Ancient fossils confirmed among our strangest cousins
2014-10-15
(Press-News.org) More than 100 years since they were first discovered, some of the world's most bizarre fossils have been identified as distant relatives of humans, thanks to the work of University of Adelaide researchers.
The fossils belong to 500-million-year-old blind water creatures, known to scientists as "vetulicolians" (pronounced: ve-TOO-lee-coal-ee-ans).
Alien-like in appearance, these marine creatures were "filter-feeders" shaped like a figure-of-8. Their strange anatomy has meant that no-one has been able to place them accurately on the tree of life, until now.
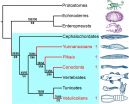
In a new paper published in BMC Evolutionary Biology, researchers at the University of Adelaide and the South Australian Museum argue for a change in the way these creatures are viewed, placing them with the same group that includes vertebrate animals, such as humans.
"Although not directly related to humans in the evolutionary line, we can confirm that these ancient water creatures are among our distant cousins," says the lead author of the paper, Dr Diego Garcia-Bellido, ARC Future Fellow with the University's Environment Institute.
"They are close relatives of vertebrates - animals with backbones, such as ourselves. Vetulicolians have a long tail supported by a stiff rod. This rod resembles a notochord, which is the precursor of the backbone and is unique to vertebrates and their relatives," he says.
Although the first specimens were studied in 1911, it took until 1997 for the fossils to be described as a group on their own: the vetulicolians. These fossils have now been discovered in countries all across the globe, such as Canada, Greenland, China and Australia.
The latest insights into vetulicolians have come from new fossils discovered on Kangaroo Island off the coast of South Australia, which the researchers named Nesonektris (Greek for "Island Swimmer").
"Vetulicolians are further evidence that life was very rich in diversity during the Cambrian period, in some aspects more than it is today, with many extra branches on the evolutionary tree," Dr Diego Garcia-Bellido says. "They were simple yet successful creatures, large in number and in distribution across the globe, and one of the first representatives of our cousins, which include sea squirts and salps."
INFORMATION:
The research involved collaboration between the University of Adelaide, South Australian Museum, University of South Australia, the Natural History Museum, London, and University of New England.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-15
Philadelphia, PA, October 15, 2014 – Are deficits in attention limited to those with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) or is there a spectrum of attention function in the general population? The answer to this question has implications for psychiatric diagnoses and perhaps for society, broadly.
A new study published in the current issue of Biological Psychiatry, by researchers at Cardiff University School of Medicine and the University of Bristol, suggests that there is a spectrum of attention, hyperactivity/impulsiveness and language function in society, ...
2014-10-15
Galaxy clusters are the largest objects in the Universe held together by gravity but their formation is not well understood. The Spiderweb Galaxy (formally known as MRC 1138-262 [1]) and its surroundings have been studied for twenty years, using ESO and other telescopes [2], and is thought to be one of the best examples of a protocluster in the process of assembly, more than ten billion years ago.
But Helmut Dannerbauer (University of Vienna, Austria) and his team strongly suspected that the story was far from complete. They wanted to probe the dark side of star formation ...
2014-10-15
Obtaining access to private outpatient psychiatric care in the Boston, Chicago and Houston metropolitan areas is difficult, even for those with private insurance or those willing to pay out of pocket, a new study by Harvard researchers shows.
The researchers, who posed on the phone as patients seeking appointments with individual psychiatrists, encountered numerous obstacles, including unreturned calls, wrong numbers and providers who were no longer taking new patients. They met with success in only one-quarter of their attempts, even after two tries.
These and related ...
2014-10-15
DURHAM, N.C. – Like discriminating thieves, prostate cancer tumors scavenge and hoard copper that is an essential element in the body. But such avarice may be a fatal weakness.
Researchers at Duke Medicine have found a way to kill prostate cancer cells by delivering a trove of copper along with a drug that selectively destroys the diseased cells brimming with the mineral, leaving non-cancer cells healthy.
The combination approach, which uses two drugs already commercially available for other uses, could soon be tested in clinical trials among patients with late-stage ...
2014-10-15
A new study published in Cancer Research shows SIRT6—a protein known to inhibit the growth of liver and colon cancers—can promote the development of skin cancers by turning on an enzyme that increases inflammation, proliferation and survival of sun-damaged skin cells.
Previously considered protective, SIRT6 is part of a family of seven proteins called sirtuins that help regulate genomic stability and prevent some of the genetic flaws associated with aging. SIRT6 helps repair DNA damage, which can lead to cancer. This study, in the journal's October 15 issue, ...
2014-10-15
Risk factors for sexual assault, including young age and alcohol consumption, must be addressed when considering preventative strategies, suggests a new study, published today (15 October) in BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology (BJOG).
The Danish study used data from all women attending the specialised centre for victims of sexual assault (CVSA) in Copenhagen for sexual assault or attempted sexual assault between March 2001 and December 2010. A total of 2541 women were included in the sample.
The study aimed to describe the victims of sexual ...
2014-10-15
It seems logical that a student who is interested in science as an academic subject would also know a lot about science, but new findings show that this link depends on the overall wealth of the country that the teen calls home. The research suggests that individual science achievement may be influenced as much by broad national-level resources as it is by personal interest and motivation.
This is a photo of students in a chemistry class."Our results suggest that children with high levels of interest in science are able to turn their scientific interest into actual science ...
2014-10-15
A new study, published online in the journal Age and Ageing today, shows that the homebound status of adults over the age of 65 in the aftermath of the 2011 Great East Japan Earthquake is still a serious public health concern. Of 2,327 older adults surveyed, approximately 20% were found to be homebound.
A team of researchers led by Naoki Kondo of the University of Tokyo's School of Public Health studied data from the city of Rikuzentakata, an area that was seriously damaged by the disaster. Of its total population of 23,302 before the events of 2011, 1,773 people died ...
2014-10-14
New Rochelle, October 14, 2014 –Big Data analytics are helping to provide answers to many complex problems in science and society, but they have not contributed to a better understanding climate science, despite an abundance of climate data. When it comes to analyzing the climate system, Big Data methods alone are not enough and sound scientific theory must guide data modeling techniques and results interpretation, according to an insightful article in Big Data, the highly innovative, peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available ...
2014-10-14
ATHENS, Ohio (Oct. 14, 2014)—It's been millions of years since T. rex took its last breath, but a team led by Ohio University scientists is breathing life back into dinosaurs using high-powered computer simulations to model airflow through dinosaur snouts. The research has important implications for how dinosaurs used their noses to not only breathe but to enhance the sense of smell and cool their brains.
"Dinosaurs were pretty 'nosy' animals," said Ohio University doctoral student Jason Bourke, lead author of the new study published today in the Anatomical Record. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Ancient fossils confirmed among our strangest cousins