(Press-News.org) Hurricane Vance was a hurricane on Nov. 4 when the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite and the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) mission satellite passed overhead and measured its rainfall from space. TRMM and GPM revealed areas of heavy rain within the storm before it weakened to a depression and made landfall on Nov. 5.
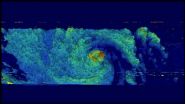
The TRMM satellite flew over hurricane Vance on Nov. 4 at 0953 UTC (4:53 a.m. EST). Rainfall derived from TRMM's Microwave Imager (TMI) data collected were overlaid on a 1000 UTC (5 a.m. EST) image from NOAA's GOES-West satellite showing cloud cover and extent. The image analysis showed that Vance had a large area of heavy rainfall near the center of the hurricane. Some intense storms in that area were dropping rain at a rate of over 50mm (2 inches) per hour.
Vance's power peaked late on November 3, 2014 with winds of about 95 knots (about 109 mph). Vertical wind shear had started to weaken the hurricane, but Vance was still a powerful category two hurricane on the Saffir-Simpson scale with sustained wind speeds of about 90 knots (about 104 mph).
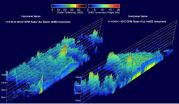
GPM, the successor to the TRMM satellite had two excellent views of Hurricane Vance on both November 3 at 0031 UTC and on Nov. 4 at 1101 UTC. GPM's Radar (Ku band), that is similar to that used on the TRMM's satellite, was used to show vertical structure of precipitation at both times. In the first view hurricane Vance was at close to peak power with a well-defined eye. On Nov. 4, the weakening hurricane had a closing eye with much lower thunderstorm tops.
Tropical Depression Vance Makes Landfall
Increasing vertical wind shear weakened Vance from a hurricane to a depression by Nov. 5. In fact, wind shear had increased so much it was blowing at over 50 knots early in the day.
Vance made landfall in western Mexico around 10 a.m. EST today, Nov. 5. At that time, an automated weather station located in the northern part of the state of Nayarit, Mexico, reported a wind gust of 52 mph (84 kph).
On Wednesday, Nov. 5 at 10 a.m. EST (7 a.m. PST/1500 UTC) the center of Tropical Depression Vance was located near latitude 22.7 north and longitude 105.7 west about 55 miles (90 km) southeast of Mazatlan, Mexico. The depression was moving toward the northeast near 13 mph (20 kph) and is expected to continue in that direction taking Vance farther inland. The estimated minimum central pressure is 1005 millibars. Maximum sustained winds had decreased to near 30 mph (45 kph) and Vance is expected to dissipate later today or tonight.
Vance may be dissipating, but the moisture associated with the depression will continue to bring heavy rainfall southeast of its center and across portions of central and northern Mexico and the south-central United States. The ocean swells creating dangerous conditions and rip currents affecting parts of the southwestern Mexico and Baja California Sur coastlines are expected to diminish late on Nov. 5.
Forecaster Cangialosi at NOAA's National Hurricane Center (NHC) noted that by 10 a.m. EST on Nov. Vance's low-level center was becoming elongated, so the cyclone barely met the qualifications for a tropical cyclone.
VIDEO:
On Nov. 3, NASA/JAXA's GPM Satellite captured data on Hurricane Vance's rainfall and cloud height that were used to create this flyover animation. Red indicates rainfall rates near 50 mm/2...
Click here for more information.
The moisture that TRMM and GPM saw when Vance was a hurricane will continue to generate heavy rainfall. Even though the tropical cyclone is forecast to dissipate soon, the NHC discussion stated that moisture from the remnants of Vance and the area to its southeast should continue to spread northeastward across Mexico and into the south-central United States. This is producing heavy rains over portions of these areas, which should continue for another day or two.
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro/Hal Pierce
SSAI/NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
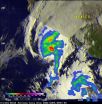
Typhoon Nuri continued moving in a northeasterly direction passing the island of Iwo To, Japan when NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA's Aqua satellite captured a visible picture of Typhoon Nuri on Nov. 5 at 4:10 UTC (11:10 p.m. EST, Nov. 4).
