'Alzheimer's in a Dish' model induces skin cells into neurons expressing amyloid-beta
2014-12-05
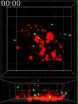
(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
This 19-second time lapse video shows the first six hours of neuronal conversion of skin fibroblasts from a patient with Alzheimer's disease.
Click here for more information.
The search for a living laboratory model of human neurons in the grip of Alzheimer's disease (AD)--the so-called "Alzheimer's in a dish"--has a new candidate. In work presented at the ASCB/IFCB meeting in Philadelphia, Håkan Toresson and colleagues at Lund University in Sweden report success in creating induced neurons that model Alzheimer's by starting with fibroblasts taken from skin biopsies. The differentiated cells express a full range of normal neuronal markers. Significantly, all the neurons derived from fibroblasts including those taken from patients diagnosed with AD, express the proteins classically associated with the neurodegenerative disorder including amyloid beta (Aβ) and the microtubule-associated protein tau, giving researchers a ready comparison between AD patients and the normal elderly.
All the fibroblast samples in Toresson's study came from patients enrolled in a large, long-term clinical research program on dementia called the Swedish BioFinder Study. The biopsies are linked to patient histories and results from batteries of longitudinal tests covering behavior, spinal fluid biochemistry, and brain imaging results including PET and MRI scans. The researchers subjected the fibroblast samples to growth factor treatment and transduction by three transcription factors, Ascl1, Brn2 and Myt1l, that induced differentiation into nerve cells. So far Toresson reports success in 12 out of 12 attempts to create induced neurons from the BioFinder samples, giving the researchers a cell biological library of neurons from elderly Swedes who exhibit signs of sporadic AD, familial AD, or robust cognitive health.
The relationship of Aβ and tau in AD progression are still hotly disputed but accumulations of tau-based tangles and Aβ plaques in the brain at autopsy are currently the only clear diagnostic of the disease. But sampling AD-damaged neurons in living patients is impossible. Using animals to model human diseases such as cancer has been a powerful instrument in bioscience but no good animal model of AD, which is first seen as impairment of human cognitive function, has been found. "Alzheimer's in a dish" or, in Toresson's studies, a series of dishes could be that long-awaited model system.
Using a cell biology approach to AD, Toresson hopes to compare the cell phenotypes on induced neurons derived from sporadic AD patients with induced neurons from familial AD cases that have the characteristic APP, PSEN1, or PSEN2 mutations. Such an approach could pave the way for personalized treatments for dementia, allowing the use of a patient's accessible skin cells to assess what's happening inside the inaccessible neurons of the brain.
NOTE: A 19-second time lapse video showing the first six hours of neuronal conversion of skin fibroblasts from an AD patient is available.
INFORMATION:
Induced patient neurons as a potential future model system for Alzheimer's disease
H. Toresson1, L. Minthon1, O. Hansson1, N. Schultz1, C. Orbjörn2, M. Parmar3, U. Pfisterer3; 1Clinical Memory Research Unit, Dept. of Clinical Sciences, Lund University and Skåne University Hospital, Malmö, Sweden, 2Clinical Memory Research Unit,
Dept. of Clinical Sciences, Lund University, Malmö, Sweden, 3Wallenberg Neuroscience Center and Lund Stem Cell Center, Department of Experimental Medical Science, Lund University, Lund, Sweden
Contact: Håkan Toresson, hakan.toresson@med.lu.se
Author presents at ASCB:
Poster Session: Neuronal Cytoskeleton 2
Tuesday, December 9
Board 610
Presentation 2088
Time: 1:30 pm to 3:00 pm
Media Contacts:
John Fleischman
jfleischman@ascb.org
513.706-0212 (mobile)
Carol Blymire
carol@carolblymire.com
301.332.8090 (mobile)
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-05
Location, location, location goes the old real estate proverb but cancer also responds to its neighborhood, particularly in the physical surroundings of bone marrow cells where human myeloid leukemias arise and where, according to two Harvard bioengineers, stiffness in the surrounding extracellular matrix (ECM) can predict how cancer subtypes react to chemotherapy. Correcting for the matrix effect could give oncologists a new tool for matching drugs to patients, the researchers say.
In work to be presented at the ASCB/IFCB meeting in Philadelphia, Jae-Won Shin and David ...
