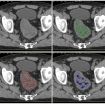
(Press-News.org) As football players are learning, a violent blow to the head has the potential to cause mild to severe traumatic brain injury -- physical damage to the brain that can be debilitating, even fatal. The long-term effects run the gamut of human functioning, from trouble communicating to extensive cognitive and behavioral deterioration. To date, there is no effective medical or cognitive treatment for patients with traumatic brain injuries.
But a new study from Tel Aviv University researchers points to an "enriched environment" -- specially enhanced surroundings -- as a promising path for the rehabilitation of mild traumatic brain injury (mTBI) patients. The research, published in Behavioral Brain Research, was led by Prof. Chagi Pick of TAU's Sagol School of Neuroscience and Sackler Faculty of Medicine and conducted by a team of researchers from both TAU and TAU-affiliated Tel Aviv Sourasky Medical Center.
Mice move on up
The study, conducted on mice at a TAU laboratory, followed two groups of animals with minimal traumatic brain injury. The first group was kept in standard cages and maintained under routine conditions, while the second enjoyed "enriched environments," replete with sensory stimuli, open space, and plentiful opportunities to eat and exercise.
"A house may survive an earthquake, but up close you will see cracks in the walls. This is what may happen following traumatic brain injury," said Prof. Pick. "An MRI might determine that the brain looks normal, but fast forward two years and the patient, who was married and successful, is suddenly unemployed, divorced, and miserable -- without any awareness or understanding that new and lasting cognitive and emotional difficulties (including various degrees of amnesia, difficulty concentrating, depression, apathy, anxiety, and even a prominent personality change) emerged due to a car accident two years earlier.
"Doctors in the emergency room harness the Glasgow Coma Scale to assess the extent of brain trauma in incoming patients -- from a child who falls off the bed to a victim of a major accident," Prof. Pick continued. "In the majority of cases, doctors determine minimal damage according to the symptoms that appear over a very short period of monitoring -- just 30 minutes. In 85% of cases, this is accurate, but in 15% of cases, a cascade of serious damage has just begun, and we don't really know why. But this is what we are trying to figure out."
An environment of riches
According to the study, an "enriched environment" may play a critical role in brain regulation, behavior, and physiology. Using a model of minimal TBI in mice, the team evaluated the effect of transition to an enriched environment on behavioral and cognitive parameters. Using the Novel Object Recognition task, in which mice exhibit different levels of curiosity about new objects placed in their cages, and run different mazes to establish navigation abilities, the researchers sought to determine the mice's level of functioning in standard cages versus enriched environments -- cages with additional stimuli, running wheels, plenty of food, open space, and water. The mice exposed to an enriched environment showed a marked improvement in recovery from brain injuries.
"We have shown that just six weeks in an enriched environment can help animals recover from cognitive dysfunctions after traumatic brain injury," said Prof. Pick. "Possible clinical implications indicate the importance of adapting elements of enriched environments to humans, such as prolonged and intensive physical activity, possibly combined with intensive cognitive stimulation. Through proper exercise, stimuli, and diet, we can improve a patient's condition. No one is promising a cure, but now we have evidence that this can help."
INFORMATION:
American Friends of Tel Aviv University supports Israel's most influential, most comprehensive, and most sought-after center of higher learning, Tel Aviv University (TAU). A leader in the pan-disciplinary approach to education, TAU is internationally recognized for the scope and groundbreaking nature of its research and scholarship -- attracting world-class faculty and consistently producing cutting-edge work with profound implications for the future.
TAU is Israel's only institution of higher learning ranked among the world's top 200 universities by the authoritative Times Higher Education World University Rankings. It is one of a handful of elite international universities rated as the best producers of successful startups, and TAU alumni rank 9th in the world for the amount of American venture capital they attract.
Technology developed at the University of Sussex helps hospitals make earlier and more accurate treatment decisions and survival assessments for patients with bowel cancer.
Bowel cancer kills more than 16,000 people a year in the UK, making it the nation's second-most common cause of cancer death (after lung cancer).
