(Press-News.org) CHARLOTTESVILLE, Va. -- The majority of streams in the Chesapeake Bay region are warming, and that increase appears to be driven largely by rising air temperatures. These findings are based on new U.S. Geological Survey research published in the journal Climatic Change.
Researchers found an overall warming trend in air temperature of 0.023 C (0.041 F) per year, and in water temperature of 0.028 C (0.050 F) per year over 51 years. This means that air temperature has risen 1.1 C (1.98 F), and water temperature has risen 1.4 C (2.52 F) between 1960 and 2010 in the Chesapeake Bay region.
"Although this may not seem like much, even small increases in water temperatures can have an effect on water quality, affecting the animals that rely on the bay's streams, as well as the estuary itself," said Karen Rice, USGS Research Hydrologist and lead author of the study.
One effect of warming waters is an increase in eutrophication, or an overabundance of nutrients The issue has plagued the bay for decades and likely will increase as temperatures of waters contributing to the bay continue to rise. Other effects of warming waters include shifts in plant and animal distributions in the basin's freshwater rivers and streams. Upstream waters may no longer be suitable for some cool-water fish species, and invasive species may move into the warming waters as those streams become more hospitable.
Chesapeake Bay is the largest estuary in the United States, with a watershed covering 166,391 square kilometers (over 64,243 square miles) that includes parts of New York, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, West Virginia and the District of Columbia. The watershed includes more than 100,000 streams, creeks and rivers that thread through it, and it supports more than 3,700 species of plants and animals. The states and DC are working with the federal government to improve conditions in the bay and its watershed and address the threats from climate change. Results from this USGS study will help inform adaptation strategies.
The study included examination of 51 years of data from 85 air-temperature sites and 129 stream-water temperature sites throughout the bay watershed. Though the findings indicated that overall both air and water temperatures have increased throughout the region, there was variability in the magnitude and direction of temperature changes, particularly for water.
"Our results suggest that water temperature is largely influenced by increasing air temperature, and features on the landscape act to enhance or dampen the level of that influence" said John Jastram, USGS Hydrologist and study coauthor.
At many of the sites analyzed, increasing trends were detected in both streamflow and water temperature, demonstrating that increasing streamflow dampens, but does not stop or reverse warming. Water temperature at most of the sites examined increased from 1960-2010. There was wide variability in physical characteristics of the stream-water sites, including:
Watershed area
Channel shape
Thermal capacity (a measure of the resistance of a body of water to temperature change)
The presence or absence of vegetation along the waterways
Local climate conditions
Land cover.
Warming temperatures in the Chesapeake Bay region's streams will have implications for future shifts in water quality, eutrophication and water column layers in the bay. As air temperatures rise, so will water temperature in Chesapeake Bay, though mixing with ocean water may buffer it somewhat, cooling the warmer water entering from the watershed. "Rising air and stream-water temperatures in Chesapeake Bay region, USA," by K.C. Rice and J.D. Jastram in Climatic Change is available online.
INFORMATION:
More information about USGS science to help restore Chesapeake Bay can be found at online.
IFrame URLs: http://gallery.usgs.gov/photo_shares/thumbs/tags/NR2014_12_08/1
USGS provides science for a changing world. Visit USGS.gov, and follow us on Twitter @USGS and our other social media channels.
Subscribe to our news releases via e-mail, RSS or Twitter.
Links and contacts within this release are valid at the time of publication.
You don't have to be a jerk to come up with fresh and original ideas, but sometimes being disagreeable is just what's needed to sell your brainchild successfully to others. However, difficult or irritating people should be aware of the social context in which they are presenting their ideas. A pushy strategy will not always be equally successful, warn Samuel Hunter of Pennsylvania State University and Lily Cushenbery of Stony Brook University in the US, in an article in Springer's Journal of Business and Psychology.
People are often labelled as jerks if they are disagreeable ...
