(Press-News.org) LA JOLLA, CA - December 1, 2014 - Researchers can now explore viruses, bacteria and components of the human body in more detail than ever before with software developed at The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI).
In a study published December 1 in the journal Nature Methods, the researchers demonstrated how the software, called cellPACK, can be used to model viruses such as HIV.
"We hope to ultimately increase scientists' ability to target any disease," said Art Olson, professor and Anderson Research Chair at TSRI who is senior author of the new study.
Putting cellPACK to the Test
The cellPACK software solves a major problem in structural biology. Although scientists have developed techniques to study relatively large structures, such as cells, and very small structures, such as proteins, it has been harder to visualize structures in the medium "mesoscale" range.
With cellPACK, researchers can quickly and efficiently process the data they've collected on smaller structures to assemble models in this mid-size range. Previously, researchers had to create these models by hand, which took weeks or months compared with just hours in cellPACK.
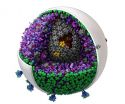
As a demonstration of the software's power, the authors of the new study created a model of HIV showing how outer "spike" proteins are distributed on the surface of the immature virus.
The new model put to the test a conclusion made by HIV researchers from super-resolution microscopic studies--that the distribution of the spike proteins on the surface of the immature virus is random. But by using cellPACK to generate thousands of models, testing alternative hypotheses, the researchers found that the distribution was not random. "We demonstrated that their interpretation of the distribution did not match that hypothesis," said Olson.
A Team Effort
The cellPACK software began as the thesis project of a TSRI graduate student, Graham Johnson, now a QB3 faculty fellow at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) who continues to contribute to the project. Johnson had more 15 years' experience as a medical illustrator, and he wanted to create an easy way to visualize mesoscale structures. cellPACK is an expansion of Johnson's autoPACK software, which maps out the density of materials--from concrete in a building to red blood cells in an artery.
The researchers see cellPACK as a community effort, and they have made the autoPACK and cellPACK software free and open source. Thousands of people have already downloaded the software from http://www.autopack.org.
"With the creation of cellPACK, Dr. Olson and his colleagues have addressed the challenge of integrating biological data from different sources and across multiple scales into virtual models that can simulate biologically relevant molecular interactions within a cell," said Veersamy Ravichandran, PhD, of the National Institutes of Health's National Institute of General Medical Sciences, which partially funded the research. "This user-friendly tool provides a new platform for data analysis and simulation in a collaborative manner between laboratories."
As new information comes in from the scientific community, researchers will tweak the software so it can model new shapes. "Making it open source makes it more powerful," said Olson. "The software right now is usable and very useful, but it's really a tool for the future."
INFORMATION:
In addition to Olson and Johnson, other authors of the study, "cellPACK: A Virtual Mesoscope to Model and Visualize Structural Systems Biology," are Ludovic Autin, Mostafa Al-Alusi, David S. Goodsell and Michel F. Sanner, all of TSRI. For more information, see http://www.nature.com/nmeth/journal/vaop/ncurrent/full/nmeth.3204.html
This study was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF 07576), Autodesk, the National Institutes of Health (P41 GM103426 and P50GM103368), the California Institute for Quantitative Biosciences and a UCSF School of Pharmacy 2013 Mary Anne Koda-Kimble Seed Award for Innovation.
PROVIDENCE, R.I. [Brown University] -- If decades of effort to bring more underrepresented minority students into science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM) fields were considered a grand chemistry experiment, then the modest results would suggest that while the formula may not be wrong, it may well be incomplete, according to a new article in the journal CBE-Life Sciences Education.
"I don't necessarily want to say that we've been doing it wrong all along, it's just that there are other ideas we can bring in," said lead author Andrew G.Campbell, a Brown ...
West Orange, NJ. December 1, 2014. Kessler Foundation researchers have authored a new article that provides insight into the variable impact of traumatic brain injury (TBI) on long-term memory. The article, "Working memory capacity links cognitive reserve with long-term memory in moderate to severe TBI: a translational approach," was epublished ahead of print on October 7 in the Journal of Neurology (10.1007/s00415-014-7523-4). The authors are Joshua Sandry, PhD, John DeLuca, PhD, and Nancy Chiaravalloti, PhD, of Kessler Foundation. This study was supported by grants ...
