(Press-News.org) VIDEO:
Research from Univ. of Iowa and Russian scientists show crows are capable of executive-level thinking.
Click here for more information.
Crows have long been heralded for their high intelligence - they can remember faces, use tools and communicate in sophisticated ways.
But a newly published study finds crows also have the brain power to solve higher-order, relational-matching tasks, and they can do so spontaneously. That means crows join humans, apes and monkeys in exhibiting advanced relational thinking, according to the research.
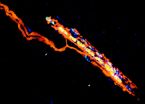
Russian researcher Anna Smirnova studies a crow making the correct selection during a relational matching trial.
"What the crows have done is a phenomenal feat," says Ed Wasserman, a psychology professor at the University of Iowa and corresponding author of the study. "That's the marvel of the results. It's been done before with apes and monkeys, but now we're dealing with a bird; but not just any bird, a bird with a brain as special to birds as the brain of an apes is special to mammals."
"Crows Spontaneously Exhibit Analogical Reasoning," which was published December 18 in Current Biology, was written by Wasserman and Anna Smirnova, Zoya Zorina and Tanya Obozova, researchers with the Department of Biology at Lomonosov Moscow State University in Moscow, Russia, where the study was conducted.
Wasserman said the Russian researchers have studied bird species for decades and that a main theme of their work is cognition. He credits his counterparts with a thoughtful and well-planned study.
"This was a very artful experiment," Wasserman says. "I was just bowled over by how innovative it was."
The study involved two hooded crows that were at least 2 years old. First, the birds were trained and tested to identify items by color, shape and number of single samples.
Here is how it worked: the birds were placed into a wire mesh cage into which a plastic tray containing three small cups was occasionally inserted. The sample cup in the middle was covered with a small card on which was pictured a color, shape or number of items. The other two cups were also covered with cards - one that matched the sample and one that did not. During this initial training period, the cup with the matching card contained two mealworms; the crows were rewarded with these food items when they chose the matching card, but they received no food when they chose the other card.
Once the crows has been trained on identity matching-to-sample, the researchers moved to the second phase of the experiment. This time, the birds were assessed with relational matching pairs of items.
These relational matching trials were arranged in such a way that neither test pairs precisely matched the sample pair, thereby eliminating control by physical identity. For example, the crows might have to choose two same-sized circles rather than two different-sized circles when the sample card displayed two same-sized squares.
What surprised the researchers was not only that the crows could correctly perform the relational matches, but that they did so spontaneously--without explicit training.
"That is the crux of the discovery," Wasserman says. "Honestly, if it was only by brute force that the crows showed this learning, then it would have been an impressive result. But this feat was spontaneous."
Still the researchers acknowledge that the crows' relational matching behavior did not come without some background knowledge.
"Indeed, we believe that their earlier IMTS (identity matching-to-sample) training is likely to have enabled them to grasp a broadly applicable concept of sameness that could apply to novel two-item samples and test stimuli involving only relational sameness," the researchers wrote. "Just how that remarkable transfer is accomplished represents an intriguing matter for future study."
Anthony Wright, neurobiology and anatomy professor at the University of Texas-Houston Medical School, says the discovery ranks on par with demonstrations of tool use by some birds, including crows.
"Analogical reasoning, matching relations to relations, has been considered to be among the more so-called 'higher order' abstract reasoning processes," he says. "For decades such reasoning has been thought to be limited to humans and some great apes. The apparent spontaneity of this finding makes it all the more remarkable."
Joel Fagot, director of research at the University of Aix-Marseille in France, agrees the results shatter the notion that "sophisticated forms of cognition can only be found in our 'smart' human species. Accumulated evidence suggests that animals can do more than expected."
Wasserman concedes there will be skeptics and hopes the experiment will be repeated with more crows as well as other species. He suspects researchers will have more such surprises in store for science.
"We have always sold animals short," he says. "That human arrogance still permeates contemporary cognitive science."
INFORMATION:
The study was funded by a grant from the Russian Foundation for Basic Research.
TORONTO -- Very small segments of genes called "microexons" influence how proteins interact with each other in the nervous system, scientists at the University of Toronto have found, opening up a new line of research into the cause of autism.