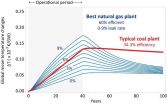
Washington, D.C.-- Natural gas power plants produce substantial amounts of gases that lead to global warming. Replacing old coal-fired power plants with new natural gas plants could cause climate damage to increase over the next decades, unless their methane leakage rates are very low and the new power plants are very efficient.
These are the principal findings of new research from Carnegie's Ken Caldeira and Xiaochun Zhang, and Nathan Myhrvold of Intellectual Ventures that compares the temperature increases caused by different kinds of coal and natural gas power plants. ...
Washington, DC (December 8, 2014) - Scrolling through the comments section on a news site is like seeing a verbal war before your eyes. Internet trolls flourish in an anonymous world, so much so that sites like Reuters and Popular Science have done away with the comment sections altogether. But there has to be a better way to let the audience engage in a civil manner. A recent study published in the Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication by researchers at the University of Texas, Purdue University, and University of Wyoming, found that having a journalist engage with ...
A technique that can identify causes of cancer invisible to genetic sequencing has uncovered large sets of previously unknown pancreatic cancer genes. It is hoped that this study will boost research into a disease that is still poorly understood and for which five-year survival rates have stood at around 5 per cent for the past four decades.
The technique works by introducing sections of DNA called piggyBac transposons into the mouse genome. Transposons jump around within the genome, reinserting themselves at random and causing a different mutation in each cell of the ...
ITHACA, N.Y. - There is cloud hanging over climate science, but one Cornell University expert on communication and environmental issues says he knows how to help clear the air.
In the December issue of Nature Climate Change, Jonathon Schuldt, assistant professor of communication, argues that only by creating a "science of climate diversity" can climate science and the larger climate change movement overcome a crippling lack of ethnic and racial diversity.
"There is an invisible, but very real barrier to climate engagement," Schuldt said. "We need to engage with all ...
A genetic misfire called the 3q26.2 amplicon can cause real havoc. In fact, it is among the most frequent chromosomal aberrations seen in many cancers, including ovarian and breast cancers.
Researchers behind a study at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center believe they may have found a molecule-based approach to halting 3q26.2's destructive nature. By manipulating a non-coding microRNA (miRNA) known as miR569 that is part of the amplicon, scientists were able to increase cell death in vitro and in vivo. MicroRNAs are short, non-coding RNA molecules that are ...
Alexandria, Va. -- Methane is often found naturally leaking from the seafloor, particularly in petroleum basins like the Gulf of Mexico or along tectonically active continental margins like the U.S. West Coast, but such plumes were not expected along passive margins, like the East Coast of North America. Now, however, the discovery of hundreds of methane seeps on the seafloor along the U.S. East Coast suggests that such reservoirs may be more common along passive margins than previously thought. The release of such methane globally may have a significant influence on climate, ...
BLOOMINGTON, Ind. -- A new treatment for adult-onset diabetes and obesity developed by researchers at Indiana University and the German Research Center for Environmental Health has essentially cured lab animals of obesity, diabetes and associated lipid abnormalities through improved glucose sensitivity, reduced appetite and enhanced calorie burning.
In preclinical trials, the new peptide -- a molecular integration of three gastrointestinal hormones -- lowered blood sugar levels and reduced body fat beyond all existing drugs, according to the work co-led by IU Distinguished ...
Scientists from the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), led by Guillermo Montoya, have developed a method for producing biological crystals that has allowed scientists to observe --for the first time-- DNA double chain breaks. They have also developed a computer simulation that makes this process, which lasts in the order of millionths of a second, visible to the human eye. The study is published today by the journal Nature Structural & Molecular Biology.
"We knew that enzymes, or proteins, endonucleases, are responsible for these double strand breaks, but ...
Sexual behaviour of teenage girls does not appear to be impacted by the human papilloma virus (HPV) vaccine, according to Queen's researchers Drs. Leah Smith and Linda Lévesque.
There are concerns the vaccine, which guards against four types of the HPV shown to cause cervical cancer and anogenital warts, may give girls a false sense of security about contracting sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and lead them to engage in riskier sexual activity.
"These findings suggest fears of increased risky sexual behaviour following HPV vaccination are unwarranted and should ...