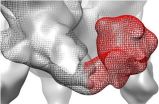
(Press-News.org) Why is Jamaica, with a population smaller than that of Los Angeles, home to so many of the world's elite sprinters - runners who compete in the 100, 200, 400 and 800-meter races?
Robert Trivers, an evolutionary biologist and professor of anthropology and biology in the School of Arts and Sciences, set out with his colleagues to find out if there was something about the symmetry of their knees that might partly explain this phenomenon. They already knew from their earlier research that the symmetry of children's knees at age 8 predicts how fast a person runs 14 years later in life.
"We then asked, "Is the degree of symmetry positively associated with sprinting ability among the very best sprinters?'" Trivers says. The answer to that question is yes.
Within all sprinters, those with the most symmetrical knees have the best times and this was particularly true of the 100-meter sprinters.
"You can easily imagine why," Trivers says. "If you watch someone running a 100-meter race, you can see his or her knees continually churning up and down, propelling the sprinter forward. Symmetry is very efficient."
Trivers and his co-authors - Bernhard Fink of the University of Gottingen in Germany; Kristofor McCarty and Mark Russell of Northumbria University in England; Brian Palaestis of Wagner College in Staten Island, New York; and Bruce James of the MVP Track and Field Club in Kingston, Jamaica -- have published their work in the journal PLOS ONE.
For their study, the researchers measured the knees of 74 elite Jamaican sprinters and a control group of 116 non-sprinting Jamaicans of the same age and sex and similar in size and weight. They discovered that the sprinters' knees were much more symmetrical than the knees of people in the control group.
The 74 sprinters were all members of the MVP Track and Field Club, and included Shelly Ann Fraser-Pryce, who holds two Olympic gold medals in the 100-meter sprint, and Nesta Carter, the man with the fifth fastest 100-meter runs ever recorded.
The 30 sprinters who specialized in the 100-meter race, which does not require turns, had the most symmetrical knees of all. Trivers attributes this finding to the fact that sprinters in longer races have to make left turns each time they run, and this turning may lead to or favor asymmetry over time, just as unbalanced wheels may lead to uneven tire wear on a car.
"So far as we know, this is the first time anyone has isolated a variable that predicts sprinting speed in the future as well as among the very best adult sprinters now," Trivers says.
Scientists have long understood that bilateral symmetry is associated with advantages in animals that have it, including humans. Symmetrical individuals tend to be stronger, healthier and better-looking. Symmetry also makes movement easier and saves energy.
While this study establishes a relationship between knee symmetry and running speed in elite sprinters, it does not establish a causal relationship.
"We don't know for sure whether the sprinters are great sprinters because their knees are symmetrical, or whether their knees are symmetrical because of all the time they spend practicing," Trivers says.
In the future, he wants to study the differences in the strength of sprinters' right and left legs, to see whether the symmetry between them changes over time, and whether the race times of the sprinters change over time. Farther into the future, Trivers is interested in isolating the particular genes that make for great sprinters. People of West African genetic origins, including many Jamaicans, are known to have more "fast-twitch" muscle fibers, which produce energy from the body's sugar rather than oxygen, and are good for short, intense bursts of activity.
INFORMATION:
The sun emitted a mid-level solar flare, peaking at 12:48 p.m. EST on Nov. 16, 2014. NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, which watches the sun constantly, captured an image of the event. Solar flares are powerful bursts of radiation. Harmful radiation from a flare cannot pass through Earth's atmosphere to physically affect humans on the ground, however -- when intense enough -- they can disturb the atmosphere in the layer where GPS and communications signals travel.
To see how this event may affect Earth, please visit NOAA's Space Weather Prediction Center at http://spaceweather.gov, ...
Here's another reason to pay close attention to microbes: Current climate models probably overestimate the amount of carbon that will be released from soil into the atmosphere as global temperatures rise, according to research from the US Department of Energy's Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab).
