(Press-News.org) Highlight
Kidney donors with hypertension had slightly fewer nephrons (the kidney's filtering units) at the time of donation than similarly aged donors with normal blood pressure; however, 6 months following their surgery, hypertensive and non-hypertensive donors both maintained excellent blood pressure control and had similarly robust compensatory kidney responses.
Nearly 6,000 people donate a kidney in the United States each year.
Washington, DC (December 18, 2014) -- With proper monitoring, kidney donation may be safe for individuals with high blood pressure, according to a study appearing in an upcoming issue of the Journal of the American Society of Nephrology (JASN). The study found that while hypertension can have negative effects on the kidneys, older adults with the condition appear to have good kidney health following donation.
Living kidney donation is an altruistic act that greatly improves quality of life and lengthens survival for patients with kidney failure. As kidney specialists strive to provide the best care for transplant recipients, they must also make every effort to ensure that living donation is as safe as possible for those who want to donate.
Jane Tan, MD, PhD (Stanford University) and her colleagues looked at the safety of kidney donation for individuals with hypertension because high blood pressure is associated with a reduced number of the kidneys' nephrons, which are filtering units that remove toxins from the blood.
The study included 51 living kidney donors. Ten donors, all of whom were older than 50 years of age, had hypertension at the time of donation. Each participant agreed to undergo a comprehensive evaluation of kidney function before and 6 months after donation. The investigators note that after removal a kidney, the remaining healthy kidney usually does about 40% more work to compensate.
Older donors with hypertension had slightly fewer functioning nephrons at the time of donation than similarly aged donors with normal blood pressure. However, 6 months following their surgery, hypertensive and non-hypertensive donors both maintained excellent blood pressure control and had similarly robust compensatory kidney responses.
"Overall, these short-term findings are reassuring; however, we do believe that regular post-donation medical follow-up, with an emphasis on continued good blood pressure control, is important for hypertensive kidney donors," said Dr. Tan.
INFORMATION:
Study co-authors include Colin Lenihan MB, BCh, PhD, Stephan Busque, MD, Geraldine Derby, RN, Kristina Blouch, PhD, and Bryan Myers, MD.
Disclosures: Funding was provided by the Satellite Extramural Grant Foundation and the John M. Sobrato Foundation. Colin Lenihan is supported by an American Society of Nephrology Research Fellowship. Jane Tan is supported by National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases Grant K23-DK08793
The article, entitled "The Association of Predonation Hypertension with Glomerular Function and Number in Older Living Kidney Donors," will appear online at http://jasn.asnjournals.org/ on December 18, 2014.
The content of this article does not reflect the views or opinions of The American Society of Nephrology (ASN). Responsibility for the information and views expressed therein lies entirely with the author(s). ASN does not offer medical advice. All content in ASN publications is for informational purposes only, and is not intended to cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, drug interactions, or adverse effects. This content should not be used during a medical emergency or for the diagnosis or treatment of any medical condition. Please consult your doctor or other qualified health care provider if you have any questions about a medical condition, or before taking any drug, changing your diet or commencing or discontinuing any course of treatment. Do not ignore or delay obtaining professional medical advice because of information accessed through ASN. Call 911 or your doctor for all medical emergencies.
Founded in 1966, and with more than 15,000 members, the American Society of Nephrology (ASN) leads the fight against kidney disease by educating health professionals, sharing new knowledge, advancing research, and advocating the highest quality care for patients.
Struggling to balance on one leg for 20 seconds or longer was linked to an increased risk for small blood vessel damage in the brain and reduced cognitive function in otherwise healthy people with no clinical symptoms, according to new research in the American Heart Association's journal Stroke.
"Our study found that the ability to balance on one leg is an important test for brain health," said Yasuharu Tabara, Ph.D., lead study author and associate professor at the Center for Genomic Medicine at Kyoto University Graduate School of Medicine in Kyoto, Japan. "Individuals ...
WINSTON-SALEM, N.C. - Dec. 18, 2014 - State and local enforcement of federal immigration laws can have an adverse impact on the use of health care services by immigrant Hispanics, according to a North Carolina-based study by Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center researchers.
