(Press-News.org) MEDFORD/SOMERVILLE, Mass. (Nov. 24, 2014, 3 P.M.) -- Researchers at Tufts University, in collaboration with a team at the University of Illinois at Champaign-Urbana, have demonstrated a resorbable electronic implant that eliminated bacterial infection in mice by delivering heat to infected tissue when triggered by a remote wireless signal. The silk and magnesium devices then harmlessly dissolved in the test animals. The technique had previously been demonstrated only in vitro. The research is published online in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Early Edition the week of November 24-28, 2014.
"This is an important demonstration step forward for the development of on-demand medical devices that can be turned on remotely to perform a therapeutic function in a patient and then safely disappear after their use, requiring no retrieval," said senior author Fiorenzo Omenetto, professor of biomedical engineering and Frank C. Doble professor at Tufts School of Engineering. "These wireless strategies could help manage post-surgical infection, for example, or pave the way for eventual 'wi-fi' drug delivery."
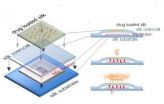
Implantable medical devices typically use non-degradable materials that have limited operational lifetimes and must eventually be removed or replaced. The new wireless therapy devices are robust enough to survive mechanical handling during surgery but designed to harmlessly dissolve within minutes or weeks depending on how the silk protein was processed, noted the paper's first author, Hu Tao, Ph.D., a former Tufts post-doctoral associate who is now on the faculty of the Shanghai Institute of Microsystem and Information Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Each fully dissolvable wireless heating device consisted of a serpentine resistor and a power-receiving coil made of magnesium deposited onto a silk protein layer. The magnesium heater was encapsulated in a silk "pocket" that protected the electronics and controlled its dissolution time.
Devices were implanted in vivo in S. aureus infected tissue and activated by a wireless transmitter for two sets of 10-minute heat treatments. Tissue collected from the mice 24 hours after treatment showed no sign of infection, and surrounding tissues were found to be normal. Devices completely dissolved after 15 days, and magnesium levels at the implant site and surrounding areas were comparable to levels typically found in the body.
The researchers also conducted in vitro experiments in which similar remotely controlled devices released the antibiotic ampicillin to kill E. coli and S. aureus bacteria. The wireless activation of the devices was found to enhance antibiotic release without reducing antibiotic activity.
INFORMATION:
Omenetto holds an adjunct appointment in the Department of Physics in the School of Arts and Sciences at Tufts as well as appointments in the Departments of Biomedical Engineering and Chemical and Biological Engineering in the School of Engineering.
In addition to Omenetto and Tao, authors on the paper were co-first author Suk-Won Hwang, formerly of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, and Frederick Seitz Materials Research Laboratory, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, and now at KU-KIST Graduate School of Converging Science and Technology, Korea University; Benedetto Marelli, Bo An, Jodie E. Moreau, Miaomiao Yang, and Mark A. Brenckle, Department of Biomedical Engineering, Tufts University; Stanley Kim, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, and Frederick Seitz Materials Research Laboratory, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign; David L. Kaplan, Department of Biomedical Engineering and Department of Chemical and Biomedical Engineering, Tufts University; and co-corresponding author John A. Rogers, Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Beckman Institute for Advanced Science and Technology, Frederick Seitz Materials Research Laboratory, Department of Chemistry, and Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Research reported in this paper was supported by the National Institutes of Health under award number P41-EB002520 and by the National Science Foundation under grant number DMR-1242240.
"Silk-based resorbable electronic devices for remotely controlled therapy and in vivo infection abatement," http://www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1407743111
Located on Tufts' Medford/Somerville campus, Tufts' School of Engineering offers a rigorous engineering education in a unique environment that blends the intellectual and technological resources of a world-class research university with the strengths of a top-ranked liberal arts college. Close partnerships with Tufts' excellent undergraduate, graduate and professional schools, coupled with a long tradition of collaboration, provide a strong platform for interdisciplinary education and scholarship. The School of Engineering's mission is to educate engineers committed to the innovative and ethical application of science and technology in addressing the most pressing societal needs, to develop and nurture twenty-first century leadership qualities in its students, faculty, and alumni, and to create and disseminate transformational new knowledge and technologies that further the well-being and sustainability of society in such cross-cutting areas as human health, environmental sustainability, alternative energy, and the human-technology interface.
