NASA catches Tropical Cyclone Bakung's remnants
2014-12-15
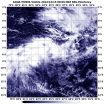
(Press-News.org) Tropical Cyclone Bakung ran into adverse conditions in the Southern Indian Ocean that weakened it to a remnant low pressure system when NASA's Aqua satellite spotted it on Dec. 15.
The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard Aqua captured a visible picture of Bakung's elongated remnants on Dec. 5 at 08:05 UTC (3:05 a.m. EST). The storm appeared to be stretched out from west to east in the visible image.
The last advisory on the tropical cyclone came on Dec. 13 when the storm was still a tropical storm with maximum sustained winds near 35 knots (40 mph/62 kph), but weakening. Bakung was located near 9.1 south longitude and 89.6 east latitude or about 466 nautical miles (536 miles/863 km) west-northwest of Cocos Islands. It was still moving to the west-northwest at 8 knots (9.2 mph/14.8 kph).
By Dec. 15 the remnants still showed some low-level circulation but it was poorly defined. Bakung's remnant low pressure area was centered near 9.6 south longitude and 85.5 east latitude, 690 nautical miles (794 miles/1,278 km) west of Cocos Island. Forecasters at the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) noted that an analysis of the upper-level of the troposphere (the layer of atmosphere closest to Earth where weather occurs) showed unfavorable conditions with vertical wind shear blowing as strong as 30 to 40 knots (34 mph/55 kph to 46 mph/74 kph).
The JTWC gives Bakung a low chance of redeveloping in the next day.
INFORMATION:
Rob Gutro
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-15
WASHINGTON (Dec. 15, 2014)--Over prescription of antibiotics is a major factor driving one of the biggest public health concerns today: antibiotic resistance. In a first-of-its-kind study, research led by the George Washington University suggests that public health educational materials may not address the misconceptions that shape why patients expect antibiotics, driving doctors to prescribe them more. The research appeared in October in the journal Medical Decision Making.
Researchers from George Washington, Cornell and Johns Hopkins universities surveyed 113 patients ...
2014-12-15
Researchers in Spain have discovered that if lead atoms are intercalated on a graphene sheet, a powerful magnetic field is generated by the interaction of the electrons' spin with their orbital movement. This property could have implications in spintronics, an emerging technology promoted by the European Union to create advanced computational systems.
Graphene is considered the material of the future due to its extraordinary optical and electronic mechanical properties, especially because it conducts electrons very quickly. However, it does not have magnetic properties, ...
2014-12-15
To the casual observer, the colonies of social insects like bees and ants appear to be harmonious societies where individuals work together for the common good. But appearances can be deceiving.
In fact, individuals within nests compete over crucial determinants of fitness such as reproductive dominance and production of male eggs. The intensity of competition often depends on the level of kinship between colony members. This is because selfish individuals lose indirect fitness when their behavior harms close relatives. A new study by Eva Schultner and colleagues from ...
2014-12-15
Just in time for Christmas, Simon Fraser University computing science professor Richard Zhang reveals how to print a 3D Christmas tree efficiently and with zero material waste, using the world's first algorithm for automatically decomposing a 3D object into what are called pyramidal parts.
A pyramidal part has a flat base with the remainder of the shape forming upwards over the base with no overhangs, much like a pyramid. A pyramidal shape is optimal for 3D printing because it incurs no material waste and saves print time.
The algorithm promises to become a big deal in ...
2014-12-15
DALLAS - Dec. 15, 2014 - UT Southwestern Medical Center researchers have identified a possible therapy to treat neurofibromatosis type 1 or NF1, a childhood neurological disease characterized by learning deficits and autism that is caused by inherited mutations in the gene encoding a protein called neurofibromin.
Researchers initially determined that loss of neurofibromin in mice affects the development of the part of the brain called the cerebellum, which is responsible for balance, speech, memory, and learning.
The research team, led by Dr. Luis F. Parada, Chairman ...
2014-12-15
Irvine, Calif., Dec. 15, 2014 - Dangerously high levels of air pollutants are being released in Mecca during the hajj, the annual holy pilgrimage in which millions of Muslims on foot and in vehicles converge on the Saudi Arabian city, according to findings reported today at the American Geophysical Union meeting in San Francisco.
"Hajj is like nothing else on the planet. You have 3 to 4 million people - a whole good-sized city - coming into an already existing city," said Isobel Simpson, a UC Irvine research chemist in the Nobel Prize-winning Rowland-Blake atmospheric ...
2014-12-15
Early discoveries by NASA's newest Mars orbiter are starting to reveal key features about the loss of the planet's atmosphere to space over time.
The findings are among the first returns from NASA's Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution (MAVEN) mission, which entered its science phase on Nov. 16. The observations reveal a new process by which the solar wind can penetrate deep into a planetary atmosphere. They include the first comprehensive measurements of the composition of Mars' upper atmosphere and electrically charged ionosphere. The results also offer an unprecedented ...
2014-12-15
A breast cancer specialist and clinical researcher at Women & Infants Hospital of Rhode Island presented research yesterday at the 2014 San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium showing that adding either the chemotherapy drug carboplatin or the blood vessel-targeting drug bevacizumab to the standard treatment of chemotherapy before surgery helped women who have the basal-like subtype of triple-negative breast cancer.
"We found that adding either carboplatin or bevacizumab to standard preoperative chemotherapy increased pathologic complete response rates for women with basal-like ...
2014-12-15
Scientists from the Department of Energy's Pacific Northwest National Laboratory will present a variety of research at the 2014 American Geophysical Union Fall Meeting, which runs Monday, Dec. 15 through Friday, Dec. 19 at the Moscone Convention Center in San Francisco. Noteworthy PNNL research presentations include the following topics:
Even with global warming cold air outbreaks will remain
Just because the climate is warming doesn't mean Cold Air Outbreaks are going away, especially in Southwestern Canada and Northwestern United States. Overall, global climate models ...
2014-12-15
Leading conservation scientists from around the world have called for a substantial role for nuclear power in future energy-generating scenarios in order to mitigate climate change and protect biodiversity.
In an open letter to environmentalists with more than 60 signatories, the scientists ask the environmental community to "weigh up the pros and cons of different energy sources using objective evidence and pragmatic trade-offs, rather than simply relying on idealistic perceptions of what is 'green' ".
Organized by ecologists Professor Barry Brook and Professor Corey ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] NASA catches Tropical Cyclone Bakung's remnants