(Press-News.org) A large active region on the sun erupted with another X-class flare on Oct. 27, 2014 -- its fourth since Oct. 24. The flare peaked at 10:47 a.m. EDT.
X-class denotes the most intense flares, while the number provides more information about its strength. An X2 is twice as intense as an X1, an X3 is three times as intense, etc.
To see how this event may affect Earth, please visit NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center at http://spaceweather.gov, the U.S. government's official source for space weather forecasts, alerts, watches and warnings.
Continuing a week's worth of substantial flares beginning on Oct.19, 2014, the sun emitted two mid-level solar flares on Oct. 26 and Oct. 27. The first peaked at 8:34 pm EDT on Oct. 26, 2014, and the second peaked almost 10 hours later at 6:09 am EDT on Oct. 27. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which constantly observes the sun, captured images of both flares.
Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel.
To see how this event may affect Earth, please visit NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center at http://spaceweather.gov, the U.S. government's official source for space weather forecasts, alerts, watches and warnings.
The first flare was classified as an M7.1-class flare. The second flare was a bit weaker, classified as an M6.7-class.
M-class flares are one tenth as strong as X-class flares, which are the most intense flares. The number provides more information about its strength. An M2 is twice as intense as an M1, an M3 is three times as intense, etc.
The series of flares over the course of the previous week all erupted from a particularly large active region on the sun, labeled AR 12192 – the largest seen on the sun in 24 years. Active regions are areas of intense and complex magnetic fields that are often the source of solar flares.
Active regions are more common at the moment as we are in what's called solar maximum, which is the peak of the sun's activity, occurring approximately every 11 years.
Images: http://www.nasa.gov/content/goddard/sdo-observes-more-flares-erupting-from-giant-sunspot/
INFORMATION:
A world without plants would be a world without oxygen, uninhabitable for us and for many creatures. We know plants release oxygen by absorbing carbon dioxide and breaking down water using sunlight through the process of photosynthesis. However, we know little about the mechanics of how plants create oxygen during photosynthesis. A breakthrough that will help advance our understanding of this critical ecological process was made recently by scientists at LSU.
"Without photosynthesis or oxygen, basically all recognizable life that we see in our landscape would be gone: ...
Chicago, October 27, 2014—The Associated Press-NORC Center for Public Affairs Research today released the results of a major new study and related reports on the recovery from Superstorm Sandy in 12 New York and New Jersey neighborhoods hard hit by the 2012 storm.
It is the second AP-NORC study that has focused on the aftermath of Superstorm Sandy, with findings that emphasize the important role social factors play in a neighborhood's resilience: the ability of people and their social systems to survive, adapt and continue moving forward after a disaster. Funding ...
This news release is available in French. One in three children who have been reunified with their families after being placed in foster care will be maltreated again, according to a study into Quebec's youth protection system by Marie-Andrée Poirier and Sonia Hélie of the University of Montreal's School of Social Services. The study, the first of its kind in the world, was undertaken in the wake of a new law intended to improve the family stability of youth receiving child protection services.
The researchers, who are also affiliated with the Centre jeunesse ...
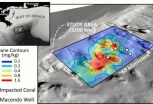
Due to its unprecedented scope, the damage assessment caused by the 2010 Deepwater Horizon spill in the Gulf of Mexico has been a challenge. One unsolved puzzle is the location of 2 million barrels of submerged oil thought to be trapped in the deep ocean.
UC Santa Barbara's David Valentine and colleagues from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institute (WHOI) and UC Irvine have been able to describe the path the oil followed to create a footprint on the deep ocean floor. The findings appear today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
For this study, the ...
Humans are the only primates with large, highly visible sclera – the white part of the eye.
The eye plays a significant role in the expressiveness of a face, and how much sclera is shown can indicate the emotions or behavioral attitudes of a person. Wide-open eyes, exposing a lot of white, indicate fear or surprise. A thinner slit of exposed eye, such as when smiling, expresses happiness or joy. Averted eyes, as well as direct eye contact, can mean several things. So the eye white, or how much of it is shown and at what angle, plays a role in the social and cooperative ...
It's an often-agonizing challenge facing any parent of a child with autism: How can I help my son or daughter socialize with his or her typically developing peers? The solution, SF State's Pamela Wolfberg found, may lie in a different type of playgroup that focuses on collaborative rather than adult-directed activities.
A new study shows that "Integrated Play Groups," or IPGs, developed by Wolfberg over several years, are effective in teaching children with autism the skills they need to interact with their peers and engage in symbolic play such as pretending. In IPGs, ...
Where's the remaining oil from the 2010 Deepwater Horizon disaster in the Gulf of Mexico?
The location of 2 million barrels of oil thought to be trapped in the deep ocean has remained a mystery. Until now.
Scientist David Valentine of the University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB) and colleagues from the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution (WHOI) and the University of California, Irvine, have discovered the path the oil followed to its resting place on the Gulf of Mexico sea floor.
The findings appear today in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy ...
The first images of a nova during its early fireball stage--when it ejects material, and gases expand and cool--show that this activity is more complicated than predicted.
That is the conclusion, published in the current issue of Nature, from a research collaboration led by Georgia State University Astronomer Gail Schaefer that includes 37 researchers (many who are National Science Foundation (NSF)-funded) from 17 institutions. The researchers observed the expanding thermonuclear fireball from a nova that erupted last year in the constellation Delphinus.
"This is ...
The uncontrolled growth of cancer cells arises from their ability to hijack the cell's normal growth program and checkpoints. Usually after therapy, a second cancer-signaling pathway will open after the primary one shuts down — creating an ingenious escape route for the cancer cell to survive. The answer, say Case Western Reserve researchers, is to anticipate and block that back-up track by prescribing two drugs from the start. The results of the project, led by Ruth Keri, PhD, Professor and Vice Chair Department of Pharmacology, and Associate Director for Basic Research ...
1. Study: Prompt isolation of symptomatic patients is key to eliminating Ebola
Isolating the sickest Ebola-infected individuals before they progress into their late phase of illness can effectively eliminate the Ebola epidemic in Liberia, according to a modeling study being published in Annals of Internal Medicine. Currently, West Africa is in the midst of the largest and deadliest Ebola epidemic ever recorded. Liberia has been especially hard-hit with more than 3,500 infections and 2,000 deaths in the past three months. Researchers developed a random transmission model ...