Contact:
Kim Thurler, 617-627-3175, kim.thurler@tufts.edu
A Jackson Laboratory research team has found that the misfolded proteins implicated in several cardiac diseases could be the result not of a mutated gene, but of mistranslations during the "editing" process of protein synthesis.
In 2006 the laboratory JAX Professor and Howard Hughes Medical Investigator Susan Ackerman, Ph.D., showed that the movement disorders in a mouse model with a mutation called sti (for "sticky," referring to the appearance of the animal's fur) were due to malformed proteins resulting from the incorporation of the wrong amino acids into proteins ...
Research that provides a new understanding of how bacterial toxins target human cells is set to have major implications for the development of novel drugs and treatment strategies.
Cholesterol-dependent cytolysins (CDCs) are toxins produced by major bacterial pathogens, most notably Streptococcus pneumoniae and group A streptococci, which collectively kill millions of people each year.
The toxins were thought to work by interacting with cholesterol in target cell membranes, forming pores that bring about cell death.
Published today in the prestigious journal Proceedings ...
A commonly prescribed muscle relaxant may be an effective treatment for a rare but devastating form of diabetes, researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis report.
The drug, dantrolene, prevents the destruction of insulin-producing beta cells both in animal models of Wolfram syndrome and in cell models derived from patients who have the illness.
Results are published Nov. 24 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) Online Early Edition.
Patients with Wolfram syndrome typically develop type 1 diabetes as very young children ...
(Edmonton) A team of researchers from the University of Alberta has discovered a new approach to fighting breast and thyroid cancers by targeting an enzyme they say is the culprit for the "vicious cycle" of tumour growth, spread and resistance to treatment.
A team led by University of Alberta biochemistry professor David Brindley found that inhibiting the activity of an enzyme called autotaxin decreases early tumour growth in the breast by up to 70 per cent. It also cuts the spread of the tumour to other parts of the body (metastasis) by a similar margin. Autotaxin is ...
High blood pressure and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) are two emerging health problems related to the epidemic of childhood obesity. In a recent study, researchers at University of California, San Diego School of Medicine sought to determine the prevalence of high blood pressure in children with NAFLD, which places them at risk for premature cardiovascular disease.
The study, published in the November 24 edition of PLOS ONE, found that children with NAFLD are at substantial risk for high blood pressure, which is commonly undiagnosed.
"As a result of our ...
PRINCETON, N.J.--A team led by researchers from Princeton University, Michigan State University and the Indonesian Institute of Sciences have confirmed the discovery of a new bird species more than 15 years after the elusive animal was first seen on the Indonesian island of Sulawesi.
The newly named Sulawesi streaked flycatcher (Muscicapa sodhii), distinguished by its mottled throat and short wings, was found in the forested lowlands of Sulawesi where it had last been observed. The researchers report in PLOS ONE that the new species is markedly different from other flycatchers ...
November 24, 2014 - Differences in breast size have a significant mental health impact in adolescent girls, affecting self-esteem, emotional well-being, and social functioning, reports the December issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
More than just a "cosmetic issue," breast asymmetry can have negative psychological and emotional effects, according to the study by ASPS Member Surgeon Dr. Brian I. Labow and colleagues of Boston Children's Hospital. They suggest that early intervention ...
November 24, 2014 - For women considering breast reduction surgery, initial evaluation at a shared medical appointment (SMA) provides excellent patient satisfaction in a more efficient clinic visit, reports a study in the December issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS).
Shared medical appointments have additional benefits, including "group learning, peer support, and a sense of solidarity and commonality" among women learning about breast reduction surgery, according to the study ...
Climate change could lengthen the growing season, make soil drier and decrease winter snowpack in the Lake Michigan Basin by the turn of the century, among other hydrological effects.
A new U.S. Geological Survey precipitation and runoff model shows that by 2100, maximum daily temperature in the Lake Michigan Basin could increase by as much as seven degrees Fahrenheit, and the minimum daily temperature by as much as eight degrees. A new USGS report published today summarizes the potential hydrological effects of these increases on the basin through 2099. The tools can ...
Lincoln, Neb., Nov. 24, 2104 -- The improvements in random access memory that have driven many advances of the digital age owe much to the innovative application of physics and chemistry at the atomic scale.
Accordingly, a team led by University of Nebraska-Lincoln researchers has employed a Nobel Prize-winning material and common household chemical to enhance the properties of a component primed for the next generation of high-speed, high-capacity RAM.
The team, which published its findings in the Nov. 24 edition of the journal Nature Communications, engineered and tested ...