A new method for determining lung cancer risk could more efficiently identify individuals for annual screening and catch more cancers early, according to a study published in this week's PLOS Medicine. The study, conducted by Martin Tammemägi of Brock University, Canada, and colleagues, evaluates a lung cancer risk prediction model and identifies a risk threshold for selecting individuals for annual lung cancer screening.
Computed Tomography (CT) screening can identify lung tumors while they are still treatable, and the US National Lung Screening Trial (NLST) found ...
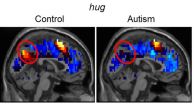
PITTSBURGH--Psychiatric disorders -- including autism -- are characterized and diagnosed based on a clinical assessment of verbal and physical behavior. However, brain imaging and cognitive neuroscience are poised to provide a powerful advanced new tool.
Carnegie Mellon University researchers have created brain-reading techniques to use neural representations of social thoughts to predict autism diagnoses with 97 percent accuracy. This establishes the first biologically based diagnostic tool that measures a person's thoughts to detect the disorder that affects many children ...
People could be putting their lives at risk by dismissing potential warning signs of cancer as less serious symptoms, according to a Cancer Research UK-funded study* published in PLOS ONE today (Tuesday).
More than half (53 per cent) of 1,700** people who completed a health questionnaire said they had experienced at least one red-flag cancer 'alarm' symptom during the previous three months***. But only two per cent of them thought that cancer was a possible cause.
Researchers sent the questionnaire listing 17 symptoms**** - including 10 widely-publicised potential cancer ...
LIMA--(2 December 2014) A new peer-reviewed study, released today at the start of the UN climate conference in Peru, reveals the unprecedented amount of carbon stored within the nine-nation network of Amazonian indigenous territories and protected natural areas. Accepted for publication in Carbon Management, the paper entitled, "Forest Carbon in Amazonia: The Unrecognized Contributions of Indigenous Territories and Protected Natural Areas," suggests that protecting the vast amount of carbon stored above ground in the forests of indigenous and protected lands - totaling ...
COLUMBIA, Mo. - According to a recent report from the Federal Reserve Board, 31 percent of Americans surveyed said they had no retirement savings, and almost half were not actively thinking about planning for retirement. Studies show that many Americans do not invest because they distrust the market and fear financial losses. Now, a University of Missouri researcher has found a way for financial planners to help decrease their clients' worries, which stem from the fear of losing money.
Michael Guillemette, an assistant professor in the MU College of Human Environmental ...
EAST LANSING, Mich. - To hunt or not hunt wolves can't be quantified as simply as men vs. women, hunters vs. anti-hunters, Democrats vs. Republicans or city vs. rural.
What's truly fueling the divisive debate is fear of wolves or the urge to care for canis lupis. The social dynamics at play and potential options for establishing common ground between sides can be found in the current issue of the journal PLOS ONE.
"People who are for or against this issue are often cast into traditional lots, such as gender, political party or where they live," said Meredith Gore, associate ...
Using a novel gene knock-in technique, effective insertion of an exogenous gene was demonstrated in human cells and in animal models, including silkworms and frogs. This strategy universally enables gene knock-in not only in cultured cells, but also in various organisms.
Genome editing using programmable nucleases enables homologous recombination (HR)-mediated gene knock-in. HR activity, however, is relatively low in most cultured cells and organisms. This problem presents technical hurdles for the application of HR-mediated knock-in technology in the field of life sciences. ...
RICHLAND, Wash. - A new study will help researchers create longer-lasting, higher-capacity lithium rechargeable batteries, which are commonly used in consumer electronics. In a study published in the journal ACS Nano, researchers showed how a coating that makes high capacity silicon electrodes more durable could lead to a replacement for lower-capacity graphite electrodes.
"Understanding how the coating works gives us an indication of the direction we need to move in to overcome the problems with silicon electrodes," said materials scientist Chongmin Wang of the Department ...