Single-dose, needle-free Ebola vaccine provides long-term protection in macaques
2014-11-12
(Press-News.org) Scientists have demonstrated for the first time that a single-dose, needleless Ebola vaccine given to primates through their noses and lungs protected them against infection for at least 21 weeks. A vaccine that doesn't require an injection could help prevent passing along infections through unintentional pricks. They report the results of their study on macaques in the ACS journal Molecular Pharmaceutics.
Maria A. Croyle and colleagues note that in the current Ebola outbreak, which is expected to involve thousands more infections and deaths before it's over, an effective vaccine could help turn the tide. Even better, taking the needle out of the inoculation process could also help prevent the accidental transmission of Ebola, as well as other diseases, such as HIV, that might otherwise spread from unintentional needle pricks and unsafe handling of medical wastes. Other vaccines are currently under development to fight the virus, but they require an injection. Croyle's team tested an adenovirus-based Ebola vaccine using a respiratory delivery route.
The researchers gave a novel formulation of an Ebola vaccine to several macaques then exposed them to the virus more than four months later. All three of the animals that received the vaccine through the nose and via a catheter into their airways did not fall ill. However, since special equipment and training are required for the current respiratory delivery method, the scientists conclude that further work is needed if this formula, or an under-the-tongue version, is to be used eventually in large-scale immunization campaigns.
INFORMATION:
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Institutes of Health.
The ACS Office of Public Affairs has developed an infographic on drug development and the status of various Ebola vaccines. It is available on the ACS Ebola resource page.
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 161,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Follow us: Twitter Facebook
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-12
Geneticists at Heidelberg University Hospital's Department of Molecular Human Genetics have used a new mouse model to demonstrate the way a certain genetic mutation is linked to a type of autism in humans and affects brain development and behavior. In the brain of genetically altered mice, the protein FOXP1 is not synthesized, which is also the case for individuals with a certain form of autism. Consequently, after birth the brain structures degenerate that play a key role in perception. The mice also exhibited abnormal behavior that is typical of autism. The new mouse ...
2014-11-12
An electronic "tongue" could one day sample food and drinks as a quality check before they hit store shelves. Or it could someday monitor water for pollutants or test blood for signs of disease. With an eye toward these applications, scientists are reporting the development of a new, inexpensive and highly sensitive version of such a device in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
S. V. Litvinenko and colleagues explain that an electronic tongue is an analytical instrument that mimics how people and other mammals distinguish tastes. Tiny sensors detect substances ...
2014-11-12
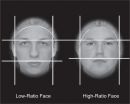
The structure of a soccer player's face can predict his performance on the field--including his likelihood of scoring goals, making assists and committing fouls--according to a study led by a researcher at the University of Colorado Boulder.
The scientists studied the facial-width-to-height ratio (FHWR) of about 1,000 players from 32 countries who competed in the 2010 World Cup. The results, published in the journal Adaptive Human Behavior and Physiology, showed that midfielders, who play both offense and defense, and forwards, who lead the offense, with higher FWHRs ...
2014-11-12
Queensland University of Technology (QUT) researchers have found the habit of Googling for an online diagnosis before visiting the doctor can be a powerful predictor of infectious diseases outbreaks.
Now studies by the same Brisbane-based researchers show combining information from monitoring internet search metrics such as Baidu (China's equivalent of Google), with a web-based infectious disease alert system from reported cases and environmental factors hold the key to improving early warning systems and reducing the deadly effects of dengue fever in China.
Dr Wenbiao ...
2014-11-12
A new peer-reviewed study found that people are contaminated with several toxic flame retardants rarely studied in the US, including one that has never before been detected in Americans called TCEP. Scientists tested urine samples of California residents for biomarkers of six chemicals, all of which were present.
The scientists discovered a way to test for this class of toxic flame retardants (phosphates), which could open up a new wave of research into a group of pervasive flame retardants that were previously not studied nearly as much as some other flame retardants. ...
2014-11-12
Depression causes an average of 10 lost working days per episode
Managers report need for better legislation, training and counseling to tackle the problem
Right Direction Initiative developed to increase awareness of depression, reduce stigma associated with the disease in the workplace, and encourage employees to increase help-seeking behaviors
Canton, Ohio- November 12, 2014 - Nearly a quarter (23 percent) of U.S. respondents indicated they have been diagnosed with depression in their lifetime and two in five (nearly 40 percent) of those patients reported taking ...
2014-11-12
Cities have more species diversity than you'd expect. A study of ants in Manhattan found not only a wide range of species, but also significant differences in the levels of biodiversity in different urban areas.
"People don't think of cities as having ecology, and urban environments haven't been well studied," says Dr. Amy Savage, a postdoctoral biological sciences researcher at North Carolina State University and lead author of a paper on the work. "But protected areas, such as national parks, have been well studied. So we wanted to see if the theories developed to predict ...
2014-11-12
ANN ARBOR, Mich. -- There's a cast of characters deep inside your ears -- many kinds of tiny cells working together to allow you to hear. The lead actors, called hair cells, play the crucial role in carrying sound signals to the brain.
But new research shows that when it comes to restoring lost hearing ability, the spotlight may fall on some of the ear's supporting actors - and their understudies.
In a new paper published online first by the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers from the University of Michigan Medical School, St. Jude Children's ...
2014-11-12
New insights into how plants regulate their absorption of an essential nutrient could help avoid pollution caused by excess use of fertiliser.
The findings could lead to the development of crop varieties that need less of the primary nutrient - nitrogen - than conventional crops. It could also inform how much nitrogen should be added to plant feed.
This would allow optimum plant growth without producing excess nitrogen in run-off from fields, which is a major source of water pollution.
Agricultural fertilisers typically contain high levels of nitrogen that boost ...
2014-11-12
JUPITER, FL, November 12, 2014 - In a pair of related studies, scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) have identified a number of new therapeutic targets for memory disorders and have developed a new screening test to uncover compounds that may one day work against those disorders.
The two studies, one published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), the other in the journal ASSAY and Drug Development Technologies, could lead new approaches to some of the most problematic diseases facing a rapidly aging ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Single-dose, needle-free Ebola vaccine provides long-term protection in macaques