miles (910 km) east-northeast of Bermuda and moving to the east at 26 mph (43 kph)..
The NHC expects Fay to merge with a frontal zone and become an extra-tropical cyclone by tonight, Oct. 13.
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
Satellites confirm Fay weakened to a Tropical Storm
2014-10-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
ORNL researchers make first observation of atoms moving inside bulk material
2014-10-14
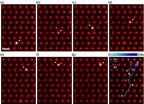
OAK RIDGE, Tenn., Oct. 13, 2014 -- Researchers at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory have obtained the first direct observations of atomic diffusion inside a bulk material. The research, which could be used to give unprecedented insight into the lifespan and properties of new materials, is published in the journal Physical Review Letters (06 October 2014, DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.155501).
"This is the first time that anyone has directly imaged single dopant atoms moving around inside a material," said Rohan Mishra of Vanderbilt University who ...
Charged graphene gives DNA a stage to perform molecular gymnastics
2014-10-14
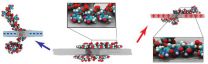
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — When Illinois researchers set out to investigate a method to control how DNA moves through a tiny sequencing device, they did not know they were about to witness a display of molecular gymnastics.
Fast, accurate and affordable DNA sequencing is the first step toward personalized medicine. Threading a DNA molecule through a tiny hole, called a nanopore, in a sheet of graphene allows researchers to read the DNA sequence; however, they have limited control over how fast the DNA moves through the pore. In a new study published in the journal Nature ...
Scientists sniff out unexpected role for stem cells in the brain
2014-10-14
For decades, scientists thought that neurons in the brain were born only during the early development period and could not be replenished. More recently, however, they discovered cells with the ability to divide and turn into new neurons in specific brain regions. The function of these neuroprogenitor cells remains an intense area of research. Scientists at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) report that newly formed brain cells in the mouse olfactory system — the area that processes smells — play a critical role in maintaining proper connections. The results ...
Light-activated drug could reduce side effects of diabetes medication
2014-10-14
Scientists have created a drug for type 2 diabetes that is switched on by blue light, which they hope will improve treatment of the disease.
Diabetes drugs that promote the release of insulin from the pancreas can in some cases cause side effects due to their actions on other organs such as the brain and heart. Some can also stimulate too much insulin release, causing blood sugar levels to drop too low.
To help create better drugs, researchers at Imperial College London and LMU Munich adapted an existing type of drug called a sulfonylurea so that it changes shape when ...
New forecasting method: Predicting extreme floods in the Andes mountains
2014-10-14
This might allow for improved disaster preparedness. As the complex systems technique builds upon a mathematical comparison that can be utilised for any time series data, the approach could be applied to extreme events in all sorts of complex systems.
"Current weather forecast models cannot capture the intensity of the most extreme rainfall events, yet these events are of course the most dangerous, and can have severe impacts for the local population, for example major floods or even landslides," says lead author Niklas Boers of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact ...
Teenage baseball pitchers at risk for permanent shoulder injury
2014-10-14
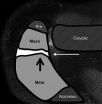
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Young baseball pitchers who throw more than 100 pitches per week are at risk for a newly identified overuse injury that can impede normal shoulder development and lead to additional problems, including rotator cuff tears, according to a new study published online in the journal Radiology.
The injury, termed acromial apophysiolysis by the researchers, is characterized by incomplete fusion and tenderness at the acromion. The acromion, which forms the bone at the top or roof of the shoulder, typically develops from four individual bones into one bone ...
New clues behind the resilience of a leading sexually transmitted pathogen, Chlamydia
2014-10-14
In the advanced online edition of Molecular Biology and Evolution, authors Domman, et al. have explored factors behind the resilience of the most common sexually transmitted disease in the U.S., chlamydia, with an estimated 1 million infected.
The research team sequenced 4 new strains of close genetic cousins of chlamydial pathogens, and examined these with existing DNA data. They found an extensive and robust shuffling of the genomic deck between chlamydia families has played a major role in the evolution of the pathogen, often serving to outwit and exploit its hosts. ...
Study sheds light on factors that may contribute to pancreatic cancer
2014-10-14
New research that provides a better understanding of pancreatic cancer may help identify individuals at increased risk. The findings are published early online in Cancer, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Pancreatic cancer is a stealthy cancer that is usually detected at very late stages and has a 5-year survival rate of less than 5 percent. Strategies that might help identify which individuals have an increased risk of developing the disease are sorely needed. Some cases seem to run in families, but the genes that are responsible for such inherited ...
Slow enteral feeding protocol can reduce instances of death in extreme preterm infants
2014-10-14
A standardized slow enteral feeding (SSEF) protocol significantly reduces the incidence of necrotizing enterocoltis (NEC), or death of intestinal tissue, and death in infants with extremely low birth weight, according to a new study.
The study, published today in the OnlineFirst version of the Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (JPEN), the research journal of the American Society for Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (A.S.P.E.N.), found the use of SSEF resulted in a significant reduction in NEC and accompanying death in infants with a birth weight below 750 grams ...
Memories of pain during childbirth tied to intensity rather than length of labor
2014-10-14
Childbirth is physically intense and, for many women, it is the most painful experience they will have. And yet, new research shows that the amount of time a woman spends in labor doesn't seem to impact how she remembers her labor pain afterwards. The research, published in Psychological Science, a journal of the Association for Psychological Science, reveals that the peak and end levels of pain women experienced, and whether they received an epidural, impacted their recall of labor pain afterward.
"This phenomenon – called duration neglect – is particularly ...