'Giant' charge density disturbances discovered in nanomaterials
Juelich researchers amplify Friedel oscillations in thin metallic films
2014-11-26
(Press-News.org) Jülich, 26 November 2014 - In metals such as copper or aluminium, so-called conduction electrons are able to move around freely, in the same way as particles in a gas or a liquid. If, however, impurities are implanted into the metal's crystal lattice, the electrons cluster together in a uniform pattern around the point of interference, resembling the ripples that occur when a stone is thrown into a pool of water. Scientists in Jülich have, with the help of computer simulations, now discovered a combination of materials that strengthens these Friedel oscillations and bundles them, as if with a lens, in different directions. With a range of 50 nanometers, these "giant anisotropic charge density oscillations" are many times greater than normal and open up new possibilities in the field of nanoelectronics to exchange or filter magnetic information. (Nature Communications, DOI: 10.1038/ncomms6558)
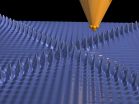
The study just published in "Nature Communications" was preceded by an extraordinary discovery: scientists at the Peter Grünberg Institute in Jülich noticed oddly-shaped electron waves in images obtained using scanning tunnelling microscopy. The pictures showed the surface of a thin film of iron with oxygen impurities. "The wave pattern did not consist of closed rings as one would normally expect, but rather spread out crosswise from the point of interference in four different directions", reported Dr. Samir Lounis.
The reason for the unusual distribution of the electron density fluctuations is the virtually square-shaped Fermi surfaces of the material. The electrons with the most energy in an atomic compound are the ones which move about on the Fermi surfaces. The shape of the Fermi surfaces and the mobility of the electrons determine the physical properties of the metals. Fermi surfaces are often circular or square-shaped with rounded edges.
"The virtually flat Fermi surfaces of our samples act as an amplifier for Friedel oscillations, which spread out perpendicular to the surfaces", explains Lounis. The researchers have found out that this effect can be substantially intensified by varying the thickness of the metal. Depending on the number of atomic layers present, piles of Fermi surfaces are formed; the more of them there are, the greater the oscillations. The researchers called this effect the "Giant Anisotropic Charge Density Oscillations".
In principle, the oscillations could be used to exchange information between individual magnetic impurities and further enhance the level of integration of nanoelectronic components. As the oscillations are mainly produced by spins of a single orientation, they could also form the basis for so-called spin filter elements, which are important components in spintronic applications.
INFORMATION:
Original publication:
Bouhassoune, M. et al.
Quantum well states and amplified spin-dependent Friedel oscillations in thin films.
Nat. Commun. 5:5558 doi: 10.1038/ncomms6558 (2014).
Image:
Electron density oscillations on the surface of a metallic film made visible with the help of low temperature scanning tunnelling microscopy.
Copyright: Forschungszentrum Jülich
Further information:
Press release (after the end of embargo): http://www.fz-juelich.de/portal/EN/Home/
Press release „Nano-Sonar Uses Electrons to Measure under the Surface" 27.2.2009: http://www.fz-juelich.de/SharedDocs/Pressemitteilungen/UK/EN/2009/index25d7_htm.html
Institute: "Quantum Theory of Materials" (PGI-1/IAS-1): http://www.fz-juelich.de/pgi/pgi-1/EN/Home/
Contact:
Dr. Samir Lounis, Quantum Theory of Materials (PGI-1/IAS-1), Forschungszentrum Jülich, Phone: +49 24 61 61-6106, Email: s.lounis@fz-juelich.de
Press:
Angela Wenzik, Science Journalist, Forschungszentrum Jülich,
Phone: +49 24 61 61-6048, Email: a.wenzik@fz-juelich.de
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-11-26
The Luxembourg Centre for Systems Biomedicine (LCSB) has succeeded for the first time in describing the complex relationships within an ecosystem in unprecedented detail. For their work, carried out in collaboration with US and Luxembourg partners, their model ecosystem was a "biological wastewater treatment plant". In it live numerous species of bacteria which are involved in the wastewater purification process.
LCSB director Prof. Dr. Rudi Balling stresses the medical importance of these research efforts: "Bacterial ecosystems also play a major role in our health. ...