At 1002 UTC (5:02 a.m. EST) a microwave image captured from NASA/JAXA's Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission or TRMM satellite showed that the low-level center of circulation was beginning to weaken. The strongest thunderstorms had become ...
DENVER – Pretreatment interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a significant risk factor for developing symptomatic and severe radiation pneumonitis in stage I non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) alone.
ILD is a group of diseases that cause scarring and stiffing of the tissue and space around the air sacs in the lungs, which results in diminished gas exchange. The incidence of ILD among lung cancer patients is higher than in the general population as tobacco smoking is a common risk factor for both. Some ...
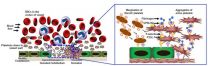
CLEVELAND—Artificial platelet mimics developed by a research team from Case Western Reserve University and University of California, Santa Barbara, are able to halt bleeding in mouse models 65 percent faster than nature can on its own.
For the first time, the researchers have been able to integratively mimic the shape, size, flexibility and surface chemistry of real blood platelets on albumin-based particle platforms. The researchers believe these four design factors together are important in inducing clots to form faster selectively at vascular injury sites while ...
Alexandria, Va. — Earth's abundant silicate minerals are degraded over time by exposure to water, chemical dissolution, and physical and chemical weathering by tree roots and even insects such as ants and termites. Such weathering plays a significant role in decreasing carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, as carbon dioxide is consumed in chemical weathering reactions and the resultant carbonate becomes sequestered in the form of limestone and dolomite.
To study the effects of weathering over time, researchers buried basalt sand at multiple test sites and dug up the ...
BUFFALO, N.Y. – Empathy is among humanity's defining characteristics. Understanding another person's plight can inspire gentle emotions and encourage nurturing behaviors.
Yet under certain circumstances, feelings of warmth, tenderness and sympathy can in fact predict aggressive behaviors, according to a recent study by two University at Buffalo researchers.
But why?
That an expression of kindness might be manifest as a punch in the nose can leave observers scratching their heads.
The answer is that it's not about anger or feeling personally threatened, says ...
"New Rochelle, NY, November 5, 2014—The e-incubator, an innovative miniature incubator that is compatible with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), enables scientists to grow tissue-engineered constructs under controlled conditions and to study their growth and development in real-time without risk of contamination or damage. Offering the potential to test engineered tissues before human transplantation, increase the success rate of implantation, and accelerate the translation of tissue engineering methods from the lab to the clinic, the novel e-incubator is described ...
INDIANAPOLIS -- Indiana University School of Medicine researchers have identified a small protein with a big role in lowering plasma glucose and increasing insulin sensitivity. Their research appeared online today in Diabetes, the journal of the American Diabetes Association.
The report indicates that Sestrin 3 plays a critical role in regulating molecular pathways that control the production of glucose and insulin sensitivity in the liver, making it a logical target for drug development for type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome, which can produce increased blood pressure, ...
Researchers from Northeastern University's Marine Science Center and the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill have found that moderate ocean acidification and warming can actually enhance the growth rate of one reef-building coral species. Only under extreme acidification and thermal conditions did calcification decline.
Their work, which was published Wednesday in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, is the first to show that some corals may benefit from moderate ocean acidification.
Justin Ries, an associate professor ...
WASHINGTON, DC—November 4, 2014—An international team of bioengineers has boosted the ability of bacteria to produce isopentenol, a compound with desirable gasoline properties. The finding, published in mBio®, the online open-access journal of the American Society for Microbiology, is a significant step toward developing a bacterial strain that can yield industrial quantities of renewable bio-gasoline.
The metabolic engineering steps to produce short-chain alcohol solvents like isopentenol in the laboratory bacteria Escherichia coli have been worked on ...
From water marks to colored threads, governments are constantly adding new features to paper money to stay one step ahead of counterfeiters. Now a longhorn beetle has inspired yet another way to foil cash fraud, as well as to produce colorful, changing billboards and art displays. In the journal ACS Nano, researchers report a new kind of ink that mimics the beetle's color-shifting ability in a way that would be long-lasting and difficult to copy.
Zhongze Gu, Zhuoying Xie, Chunwei Yuan and colleagues explain that some U.S. bills have color-changing features to help thwart ...