Cell division induces tissue ordering
2014-12-08
(Press-News.org) Nature's ingenious systems: A layer of cells called endothelial cells lines the interior of blood vessels. When blood flows through the vessels, such cells only divide to replace dead cells. However, if there is a blood clot preventing blood from flowing across the endothelial cells, they begin to divide more actively. New research from the Niels Bohr Institute demonstrates that cell division is very ordered. The new cells move away from each other and create a dynamic movement with eddies in a large area. This presumably helps to widen the vessel around the blockage. The results are published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications.
Living tissue is unlike other materials in that it is comprised of cells with a metabolism and the ability to divide and renew themselves. Normally in an adult body, cells only divide to form new cells to replace old, dead cells. But if there are abnormal conditions, the body can begin to form extraordinary new cells.
Examining the blood vessel tissue 'live'
"If, for example, there is a blood clot blocking the flow of blood across the innermost layer of the endothelial cells, they begin to actively divide. But what happens in the tissue? How do the newly formed cells move in relation to each other - and which mechanisms control their movements? This is what we wanted to investigate," explains biophysicist Lene Oddershede, head of the research group Optical Tweezers at the Niels Bohr Institute at the University Copenhagen.
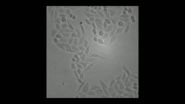
The researchers investigated the dynamics of new cell formation in a layer of endothelial cells where there was no liquid flowing over. The investigations took place in a laboratory system that mimiced the conditions in an endothelial cell layer where a blood clot blocks the blood flow. In order to follow the movement of the cells and the dynamics of the tissue 'live' they used phase-contrast microscopy, which makes it possible to follow the movements in the tissue, before, during and after cell division.
Orderly patterns
"Our experimental studies showed that the tissue behaved like a viscous material. The endothelial cell layer is contiguous and the cells are in close contact with each other. When a cell has divided, the new cells move away from the point of origin and all the other cells follow this movement, which creates large, ordered and far-reaching eddies in the tissue," says Lene Oddershede.
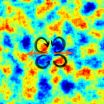
Lene Oddershede explains that well-ordered, far-reaching vortices are often a sign of turbulence, which is a normal phenomenon for fast movements in a flowing material with low viscosity like water, just like you also see in the characteristic turbulence patterns with 'eddies' in for example, weather satellite images of cloud formations. The big surprise with the tissue dynamics was that the researchers found these characteristic turbulence patterns with 'eddies' even though it was unexpected in such a slow and viscous system.
The research group has further supplemented the groundbreaking experimental results with theoretical modelling of the system and the modelling came up with the same results, providing a basic physical understanding of such a complex system as a blood vessel with a clot.
"This is a strong result, that both the experimental results and simulations say that increased cell division may help tissue to grow and heal in a beneficial way and that this process is based exclusively on a physically-dependent diffusion, requiring no biological signalling. This may be important for healing around blood clots - and it is an example of nature's ingenious ability to take care of itself," explains Lene Oddershede.
INFORMATION:
Contact:
Lene Oddershede, Associate professor and head of the group Optical Tweezers, Niels Bohr Institute, University of Copenhagen, phone: +45 2494 2534, oddershede@nbi.dk
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-08
A new study by researchers at the University of Exeter has found early warning signals of a reorganisation of the Atlantic oceans' circulation which could have a profound impact on the global climate system.
The research, published today in the journal Nature Communications, used a simulation from a highly complex model to analyse the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), an important component of the Earth's climate system.
It showed that early warning signals are present up to 250 years before it collapses, suggesting that scientists could monitor ...
2014-12-08
Cancer Research UK scientists have discovered a new line of defence used by cancer cells to evade cell death, according to research published in Nature Communications* today (Monday).
The team identified a critical pathway of molecular signals which throw a lifeline to cancer cells, enabling them to survive even though they contain vast DNA errors which would usually trigger cell death.
The PKCƐ signal pathway**, which is used by cancer cells but rarely by normal cells, could be important in targeting some cancer cells as they rely on this pathway to survive.
The ...
2014-12-08
UPTON, NY-A team of scientists from the U.S. Department of Energy's (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory, Columbia Engineering, Columbia Physics and Kyoto University has discovered an unusual form of electronic order in a new family of unconventional superconductors. The finding, described in the journal Nature Communications, establishes an unexpected connection between this new group of titanium-oxypnictide superconductors and the more familiar cuprates and iron-pnictides, providing scientists with a whole new family of materials from which they can gain deeper insights ...
2014-12-08
A new analysis has found that while clinical trial data support omitting radiation treatments in elderly women with early stage breast cancer, nearly two-thirds of these women continue to receive it. The findings are published early online in Cancer, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
Results published in 2004 from a large, randomized clinical trial showed that adding radiation therapy to surgery plus tamoxifen does not reduce 5-year recurrence rates or prolong survival in elderly women with early stage tumors. Despite the findings, many doctors still ...
2014-12-08
DURHAM, N.C. - Women over the age of 70 who have certain early-stage breast cancers overwhelmingly receive radiation therapy despite published evidence that the treatment has limited benefit, researchers at Duke Medicine report.
The study suggests that doctors and patients may find it difficult to withhold treatment previously considered standard of care, even in the setting of high quality data demonstrating that the advantages are small.
"The onus is on physicians to critically analyze data to shape our treatment recommendations for patients, weighing the potential ...
2014-12-08
Dublin, IRELAND Monday December 8th, 2014 - Millions of documents stored in archives could provide scientists with the key to tracing agricultural development across the centuries, according to new research completed at Trinity College Dublin and the University of York.
Amazingly, thanks to increasingly progressive genetic sequencing techniques, the all-important historical tales these documents tell are no longer confined to their texts; now, vital information also comes from the DNA of the parchment on which they are written.
Researchers used these state-of-the-art ...
2014-12-08
Metabolic syndrome is linked with an increased frequency and severity of lower urinary tract symptoms, but weight loss surgery may lessen these symptoms. The findings, which come from two studies published in BJU International, indicate that urinary problems may be added to the list of issues that can improve with efforts that address altered metabolism.
Lower urinary tract symptoms related to urinary frequency and urgency, bladder leakage, the need to urinate at night, and incomplete bladder emptying are associated with obesity in both men and women. To see if these ...
2014-12-08
HANOVER, N.H. - December 8, 2014 - With health systems in the U.S., U.K., and around the world trying to increase vaccination levels, it is critical to understand how to address vaccine hesitancy and counter myths about vaccine safety. A new article in the journal "Vaccine" concludes, however, that correcting myths about vaccines may not be the most effective approach to promoting immunization among vaccine skeptics. The study, which was co-authored by Brendan Nyhan, an assistant professor of government at Dartmouth College, and Jason Reifler, a senior lecturer of politics ...
2014-12-08
SAN FRANCISCO - The latest results of clinical trials of more than 125 patients testing an investigational personalized cellular therapy known as CTL019 will be presented by a University of Pennsylvania research team at the 56th American Society of Hematology Annual Meeting and Exposition. Highlights of the new trial results will include a response rate of more than 90 percent among pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia patients, and results from the first lymphoma trials testing the approach, including a 100 percent response rate among follicular lymphoma patients and ...
2014-12-08
Although it is among the most highly metastatic of all cancers, multiple myeloma is driven to spread by only a subset of the myeloma cells within a patient's body, researchers at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute have found in a study presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology (ASH).
The study suggests that attacking those subsets with targeted drugs may degrade the disease's ability to spread throughout the bone marrow of affected patients, the authors say.
The discovery was made by developing a mouse model of the disease that enabled researchers ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Cell division induces tissue ordering