Scientists uncover vast numbers of DNA 'blind spots' that may hide cancer-causing mistakes
2014-11-14
(Press-News.org) Cancer Research UK scientists have found more than 400 'blind spots' in DNA which could hide cancer-causing gene faults, according to research published* today (Friday) in Cancer Research.
The researchers found hidden faults in areas that are tricky for gene-reading technology to decode. This technique, which unravels cancer's genetic blueprint, is an important part of the research that scientists carry out to understand more about cancer's biology.
By finding new ways to unlock these blind spots in the future, the researchers hope this will help us understand these mistakes and whether they lead to cancer. This could be a step towards developing tests to spot cancers earlier or provide new tactics for discovering future cancer treatments.
The team, from the Cancer Research UK Manchester Institute, compared two giant gene databases made from cancer cells grown in labs and cross-checked all the genes that are known - or are likely to be - involved in cancer to unearth the problem areas.
They found that the 400 blind spots in the genes were hidden in very repetitive DNA areas which cause the gene-reading technology to stutter. This problem reading the genes could conceal mistakes which might play a vital role in cancer.
Lead researcher Andrew Hudson, at the Cancer Research UK Manchester Institute at The University of Manchester, said: "The genes behind cancer are like a story. While we've been able to read most of the book using gene-reading technology, the limits of these tools mean some pages are missing.
"These pages could just be unimportant filler, but we wonder if they might hold important twists in the plot which could affect our understanding of cancer. The next step in our work will be to find a way to open up these areas to help piece together the full story."
Nell Barrie, Cancer Research UK's senior science information manager, said: "We're at an unprecedented point in cancer research. As research accelerates we're revealing more and more about cancer's secrets and central to this is our better understanding of how genetic changes drive the disease."
"By delving deeper into cancer's genetic origins we can spot the ways the disease is triggered and develops. This could help us to tackle it from the root, giving more cancer patients a chance at surviving the disease."
The University of Manchester, including the Cancer Research UK Manchester Institute, joined forces with Cancer Research UK and The Christie NHS Foundation Trust to form the Manchester Cancer Research Centre, allowing doctors and scientists to work closely together to turn scientific advances into patient benefits sooner.
INFORMATION:
For media enquiries contact Emily Head in the Cancer Research UK press office on 020 3469 6189 or, out of hours, on 07050 264 059.
Notes to editors:
* Hudson et al. Discrepancies in Cancer Genomic Sequencing Highlight Opportunities for Driver Mutation Discovery. Cancer Research. DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-1020
About Manchester Cancer Research Centre
The Manchester Cancer Research Centre (MCRC) is a partnership founded by The University of Manchester, including the CRUK Manchester Institute, The Christie NHS Foundation Trust and Cancer Research UK. The MCRC brings together the expertise, ambition and resources of its partner organisations in the fields of cancer treatment and clinical research and provides outstanding facilities where researchers and clinicians can work closely together. The aim of the MCRC is to improve understanding of how cancer develops, in order to translate basic and clinical research into new diagnostic tests and treatments that benefit cancer patients.
http://www.mcrc.manchester.ac.uk
About Cancer Research UK
Cancer Research UK is the world's leading cancer charity dedicated to saving lives through research.
Cancer Research UK's pioneering work into the prevention, diagnosis and treatment of cancer has helped save millions of lives.
Cancer Research UK receives no government funding for its life-saving research. Every step it makes towards beating cancer relies on every pound donated.
Cancer Research UK has been at the heart of the progress that has already seen survival rates in the UK double in the last forty years.
Today, 2 in 4 people survive cancer for at least 10 years. Cancer Research UK's ambition is to accelerate progress so that 3 in 4 people will survive cancer within the next 20 years.
Cancer Research UK supports research into all aspects of cancer through the work of over 4,000 scientists, doctors and nurses.
Together with its partners and supporters, Cancer Research UK's vision is to bring forward the day when all cancers are cured.
For further information about Cancer Research UK's work or to find out how to support the charity, please call 0300 123 1022 or visit http://www.cancerresearchuk.org. Follow us on Twitter and Facebook.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-14
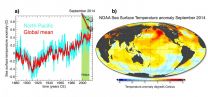
"This summer has seen the highest global mean sea surface temperatures ever recorded since their systematic measuring started. Temperatures even exceed those of the record-breaking 1998 El Niño year," says Axel Timmermann, climate scientist and professor, studying variability of the global climate system at the International Pacific Research Center, University of Hawaii at Manoa.