2014-11-26
Although the van der Waals force was discovered around 150 years ago, it is still difficult to quantify when predicting the behaviour of solids, liquids, and molecules. Precise measurements were only possible up to now for single atoms or macroscopic objects. However, the van der Waals forces are particularly important at intermediate size, where they crucially co-determine the behaviour of complex molecules, such as biomolecules and proteins. They are also responsible for the functioning of certain adhesives and are the reason why geckos can adhere so amazingly well to ...
2014-11-26
This news release is available in French. The way people with autism spectrum disorder (ASD) gather information - not the judgement process itself - might explain why they gain different perceptions from peoples' faces, according to a new study from Hôpital Rivière-des-Prairies and the University of Montreal. "The evaluation of an individual's face is a rapid process that influences our future relationship with the individual," said Baudouin Forgeot d'Arc, lead author of the study. "By studying these judgments, we wanted to better understand how people with ...
2014-11-26
The precise movements of a young hammerhead shark have been tracked for the first time and are published in the open access journal Animal Biotelemetry. The study, which ran over a 10-month period, reveals important gaps in current efforts to protect these endangered sharks and suggests key locations that should be protected to help the survival of the species.
Hammerhead sharks, which have recently received new protections from the UN Convention on the Conservation of Migratory Species of Wild Animals, are experiencing drastic population declines in excess of 90% in ...
2014-11-26
The expression of a gene involved in female birds' color vision is linked to the evolution of colorful plumage in males, reports a new study from the University of Chicago. The findings, published Nov. 26 in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B, confirm the essential role of female color perception in mate selection and sexual dimorphism.
"This is the first time an aspect of the visual system in birds has been directly associated with plumage evolution," said Natasha Bloch, PhD, who authored the study while a graduate student in ecology & evolution at the University ...
2014-11-26
Deaf teenagers have better reading skills if they were identified as deaf by the time they were nine months old, research from the University of Southampton has shown.
The Southampton team has been studying the development of a group of children who were identified with permanent childhood hearing impairment (PCHI) at a very early age in a pilot screening programme conducted in Southampton and London in the 1990s.
Follow up assessments when the children were aged eight showed those who were screened at birth had better language skills than those children who were not ...
2014-11-26
Rheumatic heart disease (RHD) - the most common acquired heart disease in children in many countries of the world - is being neglected and poorly treated, according to new findings from the Global Rheumatic Heart Disease Registry (the REMEDY study), published online today (Wednesday) in the European Heart Journal [1].
RHD accounts for up to 1.4 million deaths every year, with the highest numbers of people affected by it and dying occurring in low and middle-income countries. It is triggered by rheumatic fever (RF) that can be prevented and controlled. RF is preceded by ...
2014-11-26
The potential to quickly diagnose children with type 1 diabetes before the onset of serious illness could be achieved using a simple, non-invasive breath test, according to new research published today.
In one of the most comprehensive breath-based studies of children with type 1 diabetes performed to date, a team of researchers from Oxford, UK have linked a sweet-smelling chemical marker in the breath with a build-up of potentially harmful chemicals in the blood that accumulate when insulin levels are low.
It is hoped these results--linking an increased level of breath ...
2014-11-26
University of Adelaide-led research will help pinpoint the impact of waves on sea ice, which is vulnerable to climate change, particularly in the Arctic where it is rapidly retreating.
Published today in the Proceedings of the Royal Society A, the research reports the first laboratory experiments testing theoretical models of wave activity in frozen oceans.
"Sea ice is both an indicator and agent of climate change," says project leader Dr Luke Bennetts, Research Fellow in the School of Mathematical Sciences.
"Sea ice covering the ocean surface is white and efficiently ...
2014-11-26
Researchers have found that the spread of an exotic honey bee parasite -now found worldwide - is linked not only to its superior competitive ability, but also to climate, according to a new study published in the journal Proceedings of the Royal Society B.
The team of researchers, including Myrsini Natsopoulou from the Martin-Luther-Universität Halle-Wittenberg, who co-led the research alongside Dr. Dino McMahon from Queen's University Belfast, believes that the parasite could become more prevalent in the UK in the future and their findings demonstrate the importance ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 'Giant' charge density disturbances discovered in nanomaterials
Juelich researchers amplify Friedel oscillations in thin metallic films