2014-12-05
Alzheimer's disease (AD) progresses inside the brain in a rising storm of cellular chaos as deposits of the toxic protein, amyloid-beta (Aβ), overwhelm neurons. An apparent side effect of accumulating Aβ in neurons is the fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus, the part of the cell involved in packaging and sorting protein cargo including the precursor of Aβ. But is the destruction the Golgi a kind of collateral damage from the Aβ storm or is the loss of Golgi function itself part of the driving force behind Alzheimer's? This was the question for Yanzhuang ...
2014-12-05
VIDEO:
Nucleoli (green), small liquid-like nuclear bodies, are kept small and afloat by a fine actin mesh. When the mesh breaks, the nucleoli quickly being to fall and coalesce into larger...
Click here for more information.
Everybody knows that cells are microscopic, but why? Why aren't cells bigger? The average animal cell is 10 microns across and the traditional explanation has been cells are the perfect size because if they were any bigger it would be difficult to get enough ...
2014-12-05
Cells are restless. They move during embryogenesis, tissue repair, regeneration, chemotaxis. Even in disease, tumor metastasis, cells get around. To do this, they have to keep reorganizing their cytoskeleton, removing pieces from one end of a microtubule and adding them to the front, like a railroad with a limited supply of tracks. The EB family of proteins helps regulate this process and can act as a scaffold for other proteins involved in pushing the microtubule chain forward.
Still, how these EB proteins function in space and time has remained a mystery. Now Peng ...
2014-12-05
The antioxidant activity of citrus juices and other foods is undervalued. A new technique developed by researchers from the University of Granada for measuring this property generates values that are ten times higher than those indicated by current analysis methods. The results suggest that tables on the antioxidant capacities of food products that dieticians and health authorities use must be revised.
Orange juice and juices from other citrus fruits are considered healthy due to their high content of antioxidants, which help to reduce harmful free radicals in our body, ...
2014-12-05
Penicillin, the wonder drug discovered in 1928, works in ways that are still mysterious almost a century later. One of the oldest and most widely used antibiotics, it attacks enzymes that build the bacterial cell wall, a mesh that surrounds the bacterial membrane and gives the cells their integrity and shape. Once that wall is breached, bacteria die -- allowing us to recover from infection.
That would be the end of the story, if resistance to penicillin and other antibiotics hadn't emerged over recent decades as a serious threat to human health. While scientists continue ...
2014-12-05
Physicians often ask their patients to "Please stick out your tongue". The tongue can betray signs of illness, which combined with other symptoms such as a cough, fever, presence of jaundice, headache or bowel habits, can help the physician offer a diagnosis. For people in remote areas who do not have ready access to a physician, a new diagnostic system is reported in the International Journal of Biomedical Engineering and Technology that works to combine the soft inputs of described symptoms with a digital analysis of an image of the patient's tongue.
Karthik Ramamurthy ...
2014-12-05
Montréal, December 5, 2014 - A new study published in the scientific journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) sheds new light on a well-known mechanism required for the immune response. Researchers at the IRCM, led by Tarik Möröy, PhD, identified a protein that controls the activity of the p53 tumour suppressor protein known as the "guardian of the genome".
The researchers study the development of T cells and B cells, which are lymphocytes (or immune cells) that play a central role in protecting our ...
2014-12-05
The drugs we release into the environment are likely to have a significant impact on plant growth, a new study has revelealed.
By assessing the impacts of a range of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, researchers at the University of Exeter Medical School and Plymouth University have shown that the growth of edible crops can be affected by these chemicals - even at the very low concentrations found in the environment.
Published in the Journal of Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, the research focused its analysis on lettuce and radish plants and tested the ...
2014-12-05
CORAL GABLES, Fla (December 4, 2014) -- How does the brain determine what matters? According to a new scientific article, a brain structure called the insula is essential for selecting things out of the environment that are "salient" for an individual, and dysfunction of this system is linked to brain disorders such as autism, psychosis and dementia.
In psychology and neuroscience, the term "salient" is used to describe a thing, person, place or event that stands out, or that is set apart from others. The current article, published online by Nature Reviews Neuroscience ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] 'Alzheimer's in a Dish' model induces skin cells into neurons expressing amyloid-beta