A kingdom of cave beetles found in Southern China
2014-11-14
(Press-News.org) A team of scientists specializing in cave biodiversity from the South China Agricultural University (Guangzhou) unearthed a treasure trove of rare blind cave beetles. The description of seven new species of underground Trechinae beetles, published in the open access journal ZooKeys, attests for the Du'an karst as the most diverse area for these cave dwellers in China.
"China is becoming more and more fascinating for those who study cave biodiversity, because it holds some of the most morphologically adapted cavernicolous animals in the world. This is specifically true for fishes and the threchine beetles, the second of which is also the group featured in this study," explains the senior author of the study Prof. Mingyi Tian.
Like most cavernicolous species, Trechinae cave beetles shows a number of specific adaptations, such as lack of eyes and colour, which are traits common among cave dwellers.
The new Trechinae beetles belong to the genus Dongodytes whose members are easily recognizable by their extraordinary slender and very elongated body. Members of this genus are usually very rare in caves, with only five species reported from China before now.
During the recent study of the cave systems in Du'an karst however this numbers drastically changed, Out of the 48 visited caves 12 held populations of trechine beetles. A total of 103 samples were collected, out of which the team of scientists determined ten different species, seven of which are new to science.
"This new discovery casts a new light on the importance of the Du'an Karst as a biological hotspot for cavernicolous Trechinae in China," adds Prof. Mingyi Tian.
INFORMATION:
Original source
Tian M, Yin H, Huang S (2014) Du'an Karst of Guangxi: a kingdom of the cavernicolous genus Dongodytes Deuve (Coleoptera, Carabidae, Trechinae). ZooKeys 454: 69-107. doi: 10.3897/zookeys.454.7269
Additional Information
Lin W , Tian MY(2014) Supplemental notes on the genus Libotrechus Uéno, with description of a new species from Guangxi, southern China (Coleoptera: Carabidae: Trechinae). The Coleopterists Bulletin, 68(3):429-433
[Attachments] See images for this press release:


ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-14
Athens, Ga. - Researchers at the University of Georgia have discovered that a chemical compound commonly found in coffee may help prevent some of the damaging effects of obesity.
In a paper published recently in Pharmaceutical Research, scientists found that chlorogenic acid, or CGA, significantly reduced insulin resistance and accumulation of fat in the livers of mice who were fed a high-fat diet.
"Previous studies have shown that coffee consumption may lower the risk for chronic diseases like Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease," said Yongjie Ma, a postdoctoral ...
2014-11-14
Today's herbaria, as well as all other collections-based environments, are now transitioning their collections data onto the web to remain viable in the smartphone-in-my-pocket age. A team of researchers have examined the importance of these online plant-based resources through the use of Google Analytics (GA) in a study that was published in the open access Biodiversity Data Journal (BDJ).
The amount of plant biodiversity resources freely accessible has exploded in the last decade, but validating an impact factor for these web-based works has remained difficult. A new ...
2014-11-14
Philadelphia, PA (November 14, 2014) -- In a study of blacks with normal kidney function, those with severe periodontal disease developed chronic kidney disease (CKD) at 4 times the rate of those without severe periodontal disease. The study that will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2014 November 11¬-16 at the Pennsylvania Convention Center in Philadelphia, PA.
Periodontal disease is a chronic bacterial infection of the oral cavity, and it disproportionately affects African Americans. It's also been implicated as a potential risk factor for CKD. To investigate this ...
2014-11-14
Philadelphia, PA (November 14, 2014) -- Acute kidney injury occurs frequently in Ebola virus disease; however, providing hemodialysis to these patients was previously thought to be too risky because it involves large needles or catheters and potential contact with highly infectious blood. Clinicians recently accomplished the first known successful delivery of renal replacement therapy with subsequent recovery of kidney function in a patient with Ebola virus disease. Their protocol will be presented at ASN Kidney Week 2014 at the Pennsylvania Convention Center in Philadelphia, ...
2014-11-14
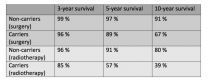
Prostate cancer patients carrying inherited mutations in the BRCA genes respond less well to conventional treatment, including surgery and/or radiotherapy - and they also have a lower survival rate than those who are non-carriers of these genetic mutations. Data from the study, which has been published in the journal European Urology, points to the need for new clinical trials aimed at targeting these mutations in order to tailor treatment for these patients.
The study has been led by David Olmos and Elena Castro at the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO) ...
2014-11-14
November 14, 2014 - After the Boston Marathon bombings, more than 100 people were treated for trauma affecting the ears and hearing--with many having persistent or worsening hearing loss or other symptoms, reports a study in the December issue of Otology & Neurotology. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
Dr. Aaron Remenschneider and principal investigator Dr. Alicia Quesnel of Massachusetts Eye and Ear Infirmary led a Boston-wide collaboration that reviewed the experience with otologic injuries caused by the 2013 ...
2014-11-14
This news release is available in German. For their study, the scientists investigated diseased nerve cells using high precision methods and subsequently simulated their electrical properties on the computer. In their view, medical interventions that preserve the structural integrity of neurons may constitute an innovative strategy for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.
Inside the brain, the nerve cells, which are also called "neurons," are woven into a network in which they relay signals to one another. Thus, neurons form intricate projections that enable ...
2014-11-14
This interview was conducted in August, released as a Web First, and appears in the November issue of Health Affairs.
Health Affairs has previously published Cheng's interviews with other world health ministers, including Thomas Zeltner of Switzerland (2010) and Chen Zhu of China (2012).
In this interview, Minister Nguyen noted that the Vietnamese parliament has voted to spend about 30 percent of the country's state fund for public health. However, that goal has yet to be reached. She also confirmed that Vietnam's 2008 Law of Health Insurance requires patients use ...
2014-11-14
Managing childhood asthma is difficult. Rather than giving daily medications -- even when children feel well -- many parents treat asthma only when symptoms become severe. This practice can lead to missed school days, trips to the ER and hospitalizations.
But a novel program at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis suggests that peer trainers who coach parents over the phone on managing their children's asthma can sharply reduce the number of days the kids experience symptoms. The program also dramatically decreased ER visits and hospitalizations among ...
2014-11-14
DUBLIN, Ireland, November 14th, 2014 - TB is an infectious disease that kills 1.5 million people each year, and smoking is the biggest driver of the global TB epidemic. Medical scientists at Trinity College Dublin and St James's Hospital in Ireland have unlocked the mechanism underlying the connection between smoking and Tuberculosis (TB). This discovery will considerably strengthen anti-smoking efforts to control TB and uncovers new therapy and vaccine options for TB. Their research has just been published in the top respiratory Journal, the American Journal of Respiratory ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A kingdom of cave beetles found in Southern China