(Press-News.org) A team led by the Lawrence Livermore scientists has created a new kind of ion channel based on short carbon nanotubes, which can be inserted into synthetic bilayers and live cell membranes to form tiny pores that transport water, protons, small ions and DNA.
These carbon nanotube "porins" have significant implications for future health care and bioengineering applications. Nanotube porins eventually could be used to deliver drugs to the body, serve as a foundation of novel biosensors and DNA sequencing applications, and be used as components of synthetic cells.
Researchers have long been interested in developing synthetic analogs of biological membrane channels that could replicate high efficiency and extreme selectivity for transporting ions and molecules that are typically found in natural systems. However, these efforts always involved problems working with synthetics and they never matched the capabilities of biological proteins.
Unlike taking a pill which is absorbed slowly and is delivered to the entire body, carbon nanotubes can pinpoint an exact area to treat without harming the other organs around.
"Many good and efficient drugs that treat diseases of one organ are quite toxic to another," said Aleksandr Noy, an LLNL biophysicist who led the study and is the senior author on the paper appearing in the Oct. 30 issue of the journal, Nature. "This is why delivery to a particular part of the body and only releasing it there is much better."
The Lawrence Livermore team, together with colleagues at the Molecular Foundry at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, University of California Merced and Berkeley campuses, and University of Basque Country in Spain created a new type of a much more efficient, biocompatible membrane pore channel out of a carbon nanotube (CNT) -- a straw-like molecule that consists of a rolled up graphene sheet.
This research showed that despite their structural simplicity, CNT porins display many characteristic behaviors of natural ion channels: they spontaneously insert into the membranes, switch between metastable conductance states, and display characteristic macromolecule-induced blockades. The team also found that, just like in the biological channels, local channel and membrane charges could control the ionic conductance and ion selectivity of the CNT porins.
"We found that these nanopores are a promising biomimetic platform for developing cell interfaces, studying transport in biological channels, and creating biosensors," Noy said. "We are thinking about CNT porins as a first truly versatile synthetic nanopore that can create a range of applications in biology and materials science."
"Taken together, our findings establish CNT porins as a promising prototype of a synthetic membrane channel with inherent robustness toward biological and chemical challenges and exceptional biocompatibility that should prove valuable for bionanofluidic and cellular interface applications," said Jia Geng, a postdoc who is the first co-author of the paper.
Kyunghoon Kim, a postdoc and another co-author, added: "We also expect that our CNT porins could be modified with synthetic 'gates' to dramatically alter their selectivity, opening up exciting possibilities for their use in synthetic cells, drug delivery and biosensing."
INFORMATION:
Other LLNL researchers include Ramya Tunuguntla, Kang Rae Cho, Dayannara Munoz and Morris Wang. The team members performed some of the work at the Molecular Foundry DOE user facility as a part of its user project.
Founded in 1952, Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (http://www.llnl.gov) provides solutions to our nation's most important national security challenges through innovative science, engineering and technology. Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory is managed by Lawrence Livermore National Security, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy's National Nuclear Security Administration.
A study led by investigators from Massachusetts General Hospital and the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania has identified a potential target for therapies to treat cocaine addiction. In their study receiving advance online publication in Molecular Psychiatry, the investigators find evidence that changing one amino acid in a subunit of an important receptor protein alters whether cocaine-experienced animals will resume drug seeking after a period of cocaine abstinence. Increasing expression of the enzyme responsible for that change within the ...
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] — To understand the extent to which human activities are polluting Earth's atmosphere and oceans, it's important to distinguish human-made pollutants from compounds that occur naturally. A recent study co-authored by a Brown University professor does just that for ammonium, a compound that is produced by human activities like agriculture, as well as by natural processes that occur in the ocean.
The research, based on two years of rainwater samples taken in Bermuda, suggests that ammonium deposited over the open ocean comes almost ...
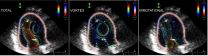
Engineers at the University of California, San Diego have determined for the first time the impact of a ring-shaped vortex on transporting blood flow in normal and abnormal ventricles within the human heart. They worked with cardiologists at the Non-Invasive Cardiology Laboratory at Gregorio Marañon Hospital, in Madrid, Spain.
In order to make the study possible, researchers have developed a novel ultrasound technology that makes screening cheaper and much easier, making it possible to reach a large number of people and even infants. Intra-ventricular flow imaging ...
VIDEO:
AHCC (Active Hexose Correlated Compound) is a natural immune-modulating compound derived from a unique fraction of specially-cultured medicinal mushroom mycelia which has been clinically shown to strengthen the body's immune...
Click here for more information.
(October 29, 2014, Beaverton, OR) New research presented at the Society for Integrative Oncology (SIO) 11th International Conference in Houston, TX showed for the first time that it is possible to eliminate HPV ...
Many factors, both genetic and environmental, have been blamed for increasing the risk of a diagnosis of schizophrenia. Some, such as a family history of schizophrenia, are widely accepted. Others, such as infection with Toxoplasma gondii, a parasite transmitted by soil, undercooked meat and cat feces, are still viewed with skepticism.
A new study by Gary Smith, professor of population biology and epidemiology at the University of Pennsylvania's School of Veterinary Medicine, used epidemiological modeling methods to determine the proportion of schizophrenia cases that ...
Some of the same chemical reactions that occur in the atmosphere as a result of smog and ozone are actually taking place in your house while you are cleaning. A researcher in Drexel's College of Engineering is taking a closer look at these reactions, which involve an organic compound -called limonene- that provides the pleasant smell of cleaning products and air fresheners. His research will help to determine what byproducts these sweet-smelling compounds are adding to the air while we are using them to remove germs and odors.
Secondary organic aerosols (SOAs) are microscopic ...
By remotely "combing" the atmosphere with a custom laser-based instrument, researchers from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), in collaboration with researchers from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), have developed a new technique that can accurately measure—over a sizeable distance—amounts of several of the major "greenhouse" gases implicated in climate change.
The technique potentially could be used in several ways to support research on atmospheric greenhouse gases. It can provide accurate data to support ...
The way a person's brain responds to a single disgusting image is enough to reliably predict whether he or she identifies politically as liberal or conservative. As we approach Election Day, the researchers say that the findings reported in the Cell Press journal Current Biology on October 30 come as a reminder of something we all know but probably don't always do: "Think, don't just react."
P. Read Montague of Virginia Tech says he was initially inspired by evidence showing that an individual's political affiliation is almost as heritable as height. Montague and his ...
Cancer suffers who lose their hair as a consequence of chemotherapy will benefit from a major research project that will improve the scalp cooling technology that prevents hair loss.
The research is being now underway and is being pioneered by global scalp cooling manufacturing company, Paxman Coolers, of Fenay Bridge, Huddersfield, in conjunction with the biology department of the University of Huddersfield.
The research will be led by key researcher Omar Hussain, who has a background in the pharmacology of cancer treatment, which he will use towards his PhD.
Omar ...
Researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have validated an EEG test to study and treat schizophrenia. The findings, published in two separate studies, offer a clinical test that could be used to help diagnose persons at risk for developing mental illness later in life, as well as an approach for measuring the efficacies of different treatment options.
One of the studies, reported online Oct. 23 in Schizophrenia Research, shows that schizophrenia patients don't register subtle changes in reoccurring sounds as well as others and that this deficit ...