A novel medical-imaging technology, TexRAD, which analyses the texture of tumours, has been shown in trials to enable early diagnosis of those bowel-cancer patients not responding to the standard cancer therapy better than other available tumour markers. ...
Changes to China's drink driving laws are catching the community off guard with more than 70 per cent of people unaware of the blood alcohol limits that could see them face criminal charges, according to new Queensland University of Technology (QUT) research conducted in two Chinese cities.
QUT's Centre for Accident Research & Road Safety - Queensland (CARRS-Q) has partnered with organisations in China to promote road safety and reduce fatalities and injuries, as alcohol-related driving offences are being brought into sharper focus because of the country's rapid motorisation ...
A new climate change modeling tool developed by scientists at Indiana University, Princeton University and the National Oceanographic and Atmospheric Administration finds that carbon dioxide removal from the atmosphere owing to greater plant growth from rising CO2 levels will be partially offset by changes in the activity of soil microbes that derive their energy from plant root growth.
Soils hold more carbon than all of the earth's plant biomass and atmosphere combined. The new work published by Benjamin N. Sulman, a postdoctoral researcher in the lab of co-author and ...
INDIANAPOLIS -- A new treatment regimen for hepatitis C, the most common cause of liver cancer and transplantation, has produced results that will transform treatment protocols for transplant patients, according to research published online today in the New England Journal of Medicine.
The investigational three-drug regimen, which produced hepatitis C cure rates of 97 percent, is an oral interferon-free therapy. Previously, the typical treatment for hepatitis C after a liver transplant was an interferon-based therapy, usually given for 48 weeks. It had a much lower response ...
Lead researcher, Dr Sarah Dunstan from the Nossal Institute of Global Health at the University of Melbourne said the study is the first large-scale, unbiased search for human genes that affect a person's risk of typhoid.
Enteric fever, or typhoid fever as it more commonly known, is a considerable health burden to lower-income countries.
This finding is important because this natural resistance represents one of the largest human gene effects on an infectious disease.
"We screened the human genome to look for genes associated with susceptibility to, or resistance ...
Weeds in the UK are still evolving hundreds of years after their introduction and are unlikely to have yet reached their full potential as invaders, UNSW Australia scientists have discovered.
The study is the first to have tracked the physical evolution of introduced plant species from the beginning of their invasion to the present day, and was made possible by the centuries-old British tradition of storing plant specimens in herbaria.
The research team, led by Habacuc Flores-Moreno, looked at three common weeds - Oxford ragwort, winter speedwell and a willow herb - which ...
A controversial medication used by breastfeeding women should not be restricted because of the benefits it offers mothers and their babies, according to researchers at the University of Adelaide.
The medication domperidone has recently been the subject of warnings from the European Medicines Agency based on research that there is a link between the medication and fatal heart conditions.
Domperidone has been banned in the United States for years because of fatal cardiac arrhythmias among cancer patients who had been prescribed the drug to prevent nausea and vomiting.
However, ...
This news release is available in German. X-rays are widely used in medicine and in materials science. To take a picture of a broken bone, it is enough to create a continuous flux of X-ray photons, but in order to study time-dependent phenomena on very short timescales, short X-ray pulses are required. One possibility to create short hard X-ray pulses is hitting a metal target with laser pulses. The laser rips electrons out of the atoms and makes them emit X-ray radiation. Electrical engineers at the Vienna University of Technology (TU Wien) together with researchers ...
With the help of mouse models, induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and the "tooth fairy," researchers at the University of California, San Diego School of Medicine have implicated a new gene in idiopathic or non-syndromic autism. The gene is associated with Rett syndrome, a syndromic form of autism, suggesting that different types of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) may share similar molecular pathways.
The findings are published in the Nov. 11, 2014 online issue of Molecular Psychiatry.
"I see this research as an example of what can be done for cases of non-syndromic ...
An international research team led by Dan Distel, director of the Ocean Genome Legacy Center of New England Biolabs at Northeastern University, has discovered a novel digestive strategy in shipworms. The breakthrough, the researchers say, may also be a game-changer for the industrial production of clean biofuels.
To start, it's important to note that shipworms, the so-called "termites of the sea," aren't actually worms--they're bizarre clams that ...