(Press-News.org) Ferns are believed to be 'old' plant species – some of them lived alongside the dinosaurs, over 200 million years ago. However, a group of Andean ferns evolved much more recently: their completely new form and structure (morphology) arose and diversified within the last 2 million years. This novel morphology seems to have been advantageous when colonising the extreme environment of the high Andes.
Dr Patricia Sanchez-Baracaldo (Bristol) and Dr Gavin Thomas (Sheffield) used molecular and morphological data to study a group of ferns which grow in a unique ecosystem of the Andean mountains.
This ecosystem, known as the páramo, was created relatively recently (around 3 to 5 million years ago), when the Andes underwent a major uplifting event. This provided new ecological opportunities for plants to exploit and flourish in. Other plants from North America and temperate southern regions were also able to colonise these new páramo environments.
In contrast to the archetypal tropical rainforest, where trees are tall and some plants have huge leaves, the páramos are more exposed, tundra-like biomes where plants are short and have much smaller leaves, some of which are very hairy.
Higher altitudes near the equator experience extreme environmental fluctuations every twenty-four hours, with very cold nights and very hot days. In order to grow there, some plants have evolved new adaptions, in form and in leaf structure, which allow them to cope with the paramos' freezing nights and high solar radiation at midday.
The Bristol and Sheffield team found that one group of páramo ferns evolved highly modified leaves, which retain the furled fronds of a young fern yet are sexually mature. Some páramo species were found to have over 300 pairs of leaflets per frond – this is in contrast to their closest relatives in the more sheltered habitat of the cloud forest, lower down the mountains, which have no more than 12 pairs of leaflets per frond. In addition, the length of these leaflets declines rapidly with the increase in altitude.
The researchers also found that the rate by which new biological species arise (speciation) is significantly higher among páramo than non-páramo ferns.
Dr Sanchez-Baracaldo of Bristol's School of Geographical Sciences said: "These ferns are remarkable because, in geological terms, they quickly evolved a new morphology as a response to new and extreme environmental conditions. It's fascinating to notice that, by a process known as convergent evolution, whereby similar features evolve independently in species of different lineages, cloud forest ferns arrived at the same 'solution' in response to the same environmental pressures."
INFORMATION:
Paper
'Adaptation and convergent evolution within the Jamesonia-Eriosorus complex in high-elevation biodiverse Andean hotspots' by Patricia Sánchez-Baracaldo and Gavin H. Thomas in PLOS ONE.
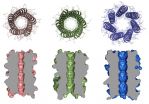
Proteins are long linear molecules that fold up to form well-defined 3D shapes. These 3D molecular architectures are essential for biological functions such as the elasticity of skin, the digestion of food, and the transport of oxygen in blood.
Despite the wide variety of tasks that natural proteins perform, they appear to use only a limited number of structural types, perhaps just a few thousand or so. These are used over and over again, being altered and embellished through evolution to generate many different functions. This raises the question: are more protein ...
A Dartmouth study suggests that it may be possible to use Diffuse Optical Spectroscopic Tomographic imaging (DOST) to predict which patients will best respond to chemotherapy used to shrink breast cancer tumors before surgery. These findings could eliminate delays in effective early treatment for tumors unlikely to respond to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC). The study, "Predicting breast tumor response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy with Diffuse Optical Spectroscopic Tomography prior to treatment," was published online in Clinical Cancer Research on October 7, 2014.
Breast ...
BOSTON - New achievements in synthetic biology announced today by researchers at the Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering, which will allow complex cellular recognition reactions to proceed outside of living cells, will dare scientists to dream big: there could one day be inexpensive, shippable and accurate test kits that use saliva or a drop of blood to identify specific disease or infection — a feat that could be accomplished anywhere in the world, within minutes and without laboratory support, just by using a pocket–sized paper diagnostic ...
(Santa Barbara, Calif.) — Volatile rainstorms drive complex landscape changes in deserts, particularly in dryland channels, which are shaped by flash flooding. Paradoxically, such desert streams have surprisingly simple topography with smooth, straight and symmetrical form that until now has defied explanation.
That paradox has been resolved in newly published research conducted by Michael Singer and Katerina Michaelides, associate researchers at UC Santa Barbara's Earth Research Institute. The pair show that simple topography in dryland channels is maintained ...
DALLAS – Oct. 23, 2014 – A hormone seen as a popular target to develop weight-loss drugs works by directly targeting the brain and triggering previously unknown activity in the nervous system, UT Southwestern Medical Center obesity researchers have found.
The fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) hormone has been a key target for developing weight-loss drugs because the protein increases energy expenditure, causing the body to burn calories. But how the hormone worked wasn't known until now.
UT Southwestern researchers tracking the hormone discovered that ...
DENVER – Sixteen institutions across Europe collaborated together to show for the first time that a semi-quantitative anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) protein expression test, immunohistochemistry (IHC), is reliable amongst several laboratories and reviewers when test methodology and result interpretation are strictly standardized and the scoring pathologists are appropriately trained on the test.
ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) shrink tumors and increase progression-free survival in late-stage non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients positive for ALK as ...
DENVER –CANARY, Computer-Aided Nodule Assessment and Risk Yield, is a novel software tool developed at Mayo Clinic that can automatically quantitate adenocarcinoma pulmonary nodule characteristics from non-invasive high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) images and stratify non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients into risk groups that have significantly different disease-free survival outcomes.
The majority of NSCLC patients are diagnosed with advanced-stage disease which is concomitant with an exceptionally poor prognosis, 5-year survival rate of 4%. In ...
In individuals living in the Arctic, researchers have discovered a genetic variant that arose thousands of years ago and most likely provided an evolutionary advantage for processing high-fat diets or for surviving in a cold environment; however, the variant also seems to increase the risk of hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, and infant mortality in today's northern populations. The findings, published online October 23 in Cell Press's American Journal of Human Genetics, provide an example of how an initially beneficial genetic change could be detrimental to future generations. ...
People may have been making their way from Easter Island to the Americas well before the Dutch commander Jakob Roggeveen arrived with his ships in 1722, according to new genomic evidence showing that the Rapanui people living on that most isolated of islands had significant contact with Native American populations hundreds of years earlier. The findings reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on October 23 lend the first genetic support for such an early trans-Pacific route between Polynesia and the Americas, an impressive trek of more than 4,000 kilometers (nearly ...
Synthetic gene networks hold great potential for broad biotechnology and medical applications, but so far they have been limited to the lab. A study published by Cell Press October 23rd in the journal Cell reveals a new method for using engineered gene circuits beyond the lab, allowing researchers to safely activate the cell-free, paper-based system by simply adding water. The low-cost, easy-to-use platform could enable the rapid detection of different strains of deadly viruses such as Ebola.
"Our paper-based system could not only make tools currently only available ...