INFORMATION:
To read the paper go to http://geology.gsapubs.org/content/early/2014/09/25/G35886.1.abstract
Massive geographic change may have triggered explosion of animal life
New analysis of geologic history may help solve the riddle of the 'Cambrian explosion'
2014-10-31
(Press-News.org) AUSTIN, Texas— A new analysis of geologic history may help solve the riddle of the "Cambrian explosion," the rapid diversification of animal life in the fossil record 530 million years ago that has puzzled scientists since the time of Charles Darwin.
A paper by Ian Dalziel of The University of Texas at Austin's Jackson School of Geosciences, published in the November issue of Geology, a journal of the Geological Society of America, suggests a major tectonic event may have triggered the rise in sea level and other environmental changes that accompanied the apparent burst of life.
The Cambrian explosion is one of the most significant events in Earth's 4.5-billion-year history. The surge of evolution led to the sudden appearance of almost all modern animal groups. Fossils from the Cambrian explosion document the rapid evolution of life on Earth, but its cause has been a mystery.
The sudden burst of new life is also called "Darwin's dilemma" because it appears to contradict Charles Darwin's hypothesis of gradual evolution by natural selection.
"At the boundary between the Precambrian and Cambrian periods, something big happened tectonically that triggered the spreading of shallow ocean water across the continents, which is clearly tied in time and space to the sudden explosion of multicellular, hard-shelled life on the planet," said Dalziel, a research professor at the Institute for Geophysics and a professor in the Department of Geological Sciences.
Beyond the sea level rise itself, the ancient geologic and geographic changes probably led to a buildup of oxygen in the atmosphere and a change in ocean chemistry, allowing more complex life-forms to evolve, he said.
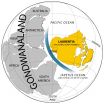
The paper is the first to integrate geological evidence from five present-day continents — North America, South America, Africa, Australia and Antarctica — in addressing paleogeography at that critical time.
Dalziel proposes that present-day North America was still attached to the southern continents until sometime into the Cambrian period. Current reconstructions of the globe's geography during the early Cambrian show the ancient continent of Laurentia — the ancestral core of North America — as already having separated from the supercontinent Gondwanaland.
In contrast, Dalziel suggests the development of a deep oceanic gateway between the Pacific and Iapetus (ancestral Atlantic) oceans isolated Laurentia in the early Cambrian, a geographic makeover that immediately preceded the global sea level rise and apparent explosion of life.
"The reason people didn't make this connection before was because they hadn't looked at all the rock records on the different present-day continents," he said.
The rock record in Antarctica, for example, comes from the very remote Ellsworth Mountains.
"People have wondered for a long time what rifted off there, and I think it was probably North America, opening up this deep seaway," Dalziel said. "It appears ancient North America was initially attached to Antarctica and part of South America, not to Europe and Africa, as has been widely believed."
Although the new analysis adds to evidence suggesting a massive tectonic shift caused the seas to rise more than half a billion years ago, Dalziel said more research is needed to determine whether this new chain of paleogeographic events can truly explain the sudden rise of multicellular life in the fossil record.
"I'm not claiming this is the ultimate explanation of the Cambrian explosion," Dalziel said. "But it may help to explain what was happening at that time."
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists replicate the tide with two buckets, aquarium tubing, and a pump
2014-10-31
Rachel MacTavish is growing salt marsh plants in microcosms that replicate the tide. She assembled them in an outdoor greenhouse at the Sapelo Island National Estuarine Research Reserve in Georgia, USA, with buckets from a hardware store, aquarium tubing, and pumps. Her tidal simulation units could be an important tool for preserving and restoring environmentally important wetlands, because they enable researchers to investigate tidal marsh plant growth in a controlled setting.
"Tidal wetlands are often influenced by many factors, and controlled experiments allow researchers ...
Are my muscular dystrophy drugs working?
2014-10-31
INDIANAPOLIS -- People with muscular dystrophy could one day assess the effectiveness of their medication with the help of a smartphone-linked device, a new study in mice suggests. The study used a new method to process ultrasound imaging information that could lead to hand-held instruments that provide fast, convenient medical information.
In the study presented Oct. 30 at the Acoustical Society of America's annual meeting, researchers determined how well muscles damaged by muscular dystrophy responded to a drug in mice with an animal form of the disease. They did so ...
Tau, not amyloid-beta, triggers neuronal death process in Alzheimer's
2014-10-31
WASHINGTON — New research points to tau, not amyloid-beta (Abeta) plaque, as the seminal event that spurs neuron death in disorders such as Alzheimer's disease. The finding, which dramatically alters the prevailing theory of Alzheimer's development, also explains why some people with plaque build-up in their brains don't have dementia.