The findings are from a new computer model that explores the feedbacks between soil carbon and climate change. It's the first such model to include several physiologically realistic representations of how soil microbes break down organic matter, a process that ...
Fruit flies do not always conform to the norm. When female fruit flies have to decide where to lay their eggs, they take their lead from what they see most others in their group do. However, some do take their personal preferences into account. So says Marine Battesti of the Université Paris-Sud in France, lead author of a study in Springer's journal Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology.
The site on which an insect chooses to lay her eggs is very important for the development and survival of future generations. Such choices are not fixed, but are influenced by the ...
UC Davis researchers are getting a new look at the workings of HIV and other viruses thanks to new techniques in electron microscopy developed on campus.
The envelope (or Env) protein of HIV is a key target for vaccine makers: it is a key component in RV144, an experimental vaccine that is so far the only candidate to show promise in clinical trials. Also called gp120, the Env protein associates with another protein called gp41 and three gp120/gp41 units associate to form the final trimeric structure. The gp120 trimer is the machine that allows HIV to enter and attack ...
WASHINGTON, Nov. 17, 2014 -- They are seemingly the most popular thing on the Internet, the subject of millions of videos and hundreds of memes: cats. This week Reactions answers some of the biggest kitty questions out there: Why does catnip make most cats go crazy? What does it mean when your cat rubs against your leg? How does kitty litter clump? Check out the nearly purr-fect video here: http://youtu.be/6_C9i-2QGeU.
Subscribe to the series at Reactions YouTube, and follow us on Twitter @ACSreactions to be the first to see our latest videos.
INFORMATION:
The American ...
ABBOTT PARK, Ill., Nov. 17, 2014 - People aged 65 and older, who were being treated for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) in the hospital and received nutrition treatment (oral nutrition supplements) had reduced lengths of stay, hospital costs and chances of returning to the hospital within 30-days, according to a study published in CHEST.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) -- which includes conditions like chronic bronchitis and emphysema -- is a lung disease that compromises breathing. As COPD often occurs among seniors, it is one of the leading ...
Alexandria, Va. -- Hurricane Sandy struck the U.S. East Coast in October 2012, leaving about $65 billion of damage in its wake and raising the question of how to mitigate the damage from future storms. It's a question that arises in the wake of most natural disasters: What steps can society take to protect itself from storms, floods, landslides, earthquakes, tsunamis or volcanic eruptions? But the question itself illustrates the complexity of preparing for natural disasters.
Our first instincts might be to protect ourselves as well as possible, but reality sets in quickly: ...
CORVALLIS, Ore. - Engineers at Oregon State University have identified a method to rapidly prepare frozen red blood cells for transfusions, which may offer an important new way to manage the world's blood supply.
It's already possible to cryopreserve human red blood cells in the presence of 40 percent glycerol, but is rarely done because of the time-consuming process to thaw and remove the glycerol from the blood. This can take an hour or more and makes it logistically difficult to use frozen blood.
However, some initial experiments and computer modeling of a proposed ...
RENO, Nev. - The everyday use of a GPS device might be to find your way around town or even navigate a hiking trail, but for two physicists, the Global Positioning System might be a tool in directly detecting and measuring dark matter, so far an elusive but ubiquitous form of matter responsible for the formation of galaxies.
Andrei Derevianko, of the University of Nevada, Reno, and his colleague Maxim Pospelov, of the University of Victoria and the Perimeter Institute for Theoretical Physics in Canada, have proposed a method for a dark-matter search with GPS satellites ...
LIVERMORE, Calif. - Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory researchers have developed an efficient method to measure residual stress in metal parts produced by powder-bed fusion additive manufacturing.
This 3D printing process produces metal parts layer by layer using a high-energy laser beam to fuse metal powder particles. When each layer is complete, the build platform moves downward by the thickness of one layer, and a new powder layer is spread on the previous layer.
While this process is able to produce quality parts and components, residual stress is a major ...