(Press-News.org) AUSTIN, Texas -- Job authority increases symptoms of depression among women, but decreases them among men, according to a new study from University of Texas at Austin sociologist Tetyana Pudrovska.
"Women with job authority -- the ability to hire, fire, and influence pay -- have significantly more symptoms of depression than women without this power," said Pudrovska, the lead author of the study. "In contrast, men with job authority have fewer symptoms of depression than men without such power."
The study, "Gender, Job Authority, and Depression," published in the December issue of the Journal of Health and Social Behavior, considers considered more than 1,300 middle-aged men and 1,500 middle-aged women who graduated from high schools in Wisconsin.
According to Pudrovska, who co-authored the study with Amelia Karraker, an assistant professor in the Department of Human Development and Family Studies at Iowa State University, women without job authority exhibit slightly more symptoms of depression on average than men without job authority. But among people with the ability to hire, fire and influence pay, women typically exhibit many more symptoms of depression than men.
"What's striking is that women with job authority in our study are advantaged in terms of most characteristics that are strong predictors of positive mental health," said Pudrovska. "These women have more education, higher incomes, more prestigious occupations, and higher levels of job satisfaction and autonomy than women without job authority. Yet, they have worse mental health than lower-status women."
So why does having job authority increase symptoms of depression in women, but decrease them in men?
"Years of social science research suggests that women in authority positions deal with interpersonal tension, negative social interactions, negative stereotypes, prejudice, social isolation, as well as resistance from subordinates, colleagues and superiors," Pudrovska said. "Women in authority positions are viewed as lacking the assertiveness and confidence of strong leaders. But when these women display such characteristics, they are judged negatively for being unfeminine. This contributes to chronic stress."
Pudrovska said men in authority positions generally deal with fewer stressors because they do not have to overcome the resistance and negative stereotypes that women often face.
"Men in positions of authority are consistent with the expected status beliefs, and male leadership is accepted as normative and legitimate," she said. "This increases men's power and effectiveness as leaders and diminishes interpersonal conflict."
In terms of the study's policy implications, Pudrovska said the findings indicate "we need to address gender discrimination, hostility and prejudice against women leaders to reduce the psychological costs and increase the psychological rewards of higher-status jobs for women."
INFORMATION:
The research was supported by funding from the National Institutes of Health's National Institute on Aging.
For more information, contact David Ochsner, College of Liberal Arts, 512-626-0788; Tetyana Pudrovska, Department of Sociology, 512-232-6300.
Pioneering use of whole genome sequencing in real time to help control a hospital outbreak is reported in an article published in the open access journal Genome Medicine. The research corroborates the use of the technique as a rapid and cost-effective way of tracking and controlling the spread of drug-resistant hospital pathogens.
Acinetobacter baumannii is a multi-drug resistant pathogen found in hospitals across the globe and emerged as a significant threat to casualties in the Iraq and Afghanistan wars. It affects severely ill patients, particularly trauma and burns ...
The Sun may be playing a part in the generation of lightning strikes on Earth by temporarily 'bending' the Earth's magnetic field and allowing a shower of energetic particles to enter the upper atmosphere.
This is according to researchers at the University of Reading who have found that over a five year period the UK experienced around 50% more lightning strikes when the Earth's magnetic field was skewed by the Sun's own magnetic field.
The Earth's magnetic field usually functions as an in-built force-field to shield against a bombardment of particles from space, known ...
A new study published online today in the journal Oxford Economic Papers has found that, on average, terrorist attacks decrease fertility, reducing both the expected number of children a woman has over her lifetime and the number of live births occurring during each year.
In recent years, terrorism has grown as a significant factor affecting our lives in unforeseen ways. Much has been written regarding the causes of terrorism, yet the ramifications of prolonged exposure to terrorism are still to be thoroughly studied. This new study, carried out by Dr. Claude Berrebi ...
Scientists at Queen's University Belfast have led the discovery of a volcanic ash cloud that travelled from Alaska to Northern Ireland and beyond - overturning previously held assumptions about how far ash deposits can drift, with major implications for the airline industry.
The discovery, which was made in partnership with an international team of academics and has been published in the journal Geology, is the first evidence that ash clouds can travel across the Atlantic Ocean, confirming Queen's as a global leader in research. This particular ash, found in sites across ...
Barcelona, Spain: Researchers have found a way of identifying which ovarian cancer patients are likely to respond well to a new anti-cancer drug called rucaparib.
Results of clinical trials have shown that women with tumours that are sensitive to platinum-based chemotherapy and who carry inherited mutations in the BRCA1/2 genes respond well to rucaparib. But in new findings presented today (Thursday) at the 26th EORTC-NCI-AACR [1] Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics in Barcelona, Spain, researchers say that they have identified a biological indicator ...
Barcelona, Spain: A drug that is already well established as a treatment for infection of the retina in people with AIDS has been shown, for the first time, to sensitise cervical cancer to chemotherapy and radiotherapy without an increase in toxic side-effects.
Cidofovir is an anti-viral drug that is effective against several viruses, including the human papilloma virus (HPV), which is implicated in the onset of cervical cancer. It targets the cancer-causing proteins (oncoproteins) produced by HPV. These oncoproteins interfere with the action of other proteins that control ...
Barcelona, Spain: Patients with B-cell Non-Hodgkin lymphomas and advanced solid tumours have responded to a new drug that is being tested for the first time in humans in a phase I clinical trial.
Preliminary results from the trial will be presented today (Thursday) at the 26th EORTC-NCI-AACR [1] Symposium on Molecular Targets and Cancer Therapeutics in Barcelona, Spain. They show responses in four lymphoma patients who have failed numerous previous treatments and also in one patient with a cancer for which there is no approved medical treatment at all - a malignant rhabdoid ...
EAST LANSING, Mich. --- Older couples in a bad marriage -- particularly female spouses -- have a higher risk for heart disease than those in a good marriage, finds the first nationally representative study of its kind.
The findings suggest the need for marriage counseling and programs aimed at promoting marital quality and well-being for couples into their 70s and 80s, said lead investigator Hui Liu, a Michigan State University sociologist.
"Marriage counseling is focused largely on younger couples," said Liu, associate professor of sociology. "But these results show ...
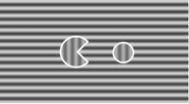
WASHINGTON, D.C. - Scientists have created video games that add an important element of fun to the repetitive training needed to improve vision in people - including adults - with a lazy eye and poor depth perception.
The training tools, including a Pac-Man-style "cat and mouse" game and a "search for oddball" game, have produced results in pilot testing: Weak-eye vision improved to 20/20 and 20/50 in two adult research participants with lazy eyes whose vision was 20/25 and 20/63, respectively, before the training began.
Unlike the common use of eye patches on dominant ...
LOUISVILLE, Ky. - One year ago, Michael Stillman, M.D., and his colleague, Monalisa Tailor, M.D., both physicians with the University of Louisville Department of Medicine, wrote a New England Journal of Medicine "Perspective" article about "Tommy Davis," their pseudonym-named patient who delayed seeing a doctor because he lacked health insurance.
After spending a year experiencing severe abdominal pain and other symptoms, Davis finally sought care in the emergency room. The diagnosis? Metastatic colon cancer.
"If we'd found it sooner," Davis said to the physicians, ...