(Press-News.org) DARIEN, IL – New research suggests that insomnia is a major contributor to deaths caused by motor vehicle crashes and other unintentional fatal injuries. The results underscore the importance of the "Sleep Well, Be Well" campaign of the National Healthy Sleep Awareness Project.
Results show that the risk of unintentional fatal injury increased in a dose-dependent manner with the number of insomnia symptoms present. People with all three symptoms of insomnia were 2.8 times more likely to die from a fatal injury than those with no insomnia symptoms, even after adjusting for potential confounders such as alcohol consumption and daily use of sleep medication.
Among the three insomnia symptoms, difficulty falling asleep appeared to have the strongest and most robust association with fatal injuries. People who almost always had difficulty falling asleep were more than two times more likely to die from a motor vehicle injury (hazard ratio = 2.40) and more than 1.5 times more likely to die from any fatal injury (HR = 1.66) than people who never had trouble initiating sleep. Further analysis found that self-reported difficulty falling asleep contributed to 34 percent of motor vehicle deaths and eight percent of all unintentional fatal injuries, which could have been prevented in the absence of insomnia.
"Our results suggest that a large proportion of unintentional fatal injuries and fatal motor vehicle injuries could have been prevented in the absence of insomnia," said lead author Lars Laugsand, MD, PhD, postdoctoral fellow in the department of public health at the Norwegian University of Science in Technology in Trondheim, Norway. "Increasing public health awareness about insomnia and identifying and treating people with insomnia may be important in preventing unintentional fatal injuries."
The study results are published in the November issue of the journal Sleep.
"Healthy sleep is essential for physical health, mental well-being, and personal and public safety," said American Academy of Sleep Medicine President Dr. Timothy Morgenthaler, a national spokesperson for the Healthy Sleep Project. "Sleep is a necessity, not a luxury, and the promotion of healthy sleep should be a fundamental public health priority."
Earlier this year the Healthy Sleep Project launched the "Sleep Well, Be Well" campaign to increase awareness of the importance of sleep as one of the three pillars of a healthy lifestyle. More details are available at http://www.projecthealthysleep.org.
The study involved that analysis of population-based survey data from 54,399 men and women between 20 and 89 years of age. Cause of death was identified using a national registry. During the 13-year follow-up period there were 277 unintentional fatal injuries, including 169 deaths from falls and 57 deaths from motor vehicle crashes.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there are more than 126,000 unintentional injury deaths in the U.S. each year, making it the fifth leading cause of death. There are more than 33,000 motor vehicle traffic fatalities and more than 27,000 unintentional fall deaths annually, as well as 29.3 million emergency department visits related to unintentional injuries.
INFORMATION:
The study was supported by the Norwegian University of Science and Technology, the Central Norway Regional Health Authority, the Swedish Council of Working Life and Social Research, and the Swedish Research Council.
To request a copy of the study, "Insomnia Symptoms and Risk for Unintentional Fatal Injuries - The HUNT Study," or to arrange an interview with the study author or an AASM spokesperson, please contact Communications Coordinator Lynn Celmer at 630-737-9700, ext. 9364, or lcelmer@aasmnet.org.
The monthly, peer-reviewed, scientific journal Sleep is published online by the Associated Professional Sleep Societies LLC, a joint venture of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine and the Sleep Research Society. The AASM is a professional membership society that improves sleep health and promotes high quality patient centered care through advocacy, education, strategic research, and practice standards (http://www.aasmnet.org).
About the National Healthy Sleep Awareness Project
The Healthy Sleep Project addresses the sleep health focus area of Healthy People 2020, which provides science-based, 10-year national objectives for improving the health of all Americans. The sleep health objectives are to increase the medical evaluation of people with symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea, reduce vehicular crashes due to drowsy driving and ensure more Americans get sufficient sleep. For more information, visit
http://www.sleepeducation.org/healthysleep.
Insomnia increases risk of motor vehicle deaths, other fatal injuries
Results emphasize the importance of healthy sleep for personal health & public safety
2014-10-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Advance directives can benefit patients, families, and health care system
2014-10-31
Nearly one out of four older Americans say that either they or a family member have experienced excessive or unwanted medical treatment, according to the latest issue of The Gerontological Society of America's Public Policy & Aging Report (PP&AR), which goes on to show that Americans strongly support holding doctors accountable when they fail to honor patients' end-of-life health care wishes.
This PP&AR, titled "Advanced Illness Care: Issues and Options," features 12 articles that present new ways of understanding the complexity of securing appropriate advanced illness ...