The researchers found that microexons are used in neurons by alternative splicing, a process in which a single gene can produce many different proteins. Microexons are pasted -- or spliced -- into gene messengers (mRNAs) to generate forms of proteins that the nervous system needs to function properly. Misregulation of this process, ...
RESEARCHERS have discovered the unique genetic paths that the childhood brain tumour medulloblastoma follows when the disease comes back, according to research* published in Cancer Cell today (Thursday).
The study - funded by Cancer Research UK, Action Medical Research and others** - shows that taking an extra tumour sample at recurrence, when there are no effective therapies, could identify subsets of patients that might be treatable with existing drugs that target the genetic faults.
The scientists, based at Newcastle University and The Institute of Cancer Research ...
There are two main families of bacteria : those that are surrounded by a single membrane (or one outer wall) and those that are surrounded by two membranes (or two outer walls). The team of Jean-François Collet, professor at the de Duve Institute at UCL, looked at this second type of bacteria.
For a bacterium to survive, it has to keep its two outer walls intact. If one of these walls is damaged, the bacterium dies. So it was vital for the UCL researchers to analyse the protection mechanisms of these bacterial "walls' (to find their weak spot), so as to be able to ...
This latest research by Joshua Brickman and his research team from Danish Stem Cell Center (Danstem) at the University of Copenhagen specifically found that inhibiting or blocking stem cells ability to make a specific decision, leads to better cell growth and could lead to defined ways to differentiate stem cells.
This research is the first comprehensive analysis of a pathway important for stem and cancer cell decisions known as Erk. As a result this work could contain clues to cancer treatment as well as helping to establish a platform to make stem cell treatments for ...
After an incomplete spinal cord injury, the body can partially recover basic motor function. So-called muscle spindles and associated sensory circuits back to the spinal cord promote the establishment of novel neuronal connections after injury. This circuit-level mechanism behind the process of motor recovery was elucidated by Prof. Silvia Arber's research group at the Biozentrum, University of Basel and the Friedrich Miescher Institute for Biomedical Research. Their findings may contribute to designing novel strategies for treatment after spinal cord injuries and have ...
Walter and Eliza Hall Institute researchers have for the first time revealed how dying cells are hidden from the immune 'police' that patrol the body.
The research answers a decades-old mystery about the death of cells, which in some situations can alert the immune system to potential danger, but in other circumstances occurs 'silently', unnoticed by immune cells.
Silent cell death, or apoptosis, is a controlled way for the body to eliminate cells that may be damaged, old, or surplus to the body's requirements, without causing collateral damage. This 'normal' cell death ...
This news release is available in Spanish. The genome is the cell's book of instructions. All the cells in our body contain the same genomic information but each of them "reads" the gene fragments that interest them in order to carry out their function. So, neurones, hepatocytes and cardiac cells are different although their genome is the same. In order to achieve this huge variety of functions from the same genome, the cells employ a mechanism known as alternative splicing. This enables them to combine several fragments - known as exons - from the same genes in order ...
Mountain View, Calif. - December 18, 2014 - 23andMe, Inc., the leading personal genetics company, today announced the publication of a study that pinpoints fine-scale differences in genetic ancestry of individuals from across the United States.
Since immigrants first arrived more than four hundred years ago, the United States has served as a meeting place for peoples from different continents. This study illuminates how American history and the ongoing mixing of peoples with African, European, and American origins can be seen in our DNA.
"The relationship between genomics ...
HOUSTON - (Dec. 18, 2014) - Cars that run on natural gas are touted as efficient and environmentally friendly, but getting enough gas onboard to make them practical is a hurdle. A new study led by researchers at Rice University promises to help.
Rather than shoehorn bulky high-pressure tanks like those used in buses and trucks into light vehicles, the Department of Energy (DOE) encourages scientists to look at new materials that can store compressed natural gas (CNG) at low pressure and at room temperature. Cage-like synthetic macromolecules called metal organic frameworks ...
LA JOLLA, CA--December 18, 2014--Collaborating scientists from The Scripps Research Institute (TSRI) and the University of California (UC) San Diego have developed a powerful new system for studying how proteins and other biological molecules form and lose their natural folded structures.
Using the new system, researchers can force a sample of molecules to unfold and refold by boosting and then dropping the temperature, so quickly that even some of the fastest molecular folding events can be tracked.
"One way of studying these structures has been to make them unfold ...