The study is published online today in the journal Molecular Neurodegeneration.
Neuronal death happens when tau, found inside neurons, fails to function. Tau's role is to provide a structure — like a train track —inside ...
Resveratrol could reverse benefits of being active
2014-10-31
Contrary to popular belief, use of the supplement resveratrol (RSV) may not actually enhance the effects of high-intensity interval training (HIIT).
Many news outlets and health blogs have long recommended RSV as a complement to exercise and to enhance performance. However, results from a study by Queen's researcher Brendon Gurd suggest that RSV may actually impede the body's response to training.
"The easiest way to experience the benefits of physical activity is to be physically active," says Dr. Gurd, a professor in the School of Kinesiology and Health Studies. "The ...
Immune cells proposed as HIV hideout don't last in primate model
2014-10-31
Where does HIV hide? Antiretroviral drugs can usually control the virus, but can't completely eliminate it. So any strategy to eradicate HIV from the body has to take into account not only the main group of immune cells the virus targets, called CD4 or helper T cells, but other infected cells as well.
New research from Yerkes National Primate Research Center, Emory University, sheds light on the question of which cells support viral replication and persistence, and the answers have implications for future efforts to eliminate HIV from the body in human patients.
The ...
Mussels on California Coast contaminated with giardia transmitted from land-based sources
2014-10-31
The pathogen Giardia duodenalis is present in mussels from freshwater run-off sites and from areas where California Sea Lions lounge along the coast of California, according to a team of researchers from the University of California, Davis. One of the G. duodenalis strains found is known to infect humans; the two others occur mostly in dogs and other canids. "Thus, the detection of these assemblages implies a potential public health risk if consuming fecally contaminated water or uncooked shellfish," says coauthor Woutrina Smith. The research is published ahead of print ...
Avivagen publishes evidence for natural alternative to antibiotic use in livestock
2014-10-31
Today the leading journal PLOS ONE published research that provides underlying scientific support for a fundamentally new type of natural alternative to the use of antibiotics in livestock feeds for growth promotion and disease prevention. The paper is the result of work by both independent and company scientists. Avivagen Inc. is a wellness company developing and delivering products that support and enhance the health and quality of life for animals and the people who care for them.
The discovery that the product formed by full, spontaneous oxidation of beta-carotene, ...
Drug tests on mothers' hair links recreational drug use to birth defects
2014-10-31
Drug tests on 517 mothers in English inner city hospitals found that nearly 15% had taken recreational drugs during pregnancy and that mothers of babies with birth defects of the brain were significantly more likely to have taken drugs than mothers with normal babies. The study found no significant links between recreational drug use and any other type of birth defect.
The study was led by a team of UCL researchers co-ordinating data collection from hospitals across London, Bristol and Birmingham and the results are published in the journal PLOS ONE. The study included ...
Bladderwrack: Tougher than suspected
2014-10-31
It is up to 30 centimetres long, it has a green-brown color and is probably known to every beach walker on the North and Baltic Sea: the bladderwrack, a seaweed, which is common on the coasts of the whole North Atlantic area. The bladderwrack provides food and habitat for many other organisms. Its abundance is considered to be an indication of whether a coastal ecosystem is intact or not. Especially in the German Baltic Sea, however, the populations have declined considerably in the past decade. The reasons for this are not yet fully known. "Against this background, it ...
Fun and games make for better learners
2014-10-31
Four minutes of physical activity can improve behaviour in the classroom for primary school students, according to new research by Brendon Gurd.
A brief, high-intensity interval exercise, or a "FUNterval," for Grade 2 and Grade 4 students reduced off-task behaviours like fidgeting or inattentiveness in the classroom.
"While 20 minutes of daily physical activity (DPA) is required in Ontario primary schools, there is a need for innovative and accessible ways for teachers to meet this requirement," says Dr. Gurd, lead researcher and professor in the School of Kinesiology ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tundra tongue: The science behind a very cold mistake
Targeting a dangerous gut infection
Scientists successfully harvest chickpeas from “moon dirt”
Teen aggression a warning sign for faster aging later in life
Study confirms food fortification is highly cost-effective in fighting hidden hunger across 63 countries
Special issue elevates disease ecology in marine management
A kaleidoscope of cosmic collisions: the new catalogue of gravitational signals from LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA
New catalog more than doubles the number of gravitational-wave detections made by LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA observatories
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
[Press-News.org] Massive geographic change may have triggered explosion of animal lifeNew analysis of geologic history may help solve the riddle of the 'Cambrian explosion'