The study, published in the Dec. 18 issue of the American Journal of Public Health, analyzed both birth records and information collected in focus groups and individual interviews.
"Our findings suggest that immigration enforcement policies negatively affect the health of immigrant Hispanics, including ...
An investigation into factors related to disparities of depression in young adults has found that higher parental education - which has a protective effect for white youth - can also increase the risk of depression for black youth. The MassGeneral Hospital for Children (MGHfC) study published online in the Journal of Pediatrics also found that, among high-socioeconomic-status black youth, greater perceptions of being discriminated against cancelled out the protective effects of parental education.
"High socioeconomic status (SES) - particularly higher parent education ...
Before Charlotte the spider spelled the word "humble" in her web to describe Wilbur the pig, she told Templeton the rat that the word meant "not proud."
That's probably what most people say if you put them on the spot. But if you give them time to think about it deeply, like a new study just did, other themes emerge that have a lot to do with learning.
And these intellectual dimensions of humility describe the spider as well or better than the pig.
"Wilbur has many of the dimensions of humility in general: regard for others, not thinking too highly of himself - but ...
Auroras are the most visible manifestation of the sun's effect on Earth, but many aspects of these spectacular displays are still poorly understood. Thanks to the joint European Space Agency and NASA's Cluster mission combined with data from a past NASA mission called the Imager for Magnetopause-to-Aurora Global Exploration, or IMAGE, a particular type of very high-latitude aurora has now been explained.
Known as a theta aurora -- because seen from above it looks like the Greek letter theta, an oval with a line crossing through the center -- this type of aurora sometimes ...
ITHACA, N.Y. - To encode data, today's computer memory technology uses electric currents - a major limiting factor for reliability and shrinkability, and the source of significant power consumption. If data could instead be encoded without current - for example, by an electric field applied across an insulator - it would require much less energy, and make things like low-power, instant-on computing a ubiquitous reality.
A team at Cornell University led by postdoctoral associate John Heron, who works jointly with Darrell Schlom, professor of Industrial Chemistry in the ...
Scientists from WCS (Wildlife Conservation Society), the Universidad Austral de Chile, the Blue Whale Center, the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH), NOAA, and other organizations are examining molecular clues to answer a big question: how many types of blue whales exist in the waters of the southeastern Pacific?
The answer seems to be two distinct populations, according to a genetic study comparing the blue whales off the southern coast of Chile with those swimming in the waters of Antarctica and other nearby regions. One of the populations could be made up of ...
By 2050, a majority of U.S. coastal areas are likely to be threatened by 30 or more days of flooding each year due to dramatically accelerating impacts from sea level rise, according to a new NOAA study, published today in the American Geophysical Union's online peer-reviewed journal Earth's Future.
The findings appear in the paper From the Extreme to the Mean: Acceleration and Tipping Points for Coastal Inundation due to Sea Level Rise, and follows the earlier study, Sea Level Rise and Nuisance Flood Frequency Changes around the United States, by the report's co-author, ...
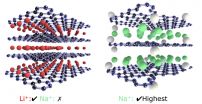
MANHATTAN, KANSAS -- A Kansas State University engineering team has discovered some of graphene oxide's important properties that can improve sodium- and lithium-ion flexible batteries.
Gurpreet Singh, assistant professor of mechanical and nuclear engineering, and Lamuel David, doctoral student in mechanical engineering, India, published their findings in the Journal of Physical Chemistry in the article "Reduced graphene oxide paper electrode: Opposing effect of thermal annealing on Li and Na cyclability."
Graphene oxide is an insulating and defective version of graphene ...
Many genetic mutations in visual pigments, spread over millions of years, were required for humans to evolve from a primitive mammal with a dim, shadowy view of the world into a greater ape able to see all the colors in a rainbow.
Now, after more than two decades of painstaking research, scientists have finished a detailed and complete picture of the evolution of human color vision. PLOS Genetics is publishing the final pieces of this picture: The process for how humans switched from ultraviolet (UV) vision to violet vision, or the ability to see blue light.
"We ...