Fires in the Egypt River Delta
2014-10-20
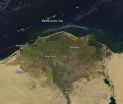
(Press-News.org) This NASA satellite image is of the Egyptian River Delta. Actively burning areas, detected by MODIS's thermal bands, are outlined in red. Each hot spot, which appears as a red mark, is an area where the thermal detectors on the MODIS instrument recognized temperatures higher than background. When accompanied by plumes of smoke, as in this image, such hot spots are diagnostic for fire. The location, widespread nature, and number of fires in this image and confirmation from the Ministry of Environment in Egypt. Fires are witnessed every year in October and November, caused by farmers burning leftover straw from the rice harvest. At least 946 fires have been set this year to burn the leftover straw.
These fires give off plumes of heavy smoke. The smoke released by any type of fire (forest, brush, crop, structure, tires, waste or wood burning) is a mixture of particles and chemicals produced by incomplete burning of carbon-containing materials. All smoke contains carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and particulate matter (PM or soot). The dark, thick smog has begun to creep into the Cairo skies and there are reports of dangerous levels of air pollution which exacerbates respiratory diseases.
This natural-color satellite image was collected by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Terra satellite on October 17, 2014.
INFORMATION:
NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team.
Caption: NASA/Goddard, Lynn Jenner
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-10-20
Looking forward in science often requires looking back, evaluating trends to extrapolate future outcomes. A classic case is Moore's Law, which predicts that the density of components on an integrated circuit will double every 24 months. The estimate has helped guide many developments in the computer industry.
In a new study, Rolf Halden, PhD, a researcher at Arizona State University's Biodesign Institute, examines the trajectory of chemicals appearing as emergent threats to human or environmental health.
Halden's meta-analysis of 143,000 peer-reviewed research papers ...
2014-10-20
About 20% of younger siblings of children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) will develop the condition by age 3. A new study by Yale School of Medicine researchers has found that 57% of these younger siblings who later develop the condition already showed symptoms at age 18 months.
Published in the October Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, this is the first large-scale, multi-site study aimed at identifying specific social-communicative behaviors that distinguish infants with ASD from their typically and atypically developing high-risk ...
2014-10-20
ROSEMONT, Ill.—Obesity affects individual patient care, the healthcare system and nearly every organ in the body. People with obesity often have other health problems, including diabetes, heart disease, certain tumors and cancers, and psychiatric disorders. However, the role of obesity in orthopaedic conditions and their treatment is less well-publicized.
According to orthopaedic surgeon William M. Mihalko, MD, PhD, of Campbell Clinic Orthopaedics in Memphis, Tenn., "obesity can accompany a multitude of comorbidities that can have a significant impact on a patient's ...
2014-10-20
Older individuals who are subliminally exposed to positive stereotypes about aging showed improved physical functioning that can last for several weeks, a new study led by the Yale School of Public Health has found.
Researchers used a novel intervention method to examine for the first time whether exposure to positive age stereotypes could weaken negative age stereotypes and their effects over time, and lead to healthier outcomes.
The study, to be published online in an upcoming issue of the journal Psychological Science, consisted of 100 older individuals (average ...
2014-10-20
Antibiotics—one of modernity's great success stories—are charms that come with a curse. Their overuse in human and animal populations can lead to the development of resistant microbial strains, posing a dire threat to global health.
In a new study, Hansa Done, PhD candidate, and Rolf Halden, PhD, researchers at Arizona State University's Biodesign Institute, examine antibiotic use in the rapidly expanding world of global aquaculture.
Done and Halden measured the presence of antibiotics in shrimp, salmon, catfish, trout, tilapia and swai, originating from ...
2014-10-20
This news release is available in German. Physical exercise in old age can improve brain perfusion as well as certain memory skills. This is the finding of Magdeburg neuroscientists who studied men and women aged between 60 and 77. In younger individuals regular training on a treadmill tended to improve cerebral blood flow and visual memory. However, trial participants who were older than 70 years of age tended to show no benefit of exercise. Thus, the study also indicates that the benefits of exercise may be limited by advancing age. Researchers of the German Center ...
2014-10-20
ATLANTA (October 20, 2014) – New data presented today indicate that consumers of frozen meals (1) had higher daily intakes of dietary fiber, potassium, calcium and protein, and lower daily intakes of calories and saturated fat than consumers of quick service restaurant (QSR) meals (2). The poster, Consumption of Frozen Meals as Compared to Quick Service Restaurant Meals is Associated with Better Nutrient Intakes in Adult Participants of The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2003-2010), was presented at the 2014 Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics Food ...
2014-10-20
Boulder, CO, USA — Ryan McKellar's research sounds like it was plucked from Jurassic Park: he studies pieces of amber found buried with dinosaur skeletons. But rather than re-creating dinosaurs, McKellar uses the tiny pieces of fossilized tree resin to study the world in which the now-extinct behemoths lived.
New techniques for investigating very tiny pieces of fragile amber buried in dinosaur bonebeds could close the gaps in knowledge about the ecology of the dinosaurs, said McKellar, who is a research scientist at the Royal Saskatchewan Museum in Saskatchewan, ...
2014-10-20
New Rochelle, NY, October 20, 2014—When it comes to picking an egg donor, until recent years, recipients tended to prefer someone with a similar appearance. Donor trait choices are changing, though, and which traits are now more preferable and why is the focus of "Beauty, Brains or Health: Trends in Ovum Recipient Preferences," an article published in Journal of Women's Health, a peer-reviewed publication from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Journal of Women's Health website at http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/jwh.2014.4792 ...
2014-10-20
Boulder, CO, USA — Venus is hiding something beneath its brilliant shroud of clouds: a first order mystery about the planet that researchers may be a little closer to solving because of a new re-analysis of twenty-year-old spacecraft data.
Venus's surface can't be seen from orbit in visible light because of the planet's hot, dense, cloudy atmosphere. Instead, radar has been used by spacecraft to penetrate the clouds and map out the surface – both by reflecting radar off the surface to measure elevation and by looking at the radio emissions of the hot surface. ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Fires in the Egypt River Delta




