(Press-News.org) November 20, 2014 - Changes in the lipid layer of the eyes' natural tear film may contribute to the common problem of contact lens discomfort, reports a study in the December issue of Optometry and Vision Science, official journal of the American Academy of Optometry. The journal is published by Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, a part of Wolters Kluwer Health.
Applying a liposomal eyelid spray appears to reduce drying of the tear film and help make wearing contact lenses more comfortable, according to the pilot study by Fiona Stapleton, PhD, FAAO, of University of New South Wales, Sydney, and colleagues.
Contact Lenses Alter Lipid Layer of Tear Film...
The researchers performed in-depth analyses of the tear film in two groups of soft contact lens wearers: ten with contact lens discomfort and ten without discomfort. The tear film is a three-layered "sandwich" of fluids that nourish and protects the eyes.
The study focused on the tear film's outermost layer, which is composed of fat- and wax-like molecules called lipids. The lipid layer performs an important barrier function in preventing evaporation of tears and maintaining stability of the tear film.
The researchers found some differences in the tear film of patients with and without contact lens discomfort. In particular, patients with discomfort showed degradation of the lipid layer after a few hours of wearing contact lenses.
A measure of drying of the surface of the eye also differed between groups. Time for the first dry spot to appear on the eye surface after blinking was less than half as long in patients with contact lens discomfort: 4.5 seconds, compared to 9.9 seconds in patients without discomfort.
...With Possible Benefit of a Liposomal Eyelid Spray
Dr Stapleton and colleagues also evaluated the effects of a liposomal spray designed to protect the tear film. After the liposomal product was sprayed on the eyelids, the stability of the tear film increased significantly. There were also increased levels of a specific enzyme (phospholipase) affecting lipid metabolism.
For the patients with contact lens discomfort, drying times were significantly longer after using the liposomal eyelid spray. Contact lens comfort was increased for up to six hours after using the liposomal spray, compared to an inactive solution.
Contact lens discomfort is a very common problem. Previous studies have suggested that the tear film plays an important role in contact lens discomfort. The liposomal eyelid spray used in the study has shown benefits in patients who have problems with dry eyes.
The new study, using detailed, laboratory-based methods, adds new evidence that the lipid layer is degraded in patients with contact lens discomfort. It also suggests that the liposomal eyelid spray can improve tear film stability and certain components of the lipid layer--potentially improving problems with contact lens discomfort.
"Discomfort is the primary reason why otherwise successful contact lens wearers don't wear contact lenses," comments Anthony Adams, OD, PhD, Editor-in-Chief of Optometry and Vision Science. "Our authors identify the changes in the lipid layer of the tear film in people who have discomfort wearing contact lenses. They also provide preliminary evidence that a lipid supplement spray can help keep the eyes from drying and provide improvement in contact lens comfort."
INFORMATION:
Click here to read "Clinical and Biochemical Tear Lipid Parameters in Contact Lens Wearers."
About Optometry and Vision Science
Optometry and Vision Science, official journal of the American Academy of Optometry, is the most authoritative source for current developments in optometry, physiological optics, and vision science. This frequently cited monthly scientific journal has served primary eye care practitioners for more than 75 years, promoting vital interdisciplinary exchange among optometrists and vision scientists worldwide.
About the American Academy of Optometry
Founded in 1922, the American Academy of Optometry is committed to promoting the art and science of vision care through lifelong learning. All members of the Academy are dedicated to the highest standards of optometric practice through clinical care, education or research.
About Wolters Kluwer Health
Wolters Kluwer Health is a leading global provider of information, business intelligence and point-of-care solutions for the healthcare industry. Serving more than 150 countries worldwide, clinicians rely on Wolters Kluwer Health's market leading information-enabled tools and software solutions throughout their professional careers from training to research to practice. Major brands include Health Language®, Lexicomp®, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Medicom®, Medknow, Ovid®, Pharmacy OneSource®, ProVation® Medical and UpToDate®.
Wolters Kluwer Health is part of Wolters Kluwer, a market-leading global information services company. Wolters Kluwer had 2013 annual revenues of €3.6 billion ($4.7 billion), employs approximately 19,000 people worldwide, and maintains operations in over 40 countries across Europe, North America, Asia Pacific, and Latin America.maintains operations in over 40 countries across Europe, North America, Asia Pacific, and Latin America. Wolters Kluwer is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands. Its shares are quoted on Euronext Amsterdam (WKL) and are included in the AEX and Euronext 100 indices. Wolters Kluwer has a sponsored Level 1 American Depositary Receipt program. The ADRs are traded on the over-the-counter market in the U.S. (WTKWY).