From 2000-2013 the global ocean surface temperature rise paused, in spite of increasing greenhouse gas concentrations. This period, referred to as the Global Warming Hiatus, raised a lot ...
2014-11-13
What makes some women more susceptible to heart disease than others?
To help answer that question, researchers at Western University's Robarts Research Institute have identified that an estrogen receptor, previously shown to regulate blood pressure in women, also plays an important role in regulating low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels. LDL, also known as bad cholesterol, drives the process that leads to heart disease.
This finding provides evidence that the hormone estrogen plays a key role in regulating two of the most common risk factors for heart disease ...
2014-11-13
VIDEO:
A multi-institutional study has defined and established criteria for a new neurological disease closely resembling Alzheimer's disease called primary age-related tauopathy (PART). Patients with PART develop cognitive impairment that can...
Click here for more information.
LEXINGTON, Ky (Nov. 13, 2014) -- A multi-institutional study has defined and established criteria for a new neurological disease closely resembling Alzheimer's disease called primary age-related tauopathy ...
2014-11-13
HOUSTON, Nov. 13, 2014 - A team of University of Houston (UH) chemistry researchers have developed a molecule that assembles spontaneously into a lightweight structure with microscopic pores capable of binding large quantities of several potent greenhouse gases.
"Greenhouse gases, such a carbon dioxide, have received much attention lately because of their potential to dramatically affect Earth's climate, primarily the temperature of the planet," said Ognjen Miljanić, a UH associate professor of chemistry and leader of the team.
While carbon dioxide presents the ...
2014-11-13
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) -- Researchers at UC Davis and other institutions have found that diets rich in whole walnuts or walnut oil slowed prostate cancer growth in mice. In addition, both walnuts and walnut oil reduced cholesterol and increased insulin sensitivity. The walnut diet also reduced levels of the hormone IGF-1, which had been previously implicated in both prostate and breast cancer. The study was published online in the Journal of Medicinal Food.
"For years, the United States government has been on a crusade against fat, and I think it's been to our detriment," ...
2014-11-13
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researches have uncovered "smoking-gun" evidence to confirm the workings of an emerging class of materials that could make possible "spintronic" devices and practical quantum computers far more powerful than today's technologies.
The materials are called "topological insulators." Unlike ordinary materials that are either insulators or conductors, topological insulators are in some sense both at the same time - they are insulators inside but always conduct electricity via the surface. Specifically, the researchers have reported the clearest demonstration ...
2014-11-13
Boulder, Colo., USA - Seismic hazards in the Puget Lowland of northwestern Washington include deep earthquakes associated with the Cascadia subduction zone and shallow earthquakes associated with crustal faults across the region. Research presented in Geosphere this month establishes not only that one of the more prominent crustal faults, the Darrington-Devils Mountain fault zone, displays evidence of strong earthquakes in the past, but that it will likely be a source of strong earthquakes in the future.
Paleoseismic investigations on the Darrington-Devils Mountain fault ...
2014-11-13
New Rochelle, NY, November 13, 2014--The two U.S. FDA approved oligonucleotide-based drugs on the market both have a modified chemical backbone made of phosphorothioates. The therapeutic advantages of the phosphorothioate group and the new types of gene expression-regulation oligonucleotide drugs that it is enabling are detailed in a Review article in Nucleic Acid Therapeutics, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. publishers. The article is available free on the Nucleic Acid Therapeutics website until December 13, 2014.
In the article "Phosphorothioates, ...
2014-11-13
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. - Researchers from Purdue and Colorado State universities have discovered that the fungus responsible for thousand cankers disease, a lethal affliction of walnut trees and related species, has a rich genetic diversity that may make the disease more difficult to control.
Adjunct assistant professor of forestry Keith Woeste and fellow researchers analyzed the genes of 209 samples of Geosmithia morbida from 17 regions of the U.S. to determine the genetic diversity of the fungus, its possible origin and how it spread throughout the West and to parts of ...
2014-11-13
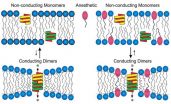
Anesthesia, long considered a blessing to patients and surgeons, has been a mystery for much of its 160-plus-year history in the operating room.
No one could figure out how these drugs interact with the brain to block pain and induce a coma-like, memory-free state. The debate has divided the anesthesia research community into two camps: one that believes anesthetics primarily act on the cell membrane (the lipid bilayer) of nerve cells, perhaps altering it to the point that embedded proteins cannot function normally. The other says the membrane proteins themselves are ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Scientists uncover vast numbers of DNA 'blind spots' that may hide cancer-causing mistakes