A new generation of storage -- ring
2014-10-31
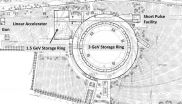
A bright synchrotron source that emits over a wide part of the electromagnetic spectrum from the infrared to hard X-rays is currently being built in Lund, Sweden. The MAX IV facility presents a range of technical challenges for the team putting together its component parts in a storage - ring synchrotron system that will have a circumference of just a few hundred metres. Nevertheless, if these various challenges can be addressed then an entirely new class of experiments that require source brightness and transverse coherence will be possible.
Pedro Tavares and colleagues ...
Viewing cancer on the move: New device yields close-up look at metastasis
2014-10-31
Johns Hopkins engineers have invented a lab device to give cancer researchers an unprecedented microscopic look at metastasis, the complex way that tumor cells spread through the body, causing more than 90 percent of cancer-related deaths. By shedding light on precisely how tumor cells travel, the device could uncover new ways to keep cancer in check.
The inventors, from the university's Whiting School of Engineering and its Institute for NanoBioTechnology (INBT), published details and images from their new system recently in the journal Cancer Research. Their article ...
Lack of oxygen delayed the rise of animals on Earth
2014-10-31
New Haven, Conn. – Geologists are letting the air out of a nagging mystery about the development of animal life on Earth.
Scientists have long speculated as to why animal species didn't flourish sooner, once sufficient oxygen covered the Earth's surface. Animals began to prosper at the end of the Proterozoic period, about 800 million years ago — but what about the billion-year stretch before that, when most researchers think there also was plenty of oxygen?
Well, it seems the air wasn't so great then, after all.
In a study published Oct. 30 in Science, ...
NASA sees remnants of Nilofar go to cyclone graveyard
2014-10-31
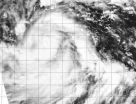
Wind shear has caused the demise of former Tropical Cyclone Nilofar in the northern Arabian Sea. NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Nilofar on Oct. 31 and captured an image that shows strong wind shear has pushed the bulk of clouds and showers away from Nilofar's center, basically sending the storm to its grave.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured an image of the remnants of Tropical Cyclone Nilofar on Oct. 31 at 08:45 UTC (4:45 a.m. EDT). The image showed that the former tropical cyclone's clouds and showers were pushed ...
Proton therapy shown to be less costly than some alternative radiotherapy techniques
2014-10-31
In terms of duration of treatment and cost, patients with early stage breast cancer may benefit from accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) with proton therapy versus whole breast irradiation (WBI), according to new research from The University of Texas MD Anderson Proton Therapy Center.
In a cost analysis study based on typical patient characteristics, researchers used Medicare reimbursement codes to analyze allowable charges for eight different types of partial and whole breast irradiation therapies and treatment schedules available to early stage breast cancer ...
Green spaces don't ensure biodiversity in urban areas
2014-10-31
Planting trees and creating green space in cities is good for attracting species, but it may not be enough to ensure biodiversity in built environments, a University of Iowa study has found.
The researchers surveyed two types of tree in an urban area in Iowa, and recorded the abundance of two insects that interact with them. They found that while there were plenty of the trees, black cherry and black walnut, they didn't find a corresponding abundance of the insects, in this case fruit flies that feed on the walnuts and black cherries and a type of wasp that feeds on the ...
Improved mouse model will accelerate research on potential Ebola vaccines, treatments
2014-10-31
In the war against Ebola one important hurdle has just been cleared – by a mouse.
Researchers at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill and colleagues have developed the first genetic strain of mice that can be infected with Ebola and display symptoms similar to those that humans experience. This work, published in the current issue of Science, will significantly improve basic research on Ebola treatments and vaccines, which are desperately needed to curb the worldwide public health and economic toll of the disease.
"You can't look for a cure for Ebola ...
Scientists trigger self-destruct switch in lung cancer cells
2014-10-31
CANCER RESEARCH UK scientists have found a drug combination that can trigger the self-destruct process in lung cancer cells - paving the way for new treatments, according to research that will be presented at the National Cancer Research Institute (NCRI) Cancer Conference in Liverpool next week*.
When healthy cells are no longer useful they initiate a chain of events culminating in self destruction. But cancer cells swerve away from this suicide path and become immortal. This means that cells grow out of control – causing tumours to form.
The Cancer Research UK ...
Tropical Depression Nuri now haunting the western Pacific Ocean
2014-10-31
Tropical Depression Nuri formed on Halloween morning, October 31, and is haunting the waters of the western North Pacific Ocean. NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured a ghostly-white image of the storm.
When Suomi NPP flew over Tropical Depression Nuri on Oct. 31 at 3:36 UTC, the Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite or VIIRS instrument aboard captured an infrared image of the storm. The infrared data shows temperature, an indicated that there were very high thunderstorms with very cold cloud top temperatures surrounding the center of the low level circulation ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] Insomnia increases risk of motor vehicle deaths, other fatal injuriesResults emphasize the importance of healthy sleep for personal health & public safety