E-cigarettes may recruit lower risk teens to nicotine use
2014-12-16
(Press-News.org) Researchers at the Norris Cotton Cancer Center and University of Hawaii Cancer Center find that one-third of Hawaiian adolescents have tried e-cigarettes, half of whom have never used another tobacco product.
"This is a markedly different pattern of use compared to their peers in the continental U.S., where teen e-cigarette use is less than half that rate and e-cigarette users are mainly also cigarette smokers (dual-users)," reported James D. Sargent, MD, a pediatrician at Dartmouth Hitchcock's Norris Cotton Cancer Center in a paper published December 15, 2014 in the journal Pediatrics.
The investigators assessed risk status for three groups (non-users, e-cigarette-only users, and dual-users) on variables that predict future use of cigarettes, and found the e-cigarette-only users to have risk that was in between the never-smokers and dual-users. "The concern is that e-cigarette advertising is recruiting intermediate risk adolescents to nicotine use--kids who would not otherwise have started smoking," said Sargent. "These are kids who might go on to smoke cigarettes, which are much better at delivering nicotine than e-cigarettes."
Sargent added, "If this pattern of use is adopted by adolescents in the continental U.S., we could be in for an epidemic of teen tobacco use in this country that could greatly reduce the overall benefits to public health of e-cigarettes."
Researchers from Dartmouth and the University of Hawaii Cancer Center collaborated in the 2013 survey-based study of 1,941 adolescents aged 14-15 years old in public and private schools in Hawaii. Statistical analysis examined risk and protective variables across a spectrum of use, comparing never-smokers with e-cigarette-only users and e-cigarette-only users with dual-users.
Risk factors for smoking cigarettes include protective variables such as parental support and academic involvement, in addition to risk factors including peer smoking and sensation seeking. On almost all of those measures, e-cigarette users ranked somewhere between the never-smokers and the dual-users.
Cigarettes are highly taxed in Hawaii and e-cigarettes, with their potent combination of lower cost and kid-friendly flavors such as mango and pineapple, may be more attractive to teens. Thomas Wills, PhD, of the UH Cancer Center commented with concern on specifics of e-cigarettes, which are widely available in Hawaii, noting "The marketing is very aggressive here." He added that manufacturers place ads in venues such as movie theaters where adolescents socialize, as well as on radio and television.
Sargent and collaborators were so concerned about the findings that they submitted them to the FDA docket to inform proposed regulations on e-cigarettes. They note that flavoring, packaging, and marketing of e-cigarettes is not regulated, and that manufacturers' opportunities to target adolescents are wide open, absent FDA regulation of these products.
INFORMATION:
Sargent's collaborators include TA Willis, R Knight, RJ Williams, and I Pagano, all from the University of Hawaii Cancer Center, Honolulu, HI.
The National Cancer Institute grant RO1 CA 153154 funded the study.
About Norris Cotton Cancer Center at Dartmouth-Hitchcock
Norris Cotton Cancer Center combines advanced cancer research at Dartmouth and the Geisel School of Medicine with patient centered cancer care provided at Dartmouth-Hitchcock Medical Center in Lebanon, NH, at Dartmouth-Hitchcock regional locations in Manchester, Nashua, and Keene, NH, and St. Johnsbury, VT, and at 12 partner hospitals throughout New Hampshire and Vermont. It is one of 41 centers nationwide to earn the National Cancer Institute's "Comprehensive Cancer Center" designation. Learn more about Norris Cotton Cancer Center research, programs, and clinical trials online at cancer.dartmouth.edu.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2014-12-16
Average chloride concentrations often exceed toxic levels in many northern United States streams due to the use of salt to deice winter pavement, and the frequency of these occurrences nearly doubled in two decades.
Chloride levels increased substantially in 84 percent of urban streams analyzed, according to a U.S. Geological Survey study that began as early as 1960 at some sites and ended as late as 2011. Levels were highest during the winter, but increased during all seasons over time at the northern sites, including near Milwaukee, Wisconsin; Chicago, Illinois; Denver, ...
2014-12-16
ATLANTA--The Paleolithic diet, or caveman diet, a weight-loss craze in which people emulate the diet of plants and animals eaten by early humans during the Stone Age, gives modern calorie-counters great freedom because those ancestral diets likely differed substantially over time and space, according to researchers at Georgia State University and Kent State University.
