(Press-News.org) New Rochelle, NY, December 3, 2014--Hereditary angioedema (HAE), a rare genetic disease that causes recurrent swelling under the skin and of the mucosal lining of the gastrointestinal tract and upper airway, usually first appears before 20 years of age. A comprehensive review of the therapies currently available to treat HAE in adults shows that some of these treatments are also safe and effective for use in older children and adolescents. Current and potential future therapies are discussed in a Review article in a special issue of Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonology, a peer-reviewed journal from Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers. The article is available free on the Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonology website at http://online.liebertpub.com/doi/full/10.1089/ped.2014.0412 until January 3, 2015.
Based on the current medical literature, Eveline Wu, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, and Michael Frank, Duke University Medical Center (Durham, NC), report that additional therapies are now approved for use in the pediatric age group. In their article "Management of Hereditary Angioedema in Childhood: A Review" they also discuss clinical trials and published experience among younger age groups for which data are most limited.
"HAE is a potentially life-threatening disease that until recently had very limited therapeutic options for children," says Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonology Editor-in-Chief Mary Cataletto, MD, Professor of Clinical Pediatrics, State University of New York at Stony Brook (Stony Brook, NY). "This special issue of Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonology, developed in collaboration with Guest Editor Dr. Timothy Craig, has been created for physicians who care for children. It focuses on recent advances in HAE-related immunophysiology, as well as current and future therapies for acute and chronic care and prophylaxis."
INFORMATION:
About the Journal
Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonology is a quarterly, peer-reviewed journal published in print and online. The Journal synthesizes the pulmonary, allergy, and immunology communities in the advancement of the respiratory health of children. The Journal provides comprehensive coverage to further the understanding and optimize the treatment of some of the most common and costly chronic illnesses in children. It includes original translational, clinical, and epidemiologic research; public health, quality improvement, and case control studies; patient education research; and the latest research and standards of care for functional and genetic immune deficiencies and interstitial lung diseases. Tables of content and a sample issue may be viewed on the Pediatric Allergy, Immunology, and Pulmonology website at http://www.liebertpub.com/ped.
About the Publisher
Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers is a privately held, fully integrated media company known for establishing authoritative peer-reviewed journals in many promising areas of science and biomedical research, including Journal of Aerosol Medicine and Pulmonary Drug Delivery, Breastfeeding Medicine, and Population Health Management. Its biotechnology trade magazine, Genetic Engineering & Biotechnology News (GEN), was the first in its field and is today the industry's most widely read publication worldwide. A complete list of the firm's 80 journals, books, and newsmagazines is available on the Mary Ann Liebert, Inc., publishers website at http://www.liebertpub.com.
Typhoon Hagupit continues to intensify as it continued moving through Micronesia on Dec. 3 triggering warnings. NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead and captured an image of the strengthening storm while the Rapidscat instrument aboard the International Space Station provided information about the storm's winds.
The International Space Station-RapidScat instrument monitors ocean winds to provide essential measurements used in weather predictions, including hurricanes. "RapidScat measures wind speed and direction over the ocean surface and captured an image of Hagupit ...
This news release is available in French.
Quebec City, December 3, 2014--Researchers at Université Laval's Faculty of Science and Engineering and Centre for Optics, Photonics and Lasers have developed smart textiles able to monitor and transmit wearers' biomedical information via wireless or cellular networks. This technological breakthrough, described in a recent article in the scientific journal Sensors, clears a path for a host of new developments for people suffering from chronic diseases, elderly people living alone, and even firemen and police officers.
A ...
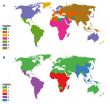
Researchers at North Carolina State University have for the first time mapped human disease-causing pathogens, dividing the world into a number of regions where similar diseases occur.
The findings show that the world can be separated into seven regions for vectored human diseases - diseases that are spread by pests, like mosquito-borne malaria - and five regions for non-vectored diseases, like cholera.
Interestingly, not all of the regions are contiguous. The British Isles and many of its former colonies, such as the United States and Australia, have similar diseases ...
Good news on the panda front: Turns out they're not quite as delicate - and picky - as thought.
Up until now, information gleaned from 30 years worth of scientific literature suggested that pandas were inflexible about habitat. Those conclusions morphed into conventional wisdom and thus have guided policy in China. But a Michigan State University (MSU) research associate has led a deep dive into aggregate data and emerged with evidence that the endangered animal is more resilient and flexible than previously believed.
Vanessa Hull is a postdoctoral research associate ...
Irvine, Calif., Dec. 3, 2014 - High fecal counts frequently detected at so-called "baby beaches" may not be diaper-related. UC Irvine researchers found that during summer months, small drainpipes emptying into enclosed ocean bays have a disproportionate impact on calmer waters. The findings were published Tuesday in the journal Environmental Science & Technology.
Researchers have long known that creeks and tributaries foul coastal waters with major winter storm runoff. But dry seasons like the one that just concluded can spell potential peril, too. Runoff from watering ...
When it comes to getting out of a tricky situation, we humans have an evolutionary edge over other primates. Take, as a dramatic example, the Apollo 13 voyage in which engineers, against all odds, improvised a chemical filter on a lunar module to prevent carbon dioxide buildup from killing the crew.
UC Berkeley scientists have found mounting brain evidence that helps explain how humans have excelled at "relational reasoning," a cognitive skill in which we discern patterns and relationships to make sense of seemingly unrelated information, such as solving problems in unfamiliar ...
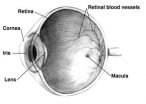
Scientists have developed a new light-sensitive film that could one day form the basis of a prosthetic retina to help people suffering from retinal damage or degeneration. Hebrew University of Jerusalem researchers collaborated with colleagues from Tel Aviv University and Newcastle University in the research, which was published in the journal Nano Letters.
The retina is a thin layer of tissue at the inner surface of the eye. Composed of light-sensitive nerve cells, it converts images to electrical impulses and sends them to the brain. Damage to the retina from macular ...
A new research brief from the US2010 Project probes the status of minorities in American suburbs. Suburbs in 2010 were as racially and ethnically diverse as were central cities in 1980, and that diversity is still increasing. Yet minorities are not finding equal access to the American dream in the suburbs where they live, a lesson illustrated recently by Ferguson, MO.
Suburbia has always been less segregated than central cities. Segregation is slowly declining between suburban blacks and whites, but has stayed about the same for Hispanics and Asians over three decades. ...
Do you consider yourself a conscientious person? Then sign up for a fixed-rate mortgage. Neurotic? You'll probably opt for home ownership over renting.
According to a new study published in the Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Economics, personality traits are strong indicators of real-estate decisions. The research, by Dr. Danny Ben-Shahar of Tel Aviv University's Faculty of Management and doctoral candidate Roni Golan of the Technion Institute of Technology, finds a correlation between personality and individual real estate choices, and a follow-up study by the ...
Those wishing to prove themselves as "doers" must not only be hands-on and demonstrate proactive behavior but also have social acumen and a feel for favorable opportunities. Those who rely on personal initiative alone will quickly be standing there as an isolated troublemaker. This is what psychologists from the University of Bonn and their colleagues from Florida State University (USA) have discovered through surveying a variety of occupational categories. The results have been published online in the renowned "Journal of Management". The printed version will be published ...