Follow our official Twitter handle: @WKHealth.
Ice-free pavement. "Smart snowplows." Vegetable juice ice-melt.
Cold-climate researchers at Washington State University are clearing the road with green alternatives to the salt, sand and chemicals typically used for highway snow and ice control.
As a nation, "we are kind of salt addicted, like with petroleum, as it's been so cheap and convenient for the last 50 years," said Xianming Shi, associate professor in civil and environmental engineering.
This winter, road salt is in short supply across the northern states and in some regions prices have increased by 10 ...
Powerful clues have been discovered about why the human immune system, metabolism, stress response, and other life functions are so different from those of the mouse. A new, comprehensive study of the mouse genome by an international group of researchers including Penn State University scientists reveals striking similarities and differences with the human genome. The study may lead to better use of mouse models in medical research.
The findings are reported by the Mouse ENCODE Consortium online on November 19, 2014 and in print on November 20 in the study's main paper ...
Case Western Reserve researchers have identified a protein mutation that alters specific gender-related tissue in males before birth and can contribute to the development of cancer as well as other less life-threatening challenges.
The discovery marks the latest in a series of findings related to the protein SRY (sex-determining region on the Y chromosome), which serves as a master switch for ensuring typical human male maturation. In this case, however, the mutation prevents the protein from folding properly and in turn impairs the protein's ability to direct the appropriate ...
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. - November 19, 2014) Gene therapy developed at St. Jude Children's Research Hospital, University College London (UCL) and the Royal Free Hospital has transformed life for men with a severe form of hemophilia B by providing a safe, reliable source of the blood clotting protein Factor IX that has allowed some to adopt a more active lifestyle, researchers reported. The results appear in the November 20 edition of The New England Journal of Medicine.
In this study, participants received one of three doses of gene therapy that used a modified adeno-associated ...
Nanyang Technological University in Singapore (NTU Singapore) has invented a unique biomarker with two exceptional functions.
First, it lights up when it detects tumour cells to allow scientists to take a better look. And it can also release anti-cancer drugs at the same time to the specific cells.
This new biomarker, which has immense potential for drug development, is made from a nanophosphor particle, ten thousand times smaller than a grain of sand.
NTU Singapore associate professors Zhang Qichun and Joachim Loo have found a way to make the nanoparticle light up ...
SALT LAKE CITY, Nov. 20, 2014 - University of Utah engineers have developed a polarizing filter that allows in more light, leading the way for mobile device displays that last much longer on a single battery charge and cameras that can shoot in dim light.
Polarizers are indispensable in digital photography and LCD displays, but they block enormous amounts of light, wasting energy and making it more difficult to photograph in low light.
The Utah electrical and computer engineering researchers created the filter by etching a silicon wafer with nanoscale pillars and holes ...
Researchers in Japan have revealed the mechanism that determines the direction of the transportation of eggs in the fallopian tube.
Fallopian tubes, or oviducts, connect the ovaries and uterus. They are also the place where the egg and sperm meet and fertilization occurs, in addition the tubes have the ability to carry the eggs/embryos to the uterus. Because of these important roles they are an absolutely essential part of the reproductive system. The luminal cells of the fallopian tubes have cilia (hair-like structures) on their surfaces, and by the ciliary movement ...
Oats contain more fat than other cereals, and oat oil has a unique composition. A new study from Lund University, Härröd Research and Swedish Oat Fiber AB, shows a special oat oil preparation can produce greater satiety.
The study followed 34 healthy individuals who were given different quantities of the oat oil preparation as part of a normal breakfast. The researchers found that levels of satiety hormones in the intestines rose more with the oat oil preparation than with the placebo 3-7 hours after the meal (by anything from a tenth to half, depending on the ...
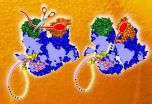
If you planned to sabotage a factory, a recon trip through the premises would probably be much more useful than just peeping in at the windows. Scientists looking to understand - and potentially thwart - the influenza virus have now gone from a similar window-based view to the full factory tour, thanks to the first complete structure of one of the flu virus' key machines. The structure, obtained by scientists at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) in Grenoble, France, allows researchers to finally understand how the machine works as a whole. Published today ...
Shedding pounds is all the rage these days and the global trend toward weight reduction has even spread to the automobile industry. Cars are to get even lighter - using new materials such as ultra-high-strength steels or carbon, and carbon-fiber-reinforced plastics (CFRP). But no matter which diet regime and which lightweight components manufacturers choose, they all want the same thing: the best and longest-lasting joining method for vehicle components. Since Duroplast, which often serves as the matrix component for CFRPs, can't be welded, another joining technique is ...