Their findings are published in The Quarterly Review of Biology.
"Based on evidence that's been gathered over many decades, there's very little evidence that any early hominids had very specialized diets ...
2014-12-16
Los Angeles, CA (November 16, 2014) A new article reports that despite a clear lack of research on male survivors of Ebola, the current recommended practice of waiting at least three months after recovery to have unprotected sex should be upheld. This study was published today in Reproductive Sciences, a SAGE journal.
"Our exercise demonstrated that the current recommendations to prevent the sexual spread of Ebola are based on one mere observation," the researchers wrote. "Despite the evident need to conduct more research, for now, health care professionals should strongly ...
2014-12-16
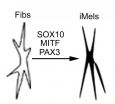
PHILADELPHIA - As the main component of connective tissue in the body, fibroblasts are the most common type of cell. Taking advantage of that ready availability, scientists from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, the Wistar Institute, Boston University School of Medicine, and New Jersey Institute of Technology have discovered a way to repurpose fibroblasts into functional melanocytes, the body's pigment-producing cells. The technique has immediate and important implications for developing new cell-based treatments for skin diseases such as ...
2014-12-16
Two studies published in the January issue of Anesthesiology, the official medical journal of the American Society of Anesthesiologists® (ASA®), shed new light on the prevalence of transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI) and transfusion-associated circulatory overload (TACO), the number one and two leading causes of blood transfusion-related deaths in the United States. According to researchers, postoperative TRALI is significantly underreported and more common than previously thought, with an overall rate of 1.4 percent. While the rate of TACO was found ...
2014-12-16
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most common form of dementia and is characterized by the formation of β-amyloid plaques throughout the brain. Proteins known as chemokines regulate inflammation and the immune response. In both patients with AD and mouse AD models, the chemokine CXCL10 is found in high concentrations in the brain and may contribute to AD. A new study in the Journal of Clinical Investigation indicates that activation of the CXCL10 receptor, CXCR3, contributes to AD pathology. Using a murine model of AD, Michael Heneka and colleagues at the University ...
2014-12-16
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common liver disorder and affects approximately 1 billion people worldwide. It is not clear how this disease develops, but recent studies suggest that the bacterial population in the gut influences NAFLD. A new study in the Journal of Clinical Investigation provides a link between molecular signaling pathways in the gut, the intestinal microbiome, and development of NAFLD. Frank Gonzalez and colleagues at the National Cancer Institute found that disruption of the gut microflora prevented development of NAFLD in mice fed ...
2014-12-15
A pregnant woman in Africa who has contracted Ebola is likely to suffer with a spontaneous abortion, pregnancy-related hemorrhage, or the death of her newborn. Although the risk of caring for a pregnant woman with Ebola in the United States may be rare, the Association of Women's Health, Obstetric and Neonatal Nurses (AWHONN) has published a practice brief in its Journal of Obstetric, Gynecologic, & Neonatal Nursing to guide nursing care for pregnant women and newborns.
"Nurses play a vital role in caring for patients with Ebola," said Dr. Debra Bingham, who is Vice President ...
2014-12-15
Emotions are complicated and never more so than in the realm of the scientific, where commonly accepted definitions are lacking.
In a paper published in the journal Qualitative Inquiry, UC Santa Barbara's Thomas Scheff examines the basic emotions of grief, fear/anxiety, anger, shame and pride as they appear in scientific literature in an attempt to take a first step in defining them. "Emotion terms, especially in English, are wildly ambiguous," Scheff writes in the paper's introduction.
An emeritus professor of sociology at UCSB, Scheff set out to explore why the language ...
2014-12-15
VCU Massey Cancer Center physician-researcher Charles E. Geyer, Jr., M.D., was the National Protocol Officer for one component of a large national study involving two National Cancer Institute (NCI)-supported clinical trials that demonstrated that trastuzumab significantly improves the long-term survival of HER-2 positive breast cancer patients. The combined study was designed to determine the long-term safety and efficacy of the drug trastuzumab, which is commonly known as Herceptin and is primarily used alongside chemotherapy to treat HER2-positive breast cancer. The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] E-cigarettes may recruit lower risk teens to nicotine use